CONTEXT: On 18 February 2022 India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to boost the bilateral trade between the two countries. This write-up examines the issue in detail.
THE SALIENT FEATURES OF INDIA-UAE CEPA
- CEPA is a balanced, fair, comprehensive & equitable partnership agreement, which will give enhanced market access for India in both goods and services.
- India and UAE aim to increase bilateral goods trade over the next five years to $100 billion.
- Under the agreement, the UAE is set to eliminate duties on 80 percent of its tariff lines which account for 90 percent of India’s exports to the UAE by value. This is particularly important for exports in highly competitive areas such as textiles and garments.
- The partnership agreement will open doors, especially to labor-intensive Indian products which are exported to UAE – such as textiles, gem & jewelry, medicines, agricultural products, footwear, leather, sports goods, engineering goods, auto components, and plastics.
- The agreement which is expected to come into effect in the first week of May is expected to generate “an additional 10 lakh jobs” in India.
- It will help India in realizing the ambitious target of U.S $1 trillion of merchandise exports and the U.S $1 trillion of services exports by the year 2030.
THE ROADMAP ENVISAGED FOR THE ACHIEVING THE OBJECTIVES OF THE AGREEMENT
The roadmap will ensure that the two countries work together even more closely to address the shared global challenges, achieve shared objectives, and build a future-ready robust and resilient relationship. The roadmap will promote the development of new trade, investment, and innovation dynamics, and intensify bilateral engagement in diverse areas including:
ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP:
- This will create investment opportunities for Indian investors in establishing specialized industrial advanced technology zones. Integrating local value chains of the existing and future specialized economic zones in areas of logistics & services, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, agriculture, agri-tech, steel, and aluminum.
CULTURAL COOPERATION ENERGY PARTNERSHIP, CLIMATE ACTION, AND RENEWABLE:
- Recognizing shared cultural heritage and strong ties rooted in history, the Leaders agreed to set up an India – UAE Cultural Council to facilitate and promote cross-cultural exchanges, cultural projects, exhibitions, and dialogue between thought leaders of the two countries.
- This will identify new collaboration opportunities to support India’s energy requirements, including new energies, and ensure the provision of affordable and secure energy supplies to India’s growing economy.
- As the UAE and India collectively navigate the global energy transition, both countries remain committed to working together to create a just and equitable transition to a low-carbon future
- To bring significant opportunities, for societies, economic growth, and businesses, the Leaders agreed to support each other’s clean energy missions.
FOOD SECURITY AND HEALTH COOPERATION:
- India and UAE will contribute to promoting and strengthening the infrastructure and dedicated logistic services connecting farms to ports to final destinations in the UAE.
- The countries will collaborate in the research, production, and development of reliable supply chains for vaccines and to enhance investments by UAE entities in the rapidly growing health infrastructure in India.
- The leaders also agreed to collaborate in providing health care in underprivileged countries.
EDUCATION COOPERATION AND SKILL COOPERATION:
- India and UAE agreed to establish an Indian Institute of Technology in the United Arab Emirates to establish world-class institutions that encourage and support innovation and technological progress.
- India-UAE agreed to enhance their cooperation to develop a mutually agreed professional standards and skills framework.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES:
- Recognizing the rapidly digitizing world, the two countries agreed to expand cooperation and collaborate on critical technologies and mutually promote e-businesses and e-payment solutions.
- They agreed to collaborate to promote start-ups from both countries to expand into the two regions and utilize such platforms as a basis for growth.
COOPERATION IN THE INTERNATIONAL ARENA:
- Reflecting shared values and principles, and growing strategic convergence, both countries have resolved to reinforce mutual support in multilateral areas to promote collaboration in economic and infrastructure spheres. They can also intensify cooperation in UNSC etc.
DEFENCE AND SECURITY:
- The countries agreed to enhance maritime cooperation contributing to the maintenance of peace and security in the region.
- Maintaining and strengthening peace in the Middle East through dialogue and cooperation must be the cornerstone of a more integrated, stable, and prosperous region.
- Joint commitment to the fight against extremism and terrorism, including cross-border terrorism, in all forms, at both regional and international levels.
MANY FIRSTS OF THE AGREEMENT
- Finalized and signed in a record time of just 88 days.
- The CEPA provides for automatic registration and marketing authorization of Indian generic medicines in 90 days, once they are approved in any of the developed countries. This will give big market access to Indian medicines.
- Indian jewelry exporters will get duty-free access to the UAE, which currently imposes a 5% customs duty on such products. This will substantially raise its jewelry exports.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE AGREEMENT FOR INDIA
STRATEGIC LOCATION OF UAE: The UAE, due to its strategic location, has emerged as an important economic hub not just within the context of the Middle East/ West Asia, but also globally. A trade agreement with the UAE could well be a springboard to realize our ambitious export targets.
INCREASE IN REMITTANCES: The CEPA will also help in increasing remittances as Indian investments in UAE will bring Indian employees into the Gulf country. The remittances are expected to rise with the full economic recovery of the UAE’s post-pandemic economy. According to a study, (82% of India’s total remittances originated from seven countries that included Gulf countries like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Kuwait.) *Total Remittances to India is estimated to be US $ 83.3 Billion in FY20.
MARKET FOR INDIAN GOODS: Will allow increased visibility of Indian products in the UAE. Due to the reduction in tariff for Indian jewelry and gems, food items such as cereals, sugar, fruits and vegetables, tea, meat and seafood, textiles, engineering and machinery products, chemicals.
MAKING INDIAN MANUFACTURING EXPORT-ORIENTED:
- The CEPA which covers almost 90% of exports will make it more attractive for Indian companies to invest in export-oriented businesses because of the zero-tariff facility that the UAE is expected to provide to Indian products.
- The agreement will provide significant benefits to Indian and UAE businesses, including enhanced market access and reduced tariffs. The CEPA will boost bilateral trade from the current $60 billion to $100 billion in the next 5 years.
- CEPA is expected to create new jobs, raise living standards, and provide wider social and economic opportunities in both nations.
ENTRY TO AFRICAN MARKET:
- This FTA with the UAE will pave the way for India to enter the UAE’s strategic location and have relatively easy access to the Africa market and its various trade partners which can help India to become a part of that supply chain, especially in handlooms, handicrafts, textiles, and pharma.
- This can be achieved by offering attractive investment opportunities in India with a globally competitive infrastructure and an investor-friendly regulatory framework.
- The UAE is a major global redistribution center and much of exports to Africa are routed through Dubai. The CEPA will encourage Indian Businesses for setting up warehousing or distribution centers in the UAE for exports to Africa.
ACCESS TO GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL (GCC) COUNTRIES’ COOPERATION ON MULTILATERAL PLATFORMS:
- The UAE is a party to several regional and bilateral FTAs and has strong economic ties with GCC Countries which may open the gates for India to have strong economic ties with these GCC countries.
- UAE has become a non-permanent member of UNSC for 2022-23 and India will assume the Presidency of G-20 in Dec-2022; both countries may complement each other on multilateral platforms on various issues.
- India’s major exports to the UAE: include petroleum products, precious metals, stones, gems and jewelry, minerals, food items such as cereals, sugar, fruits and vegetables, tea, meat, seafood, textiles, engineering, and machinery products, and chemicals.
- India’s top imports from the UAE: include petroleum and petroleum products, precious metals, stones, gems and jewelry, minerals, chemicals, wood, and wood products.
POTENTIAL CHALLENGES IN THE IMPLEMENTATION
UAE IS A LOW TARIFF ECONOMY: The scope of tariff reduction is limited and hence the gains to Indian exporters. In most of the labor-intensive sectors like textiles, clothing, leather, footwear, etc., while the maximum tariff rate is 5 percent, the average tariff rate is either 5 percent or less. In other manufacturing sectors such as non-electrical machinery, electrical machinery, transport equipment, which constitute a significant proportion of the Indian export basket to the UAE, the maximum tariff rate is again 5 percent and the average tariff rate is less than 5 percent.
SURGE IN IMPORTS: The issue for India is the possibility of a surge in imports from the UAE. This is mainly because it is an entrepot economy and re-exports form a large proportion of its gross exports.
RISK OF TREATY ABUSE: While the agreement will be mutually beneficial for both countries, India needs to ensure that goods originating from outside the UAE are not allowed duty-free into India under this treaty. The risk of treaty abuse arises because the UAE is a global transshipment hub and hence, India should guard against duty-free imports of transshipped products.
THE WAY FORWARD
- It is imperative for India to not only have strong rules of origin provision under the CEPA but also it must enforce them.
- To get duty-free access to the Indian market under the CEPA, the required value addition in the UAE has been kept at 40 percent, which is significantly higher than other FTAs where value addition requirement is generally 30-35 percent.
- The CEPA would also have an effective enforcement mechanism in place. This will reduce the excessive surge in imports.
- To enhance the utilization of CEPA it is also important to ensure that the cost of compliance remains at the minimum level.
Exploring Other Trade OpportunitiesIn Future: The success of India-UAE CEPA will also provide much-needed insight and confidence to India to have other similar FTAs with other countries having a potential market for the Indian Goods and Services. The Government of India has prioritized at least six countries to engage with under the new FTA policy, with the UAE at the top of the list for an early harvest deal. The United Kingdom, the European Union, Australia, Canada, Israel, and a group of Gulf Cooperation Council countries are the others (GCC). In due future, the early harvest agreement will be expanded into a comprehensive FTA.
THE CONCLUSION: The CEPA brings the two nations closer, will open many new opportunities for Indians to work in UAE, including in fintech, tech, green tech, automation, and Artificial Intelligence. Technology, digital trade, and sustainability have a big focus in the partnership. The CEPA will not only improve the competitiveness of Indian products but also provide strategic advantages to India. Both countries will identify clear areas of focus and establish ways of working together to resolve trade remedy cases as envisaged in the MoU signed in January 2017.
BACK TO BASICS
INDIA-UAE RELATIONS IN THE RECENT PAST
- The UAE is the eighth-largest investor in India: The UAE has invested $11 billion between April 2000 and March 2021.
- Investment by Indian companies in the UAE is estimated to be over $85 billion
- The UAE is India’s second-largest export destination after the US, with exports valued at approximately $29 billion in FY20.
- India was the UAE’s second-largest trading partner in 2019, with bilateral non-oil trade valued at $41 billion
- The UAE is currently India’s third-largest trading partner with bilateral trade in FY20 valued at $59 billion.
- Indian Diaspora in UAE: Indian expatriate community of approx. 3.5 million (as per International Migrant Stock 2020 released by the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) is reportedly the largest ethnic community in UAE constituting roughly about 30 percent of the country’s population.
- Military exercises between India and UAE: Both countries have come together in the past to have bilateral as well as multilateral military exercises:

VARIOUS TYPES OF TRADE AGREEMENTS
Free Trade Agreement (FTA): To establish a fair set of rules of trade between the agreeing countries. They provide favorable treatment to each other by reducing trade barriers such as cutting the import duties to/from the other country. They also work on easing out non-tariff barriers to exports like easing quantitative import restrictions, easing customs procedures, improving market access for service exports, and better investment rules.
FTAs help in trade, job creation, and economic growth and also serve as a diplomatic tool for improving international relations Eg: ASEAN countries impose a 20% duty on the import of leather goods however for India this is 0%.
There are various types of trade agreements such as
- Preferential Trade Agreements (PTA): In a PTA, two or more partners agree to reduce tariffs on the agreed number of tariff lines. The list of products on which the partners agree to reduce duty is called a positive list. India MERCOSUR PTA (Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Venezuela) is such an example. However, in general, PTAs do not cover substantially all trade.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): These terms describe agreements that consist of an integrated package on goods, services, and investment along with other areas including IPR, competition, etc. The India UAE CECA is one such example and it covers a broad range of other areas like trade facilitation and customs cooperation, investment, competition, IPR, etc.
- Broad-Based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA): India and the European Union (EU) are set to resume negotiations for a (BTIA). The BTIA talks have been suspended since 2013
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CECA/CEPA AND FTA
CECA/CEPA: More comprehensive and ambitious than FTA in terms of coverage of areas and the type of commitments i.e. a holistic coverage of many areas like services, investment, competition, government procurement, disputes, etc. CECA/CEPA looks deeper at the regulatory aspects of trade than an FTA.
FTA: FTA focuses mainly on goods. A free trade agreement is a pact between two or more nations to reduce barriers to imports and exports among them. Under a free trade policy, goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
FTAS OF INDIA WITH OTHER COUNTRIES AND THEIR ANALYSIS
- Presently, India shares preferential market access and economic cooperation through trade agreements with over 50 countries.
- India actively engages in regional and bilateral trade negotiations to diversify and expand its export markets while ensuring access to the raw materials, intermediates, and capital goods needed to stimulate value-added domestic manufacturing.
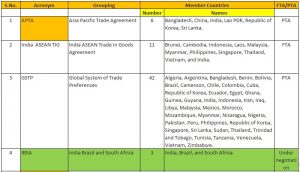
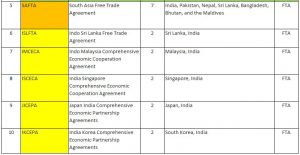
Table 1 https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/india-trade-agreements
It’s true that most of the trade agreements have not delivered the expected results in terms of FTA utilization rate, market penetration, integration with regional or global production networks, etc. Given the complementarities in economic structures of the two countries, the India-UAE CEPA could be a win-win for both economies as India is highly dependent on oil imports and is an agriculture surplus economy, whereas UAE is an oil rich and agriculture deficit economy.
Mains Ques
- The India-UAE CEPA will not only improve the competitiveness of Indian products but also provide strategic advantages to India. Explain
- UAE being an entrepot economy, how the CEPA can enhance India’s export prospects not only to the UAE but also to West Asia and even Africa regions.
- India –UAE CEPA may provide the much-needed boost to labour intensive sectors in India. Elaborate




