INDIAN ECONOMY
1. REPORT ON TREND AND PROGRESS OF BANKING IN INDIA 2020-21: RBI
THE CONTEXT: According to the report, Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2020-21”, published by the RBI, which states that the banking sector managed to improve asset quality during the Covid year with the ratio of gross non-performing assets to advances declining from 8.2 per cent at March-end 2020 to 7.3 per cent at March-end 2021 — and further to 6.9 per cent at September-end 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Also, the report says, the loan write-offs were the predominant recourse for lowering gross NPAs in 2020-21. This improvement was also driven by lower slippages, partly due to the asset classification standstill.
- In absolute terms, gross NPAs declined to Rs 8,37,771 crore in March 2021 from Rs 8,99,803 crore in March 2020. NPAs worth Rs 4 lakh crore were added during the year while bad loans of Rs 2.08 lakh crore were written off by banks. Of the total NPAs, Rs 6.16 lakh crore in bad loans were accounted for by public sector banks.
- The ratio of gross NPAs to advances indicates the proportion of loans out of the total lending that has not been repaid within the due period. Banks normally write off a non-performing asset when all recovery measures are exhausted and chances of recovery are remote.
- In April 2020, when Covid hit the economy, the RBI decided to provide relief to standard bank accounts availing a loan moratorium between March 1 and May 31 that year. The 90-day NPA norm excluded the moratorium period for such accounts. The RBI provided a standstill on asset classification for standard bank accounts, implying these couldn’t be classified as bad assets after the stipulated 90-day period.
- The report highlights, that during 2020-21, the consolidated balance sheet of banks expanded in size, notwithstanding the pandemic and the resultant contraction in economic activity. “In 2021-22 so far, nascent signs of recovery are visible in credit growth. Deposits grew by 10.1 per cent at end-September 2021 as compared with 11.0 per cent in 2020.
- The RBI said the share of large borrowable accounts (exposure of Rs 5 crore or more) in total advances declined to 51 per cent at end-March 2021 from 54.2 per cent a year ago. Their contribution to total NPAs also declined in tandem from 75.4 per cent to 66.2 per cent during the same period.
- The consolidated balance sheet of NBFCs expanded during 2020-21, driven by credit and investments of non-deposit taking systemically important NBFCs (NBFCs-ND-SI). Their asset quality and capital buffers also improved.
LOAN RECOVERY VIA LOK ADALATS, IBC FALLS IN FY21
- According to the report, the banks reported 4,071 frauds involving Rs 36,342 crore during the six-month period ended September 2021 as against 3,499 frauds involving Rs 64,261 crore in the same period of 2020.
- Loan recovery through various channels, most notably Lok Adalats, witnessed a sizeable decline in the cases referred for resolution during 2020-21.
- While 20.35 lakh cases were reported in FY21 involving Rs 4.56 lakh crore, only Rs 64,228 crore was recovered. In 2019-20, 61.27 lakh cases involving Rs 6.94 lakh crore were reported, with Rs 1.52 lakh crore of loans recovered.
- Even though initiation of fresh insolvency proceedings under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) of India was suspended for a year till March 2021 and Covid-19 related debt was excluded from the definition of default, it constituted one of the major modes of recoveries in terms of amount recovered.
- In the year 2020, out of Rs 2,24,935 crore referred, only Rs 1,04,117 crore was recovered.
- Recoveries through Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs) were lower at Rs 8,113 crore, as against Rs 9,986 crore in the year 2020, and at Rs 27,686 crore through SARFAESI Act, against Rs 34,283 crore.
- Allowing pre-pack resolution window for MSMEs is expected to assuage the mounting pressure of pending cases before NCLTs, reduce haircuts and improve declining recovery rates.
Trends on Banking frauds
- There was a marked increase in frauds related to private banks, both in terms of number as well as the amount involved. In the first half of 2021-22, private banks accounted for more than half of the number of reported fraud cases.
- However, in value terms, the share of PSU banks was higher, indicating predominance of high value frauds. While the major share of loan-related cases pertained to PSU banks, private banks accounted for a majority of card/ internet and cash-related cases.
Value Addition:
What is the difference between Loan Waiver and Loan Write-offs?
- The major difference between “Write off” & “Waive off” Loan is that Loan Waive-off is something where the loan-taker is released from the burden of paying back the loan amount, while in the case of Loan Write-off; the financial institute still hopes to recover the loan amount from the person who not repaid it back.
- The decision of waiving off a loan is taken by the Government under certain conditions while Loan Write-off is carried out by the banks to keep a clear record of the unrecovered loan amount in their balance sheets.
NPA Classification
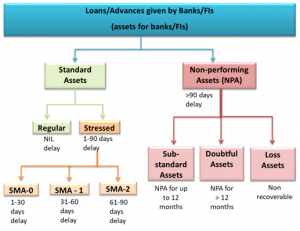
About Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC)
- The IBC, 2016 is the bankruptcy law of India that seeks to consolidate the existing framework by creating a single law for insolvency and bankruptcy.
- It is a one-stop solution for resolving insolvencies which previously was a long process that did not offer an economically viable arrangement.
- The code aims to protect the interests of small investors and make the process of doing business less cumbersome.
What is Lok Adalat?
- It is one of the components of the Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) system and delivers informal, cheap and expeditious justice to the common people.
- The first Lok Adalat camp was organised in Gujarat in 1982 as a voluntary and conciliatory agency without any statutory backing for its decisions.
- In view of its growing popularity over time, it was given statutory status under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987. The Act makes the provisions relating to the organisation and functioning of the Lok Adalats.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. BIHAR GOVERNMENT PLANS TO STERILISE NILGAI’S
THE CONTEXT: The Bihar forest department officials, caught six nilgais from the premises of Bihta Airport Station near Patna and sterilised them. They were taken to Valmiki Tiger Reserve in the state’s West Champaran district.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Forest officials that they will not cull the Blue Bull, locally known as the nilgai or ghurparas, anymore. It will, instead, sterilise them to control their increasing population in the state.
- The state government will sterilise 5,000 nilgais in 2022. “All district forest officers have been asked to do so in their respective jurisdiction. Sterlising Nilgais is easier and eco-friendly. This will not harm them and provide much-needed relief to farmers”.
- The step was the result of a December 1, 2015, notification by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) that declared the nilgai and wild boar vermin in some districts of Bihar.
What is the Issue?
- Farmers in flood-prone north Bihar districts to drought-prone south Bihar districts have been troubled with nilgais, which regularly forage into farmland in search of food and damage crops.
- Farmers Baban Mahto and Ramji Singh Buxar districts said the animal has been destroying their wheat, mustard, seed and potato crops since early December of 2021. Their numbers have increased in the last two-three years.
About Nilgai:

- The Nilgai (Boselaphus tragocamelus) is one of the largest species of Asian antelope native to the Indian subcontinent. The name ‘nilgai’ translates to ‘blue cow’.
- Major populations of the Nilgai are found in India, Nepal and Pakistan. It is found in large numbers across northern India.
- Nilgai are herbivores feeding on grass and herbs. Nilgai are better adapted to interference from livestock regarding forage competition as they can reach high branches and do not primarily depend on ground vegetation.
- The preferable habitat of a nilgai is the one replete with short bushes with scattered trees and grassy plains. They are common in agricultural lands as well.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN status: Least Conservation
- Wildlife Protection Act of 1972: Schedule III
What is Vermin?
Vermin means wild mammals and birds which are harmful to crops, farm animals or which carry disease. In India, wild animals can be declared as vermin if they have become (i) dangerous to human life or property (including standing crops on any land). (ii) become disabled or diseased as to be beyond recovery.
How are they declared?
- Wildlife laws divide species into ‘schedules’ ranked from I to V. Schedule I members are the best protected, in theory, with severe punishments meted out to those who hunt them. Wild boars, nilgai and rhesus monkeys are Schedule II and III members — also protected but can be hunted under specific conditions. Crows and fruit bat fall in Schedule 5, the vermin category.
- Section 11(1)a of the Wildlife Protection Act (WPA) authorizes chief wildlife warden to permit hunting of any problem wild animal only if it cannot be captured, tranquillized or translocated.
- For wild animals in Schedule II, III or IV, chief wildlife warden or authorized officers can permit their hunting in a specified area if they have become dangerous to humans or property (including standing crops on any land).
- Section 62 of Act empowers Centre to declare wild animals other than Schedule I & II to be vermin for specified area and period.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3. CHINA LAUNCHES MINERAL SURVEY AND SCIENCE OUTREACH SATELLITES
THE CONTEXT: China launched the Ziyuan 1 (02E) Earth resources observation satellite and a small amateur radio satellite, marking the country’s 53rd orbital launch of the year.
THE EXPLANATION:

- China has deployed a new Earth resources observation satellite via its Chang Zheng 4C rocket. The Ziyuan-1 02E satellite, along with an amateur radio CubeSat, lifted off from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center.
- Ziyuan (ZY), meaning Resource, is a series of remote-sensing satellites which China uses to acquire high-resolution images that can be used for surveying Earth resources, disaster management, and ecological and land use monitoring.
- The first Ziyuan satellite, Ziyuan-1 01, was launched in 1999 in a partnership between China and the Brazilian national space agency, INPE. Six of the nine Ziyuan satellites launched to date have been part of the China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS) program, with the other three – including Ziyuan-1 02E – being solely Chinese-operated. Three more all-Chinese Ziyuan-3 satellites have also been launched, while the designation Ziyuan-2 was applied to a trio of military reconnaissance satellites deployed in the early 2000s, which are not part of the civilian Ziyuan series.
- Ziyuan-1 02E is believed to be similar in design to the Ziyuan-1 02D satellite launched in September 2019. It carries the same two imaging payloads: a high-resolution visible and near-infrared camera and a hyperspectral imager, as well as a new long-wave infrared camera.
- The high-resolution camera will be able to produce images with resolutions of up to five meters when operating in panchromatic mode. When operating in multispectral mode, it can produce images across three bands with a resolution of up to 10 meters. The hyperspectral payload can image across 166 spectral bands.
|
Some India’s earth observation satellites are:
|
4. LOG4J VULNERABILITY
THE CONTEXT: A new vulnerability named Log4 Shell is being touted as one of the worst cybersecurity flaws to have been discovered.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The vulnerability is dubbed Log4 Shell and is officially CVE-2021-44228.
- CVE number is the unique number given to each vulnerability discovered across the world).
- It is based on an open-source logging library used in most applications by enterprises and even government agencies.
- The exploits for this vulnerability are already being tested by hackers and it grants them access to an application, and could potentially let them run malicious software on a device or servers.
- The problem impacts Log4j 2 versions which is a very common logging library used by applications across the world.
- Logging lets developers see all the activity of an application.
Concerns:
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Most of the attacks they have observed appear to focus on the use of cryptocurrency mining at the expense of the victims. However, new variations of the original exploit are being introduced rapidly.
- Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to disclosure of sensitive information, addition or modification of data, or Denial of Service (DoS).
- Global: The Australia-New Zealand (ANZ) area was the most impacted region with 46% of corporate networks facing an attempted exploit.
- While North America was the least impacted with 36.4% of organizations facing such an attempt.
- India: About 41% of corporate networks in India have already faced an attempted exploit.
- Indian companies are not more vulnerable than their western counterparts because they use Java-based applications.
- Indian companies are at high risk because of their weak security posture, especially the smaller companies that may not have the know-how or resources to detect and fix the issue quickly.
- In other countries such as China, some of the telcos such as China Unicom had started 5G trials as early as 2018, and have since rolled out the commercial services for users.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTION
Q1. The term ‘ACE2’ is talked about in the context of
a) genes introduced in genetically modified plants.
b) developments of India’s own satellite navigation system
c) radio collars for wildlife tracking
d) spread of viral diseases
ANSWER FOR 28TH DECEMBER 2021
ANSWER: D
EXPLANATION:
- Shah Nawaz Khan, Prem Kumar Sehgal and Gurubaksh Singh Dhillon were officers of Indian National Army. Their whose was held in 1945 at the Red Fort in Delhi.




