THE CONTEXT: An ongoing debate in India is whether or not Indian non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) are “shadow banks”. This question appears important because we have learned from the ongoing global financial crisis that shadow banking might create systemic risks which have been defined “broadly as the expected losses from the risk that the failure of a significant part of the financial sector leads to a reduction in credit availability with the potential for adversely affecting the real estate and economy at large.
WHAT IS SHADOW BANKING?
- Shadow banking is a blanket term to describe financial activities that take place among non-bank financial institutions outside the scope of federal regulators. These include investment banks, mortgage lenders, money market funds, insurance companies, hedge funds, private equity funds, and payday lenders, all of which are significant and growing sources of credit in the economy.
- Although these entities do not accept traditional demand deposits offered by banks, they do provide services similar to what commercial banks offer.
- The shadow banking system had overtaken the regular banking system in offering loans in the US before the financial crisis erupted in 2008.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH SHADOW BANKING?
- The 2008 financial crisis has shown that shadow banking can be a source of systemic risk to the banking system. The risks can be transmitted directly and through the interconnectedness of partially-regulated entities with the banking system.
WHY IS RBI TIGHTENING SHADOW BANKING RULES?
- The Reserve Bank is simply following the trend of global central banks increasing surveillance on shadow banking. Basel III norms require central banks to tighten supervision on shadow banks across the globe through steps such as defining minimum capital.
WHAT STEPS IS RBI TAKING?
- The Usha Thorat committee has come out with draft regulations on NBFCs, such as increasing tier I capital and risk weight on certain assets. After the recommendations, smaller NBFCs with asset sizes of less than 25 crores are likely to go out of business.
WHAT IS THE GLOBAL SITUATION?
- The size of shadow banking has reached a record $67 trillion in 2011, according to a report by the Finance Stability Board, a regulatory task force for the world’s group of 20 economies. America has the biggest shadow banking system, followed by the Eurozone and the United Kingdom.
Key Takeaways:
- The shadow banking system consists of lenders, brokers, and other credit intermediaries who fall outside the realm of traditional regulated banking.
- It is generally unregulated and not subject to the same kinds of risk, liquidity, and capital restrictions as traditional banks are.
- The shadow banking system played a major role in the expansion of housing credit in the run-up to the 2008 financial crisis but has grown in size and largely escaped government oversight even since then.
WHY SHADOW BANKING SHOULD WORRY POLICYMAKERS?
- RBI has warned that economic disruptions may intensify systemic risks to India’s financial sector, primarily because NBFCs remain vulnerable with their deteriorating asset quality and the reluctance of the market to lend them money.
- The banking regulator RBI issued a clear warning in its Fiscal Stability Report, that the economic disruptions may intensify risks to its shadow banking firms, the Non-Banking, Financial Companies (NBFCs), “and consequently” the systemic risks to the entire financial sector.
THREAT TO INDIA’S FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- The threats to the NBFCs come from two sources: (i) their deteriorating asset quality and (ii) continued reluctance of the market to lend money in the aftermath of implosion in two leading NBFC players, Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Limited (IL&FS) and Dewan Housing Finance Corporation Ltd (DHFL) in 2018 and 2019. Both were taken over by the RBI for loan defaults and now face bankruptcy proceedings.
- About 50% of the NBFCs’ aggregate assets were under the moratorium on loan repayment as per the latest analysis. Banks, which have been fighting shy of lending directly to the industry because of the growing threat of bad loans (non-performing assets or NPAs), increased their lending to the NBFCs in recent years, as a result of which bank lending accounted for 28.9% of the total NBFC borrowings in December 2019 – up from 23.1% in March 2017.
- The RBI noted that, notwithstanding this support from banks, the real risks to the NBFCs’ liquidity come from declining market borrowings. It said that under the stress tests, 11.2% to 19.5% of NBFCs would not be able to comply with the minimum regulatory capital requirements (CRAR) of 15%.
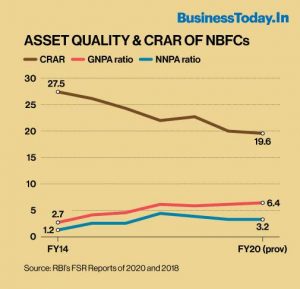
The following graph maps the NBFCs’ assets quality (GNPA and NNPA ratios) and capital-to-risk-assets ratio (CRAR) since FY14.
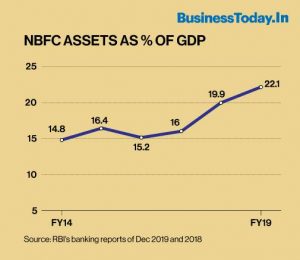
In the meanwhile, the NBFCs have grown in influence, as is evident from the RBI data mapped below, against the GDP (at constant prices).
- Shadow banking not only poses a threat to India but is equally a risk to the global financial order. For better appreciation, the 2007-08 financial crisis needs to be revisited.
ENDURING OVERALL GROWTH IN SHADOW BANKING
- When the world woke up and started monitoring shadow banking, Kodres recorded the growth in their assets. In 2015, she wrote, their assets in the US was 28% of the total financial sector (down from 32% in 2011); in the euro area, it was 33% (up from 32% in 2011) and globally they accounted for $92 trillion (up from $62 trillion in 2007 and $59 trillion during the crisis).
- One big initiative to monitor shadow banking was the multinational Financial Stability Board (FSB), set up in 2011. India is a part of this initiative.
- But Kodres was not happy. She commented: “The authorities (monitoring shadow banking) are making progress, but they work in the shadows themselves – trying to piece together disparate and incomplete data to see what, if any, systemic risks are associated with the various activities, entities, and instruments that comprise the shadow banking system.”
- Initially, the FSB defined shadow banks broadly to include all entities “outside the regulated banking system that perform core banking function”, which meant credit intermediation (taking money from savers and lending it to borrowers) and they were called Non-Banking Financial Intermediation (NBFI).
- In its latest report of January 2020, the FSB divided those into three categories: (a) MUNFI (Monitoring Universe of Non-bank Financial Intermediation): “broad measure” of all NBFIs that are not central banks, banks, or public financial institutions (b) OFIs (Other Financial Intermediaries): a subset of MUNFI that excludes insurance corporations, pension funds or financial auxiliaries and (c) NBFIs: “narrow measure” of NBFI comprising of non-banks that authorities have identified as the ones that may pose bank-like financial stability risks and/or regulatory arbitrage.
- The NBFIs (narrow measure) are the ones identified as posing systemic risks.
HEIGHTENED SYSTEMIC RISKS FROM SHADOW BANKING
- The 2020 FSB report shows that global estimates for the MUNFI assets stood at $183.6 trillion in 2018 or 49% of the total financial assets ($379 trillion). Of this, OFIs accounted for $114.3 trillion (30% of the total); NBFI for $50.9 trillion (13.4% of the total), and the rest for $18 trillion.
- The FSB 2020 report says the “systemic risk” comes from activities that are “typically performed by banks, such as maturity/liquidity transformation and the creation of leverage”.
- The alarming aspect of the NBFI is that it is growing.
- The FSB 2020 report says it “has grown faster than GDP since 2012, increasing to 77% of all participating jurisdictions’ GDP in 2018 from 64% in 2012. This trend is observed in most jurisdictions”.
- The FSB measures 29 jurisdictions (including India and China), representing over 80% of global GDP.
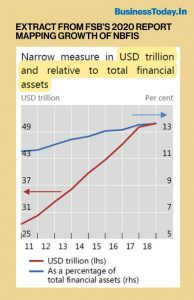
GROWTH IN INDIA’S SHADOW BANKING (NBFCS)
- What does the FSB of 2020 say about India? (India’s NBFCs correspond to the NBFIs.) It shows India is an outlier – in a negative way.
Here are two examples
- India recorded 22.4% growth in OFI assets in 2018, while the global growth was 0.4%.
- As for NBFIs (NBFCs in India), a major drawback is their over-dependence on short-term funding for long-term lending (technically called EF2 function).
- Globally, such funding accounted for 7% of the total in 2018 and it grew 6.9%. In sharp contrast, India recorded a 17.4% growth in 2018. As for its share in the total NBFC funding, the RBI’s banking trend report released in December 2017 revealed that it stood at an unbelievably high of 99.7%.
- In the NBFC context, short-term means a period of up to three years and long-term for up to 15 years, as in the case of housing and infrastructure loans. Why such anomaly continues in the NBFCs’ functioning is an abiding mystery.
- Little wonder, when the NBFC crisis hit India in 2018 and 2019, the two big players to implode (IL&FS and DHIL) were associated with infrastructure and housing sectors, though this is only one part of the saga.
IS SHADOW BANKING A SERIOUS THREAT IN EMERGING MARKETS?
- The IL&FS crisis has exposed the vulnerabilities of non-bank lending. But in India, the problem is one of a huge bad debt pile-up despite low credit disbursal.
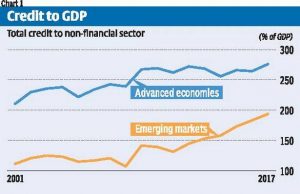
- Everyone seems to have woken up to the fact that global debt levels are too high and portent difficulties ahead. As Figure 1 indicates, the levels of credit to GDP, which were so high as to be unsustainable and resulted in the big crisis of 2008, have increased even more since then.
- There was a phase of deleveraging in the advanced economies until around 2014, and in developing countries and emerging markets until 2011, but since then, credit/debt has been expanding again.
- So much so that the credit GDP levels in 2017 were 15 percent higher than in 2008 in the advanced economies, and more than 80 percent higher for emerging markets (Figure 1).
- More recently, the attention has shifted from bank lending to shadow banking activities, which are by those institutions that do not collect deposits but still provide loans. These include a variety of institutions, ranging from trusts, investment funds, and similar corporations to kerb lenders.
- Because they do not come under the regulatory framework for banks, yet tend to be interlinked with them in various ways, there are concerns that overlending and default in such institutions can destabilize the financial system.
LINGERING FRAGILITIES
- Ever since the IL&FS crisis broke in India, there has been much discussion of the fragilities posed by non-bank lending and the potential for financial and economic crises in emerging markets that could be led by the collapse of shadow banks. This is in no small measure due to the significant role played by such shadow lending in the core capitalist countries (especially the US) in the build-up to the Great Financial Crisis in 2008.
- However, since then, shadow lending appears to have reduced or at least been contained relative to GDP, as indicated by Figure 2. For the G20 countries taken as a group, credit from non-banks as a percent of GDP was about 6 percentage points lower in 2017 than in 2007, while bank credit had actually increased by 15 percentage points. This suggests that excessive debt creation is much more a problem of the banking sector as a whole than the non-bank or shadow bank sector.
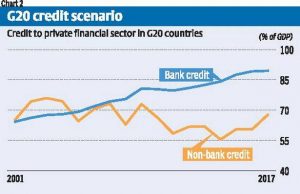
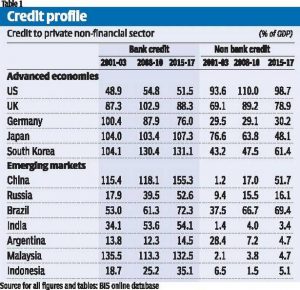
- Table 1 provides data for some important advanced and emerging economies to assess the extent to which this argument is valid. Significantly, the reliance on shadow banking appears to have reduced significantly in the advanced economies by 2015-17 from what it was during 2008-10, other than in Germany, where it seems to have remained at roughly the same level of around 30 percent. Even the increase in bank credit was confined to Japan and South Korea, rather than the US, UK, or Germany, where it has fallen relative to the levels of 2008-10.
WAY FORWARD:
- It is also increasingly suggested that the problem of shadow banking has become more significant in emerging markets rather than in advanced economies and that the dramatic increase in such loans in these economies is what will be associated with the next big systemic risk to global finance.
- In particular, it is suggested that the rapid increase of shadow banking in Asia, especially China, points to the likely area of greatest future concern.
CONCLUSION:
NBFC sector has been stung by a crisis set off by the shock collapse of non-bank lender IL&FS group in 2018. India’s shadow banks, which lend to everyone from teashop merchants to property tycoons, get a mixed bill of health in Bloomberg’s latest check. Revitalization of the industry, whose woes mounted when major mortgage lender Dewan Housing Finance Corp. missed repayments is key to helping staunch a further slowdown in the nation’s economy. In a sign that creditors remain jittery, borrowing costs rose. The extra yield investor’s demand to hold five-year AAA-rated bonds from shadow banks over government notes increased, one of the gauges shows. Shadow lender woes have made it harder for policymakers to prop up the economy, which grew at its weakest pace since 2009. The slowdown hurts borrowers’ ability to repay debt and has prompted the central bank to predict that an improvement in banks’ bad-loan ratios will reverse. So, it is established that Indian NBFCs are shadow banks and they do pose systemic risks to a certain extent. Hence, the RBI should make a long-term policy for the Indian NBFC sector to mitigate any risk that may crop up in the already fragile financial sector in India.
Spread the Word



