GEOGRAPHY: DISTRIBUTION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
1. GOA APPROVES EXPORT OF LOW-GRADE IRON ORE
THE CONTEXT: The Goa state Government permitting mining companies to export low-grade iron ore, paving the way for the resumption of mining activity that has been stalled since 2018.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Government, about 10 to 20 million tonnes of low-grade iron ore were lying at different locations outside the mining leases and could sustain mining activity in Goa for the next four-five years.
- “The State government has formulated a policy for regularisation of mining dumps on government and private land. The Chief Minister stated that in the past the State Land Revenue Code had empowered the government to impose fines if the land was used for dumping mining rejects or similar materials without permission.
- Goa’s mining sector, which contributed about 15-16% of the State’s Gross Domestic Product in 2011-12, now accounts for barely 2%.
- In March, the Supreme Court had deemed Goa’s mining lease renewals to be illegal and canceled 88 such leases that had been renewed by the State government in 2014-15.
- In March 2021 the Supreme Court had deemed Goa’s mining lease renewals to be illegal and canceled 88 such leases that had been renewed by the State government in 2014-15.
- The government would take over the mining dumps where the penalty was not paid and auction the ore.
Value Addition:
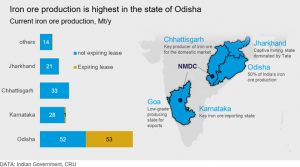
The total recoverable reserves of iron ore in India are about 9,602 million tonnes of hematite and 3,408 million tonnes of magnetite. Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Jharkhand, Odisha, Goa, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are the principal Indian producers of iron ore.
INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
2. TUSSLE OVER THE ELECTION OF MAHARASHTRA ASSEMBLY SPEAKER
THE CONTEXT: Amid ongoing tensions between the Governor of Maharashtra and the State Government over the election to the Speaker of the Assembly, and the winter session of the state assembly ends but the Governor has not given his consent to the election programme recommended by the Cabinet.
THE EXPLANATION:
What Constitution says?
Article 178 of the Constitution states: “Every Legislative Assembly of a State shall, as soon as may be, choose two members of the Assembly to be respectively Speaker and Deputy Speaker thereof and, so often as the office of Speaker or Deputy Speaker becomes vacant, the Assembly shall choose another member to be Speaker or Deputy Speaker, as the case may be.”
The Constitution does not specify the process of holding these elections; that is left to the state legislatures. It also does not set a timeframe other than to say the elections should be held “as soon as maybe”.
Some states lay down timeframes
- In Haryana, the election of the Speaker must be held as soon as possible after the Assembly election, and the Deputy Speaker must be elected within another seven days.
- In UP, the Speaker’s election is required to be held within 15 days if the post falls vacant during the term of the Assembly.
- The date for the Speaker’s election is notified by the Governor.
A crucial case in Maharashtra
- As per Rule 6 of the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly Rules, “The Governor shall fix a date for the holding of the election and the Secretary shall send to every member notice of the date so fixed.”
- A former Secretary of the state Assembly said the election of the Speaker can take place only after the Governor fixes the date for it.
What are the recent amendments?
- The govt has moved a motion in the Assembly seeking amendments to Rules 6 (election of Assembly Speaker) and 7 (election of Deputy Assembly Speaker) by voice vote instead of a secret ballot.
- The amendments excluded the words “holding of the election” and included the words “to elect the Speaker on the recommendation of the Chief Minister” in Rule 6 of Maharashtra Assembly Rules.
What are the objections to these amendments?
- The Opposition accused the govt of running the “most insecure government” that does not trust its MLAs and fears there would be cross-voting in the election of the Speaker.
- It argued that the Rules cannot be amended in the absence of the Speaker.
What is the government’s position?
- The government has argued that the amendments are in line with the Rules that are in practice in Lok Sabha, the Upper House of the state legislature, and in the Assemblies of several other states.
- It has also been said that the amendments would put an end to horse-trading.
What is the way ahead?
- The govt can explore legal options to see whether the election of the Speaker could be held without the consent of the Governor. However, the situation is very odd.
- While Rule 6 mandates that the Governor should fix the date for the election, the amendment says that the Governor should fix the date on the advice of the CM.
3. NORTHEASTERN REGION DISTRICT SDG INDEX: NITI AAYOG
THE CONTEXT: Niti Aayog with technical support from UNDP, released the first its kind Northeastern Region District SDG Index. The index measures the performance of the district of the eight NE States. This SDG Index will be used as a base for planning of development and welfare activities, education, health care.
THE EXPLANATION:
According to the report, the East Sikkim district of Sikkim has topped the Northeastern Region (NER) District SDG Index 2021-22 while the Kiphire district of Nagaland was ranked last amongst 103 districts in the ranking. Gomati, North Tripura is second, West Tripura is third in the ranking.
What is NER District SDG Index?
- The Index measures the performance of the districts of the eight states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura on the Sustainable Development Goals and ranks these districts on the basis of the same.
- The index offers insights into the social, economic, and environmental status of the region and its districts in their march towards achieving the SDGs. East Sikkim was ranked first in the region, followed by districts Gomati and North Tripura in the second position.
- “The North-eastern Region District SDG Index will help in evidence-based planning, resource allocation, both financial as well as others, and effective supervision and monitoring of developmental efforts for focused and balanced regional development”.
Objectives:
- To strengthen the monitoring of SDGs for all States and Districts of the region
- To establish the NER District SDG Index as the comprehensive progress monitoring tool at the district level
- To enable the States and Districts to identify critical sectoral gaps
- To promote healthy competition in the region among States and Districts
- To facilitate cross-learning through good practices and challenges
4. ATAL RANKINGS FOR INNOVATION
THE CONTEXT: Ministry of Education released the “Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements (ARIIA),” out of which Sevan Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) have made it to the top 10.
THE EXPLANATION:
- IIT Madras, IIT Bombay and IIT Delhi topped the rankings for technical central universities, for their innovative approach. The IITs in Kanpur, Roorkee, Hyderabad and Kharagpur also feature in the top 10.
- Other institutions on the list are Bengaluru’s Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Prayagraj’s Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, and the National Institute of Technology in Kozhikode (formerly Calicut).
- According to Education Ministry, the ARIIA rankings will “inspire Indian institutions to reorient their mindset and build ecosystems to encourage high-quality research, innovation and entrepreneurship in their campuses”. The rankings will inspire institutions to ‘reorient their mindset’, promote innovation to achieve $5 trillion economies by 2025.
What is ARIIA?
- ARIIA is an annual ranking released by the education ministry to recognize the contribution of institutions in research and innovation. It systematically ranks all major higher education institutions and universities in India on indicators related to the promotion and support of “innovation and entrepreneurship development” among students and faculty.
- The first edition of ARIIA was released in 2019 when a total of 496 institutes competed to get a ranking. This year, 1,438 institutions (including all IITs, NITs, IISc, etc.) participated.
Parameters:
- The parameters on which institutes were judged include academic courses offered on innovation and start-up, successful innovation and start-ups that emerged from campus, investment, collaboration and partnerships with ecosystem enablers, research outputs and technology transfer and commercialization efforts.
- The ranking is divided into two categories — technical and non-technical institutions. There are five sub-categories under the ‘technical’ category— central universities, state universities, private universities, government-aided institutions, and deemed private universities. Under ‘non-technical’ institutions, the categories are ‘central government’ and ‘general’.
THE DEFENCE AND SECURITY
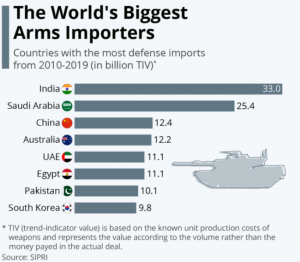
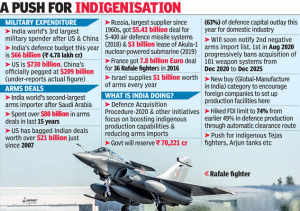
5. INDIGENISATION2500 SUBSYSTEMS BARRED FROM IMPORTS: MOD
THE CONTEXT: Following the two positive indigenization lists barring the import of 209 major platforms and systems, the Defence Ministry notified a list of another 2,500 subsystems and components and 351 more imported items to be made locally in the next three years.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Ministry of Defence, “The Atmanirbhar initiative will save foreign exchange approximately equivalent to ₹3,000 crores every year”.
- A positive indigenization list of subsystems and components had been notified by the Department of Defence Production as part of the MoD’s efforts to achieve self-reliance in manufacturing and minimize imports by the Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs). They would only be procured from the Indian industry after the timelines indicated in the list.
- “DPSUs will work in close coordination with local industrial supply chain to ensure strict adherence to the stipulated timelines.” Necessary certifications/approval of all items included in the list shall be granted on priority by the stakeholders concerned.
To reduce imports
- The positive indigenization list is among a series of measures announced recently to reduce defence imports and give a push to domestic manufacturing.
- At present, India’s defence and aerospace manufacturing market was worth ₹85,000 crores, of which the present contribution of the private sector was ₹18,000 crore. In 2022, the country’s defence and aerospace manufacturing market would increase to ₹1 lakh crore and could reach ₹5 lakh crore by 2047.
- The Ministry is also expected to put out the final version of the ‘Defence Production and Export Promotion Policy (DPEPP) 2020’, the draft of which has been released for public feedback.
Emerging technologies
- Indian Army said in its statement, “Army has also established an Artificial Intelligence (AI) Centre at the same institution with over 140 deployments in forwarding areas and active support of industry and academia. Training on cyberwarfare is being imparted through a state of art cyber range, and cyber security labs”.
- Ideation for the Army’s involvement in Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations was done in a seminar on Electromagnetic Spectrum and National Security organized in October 2020, the statement noted and added that since then an impetus had been given to the Army’s technology institutions for investing in AI, quantum and cyber.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
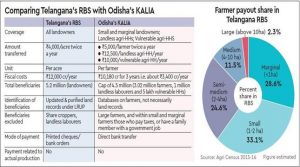
6. RYTHU BANDHU SCHEME OF TELANGANA
THE CONTEXT: Ahead of the ongoing Rabi season, the Telangana government started crediting money into the bank accounts of eligible beneficiaries in the state.
THE EXPLANATION:
Under the Rythu Bandhu scheme, as many as 66.56 lakh farmers identified as beneficiaries, regardless of the extent of land owned by them, would receive financial assistance in 10 days.
With this, the state government would have disbursed Rs 50,405.63 crore to farmers under the scheme to date, a major landmark since its inception in May 2018.
What is Rythu Bandhu?
- Rythu Bandhu is a scheme under which the state government extends financial support to land-owning farmers at the beginning of the crop season through direct benefit transfer so that they can take care of the initial investment needs and do not fall into a debt trap.
- This in turn instills confidence in farmers, enhances productivity and income, and breaks the cycle of rural indebtedness.
- Each farmer gets Rs 5,000 per acre per crop season without any ceiling on the number of acres held. So, a farmer who owns two acres of land would receive Rs 20,000 a year, whereas a farmer who owns 10 acres would receive Rs 1 lakh a year from the government. The grant helps them cover the expenses on input requirements such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and labour.
How does it compare with the PM-KISAN scheme?
The state government has often said that the Centre’s PM-KISAN (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi) scheme is a “copy” of Rythu Bandhu. The Telangana government further claims that its own scheme is much better than PM-KISAN.
What about landless farmers?
- The Rythu Bandhu scheme has also come in from criticism from several quarters, with one of the major ones being that it ignores the plight of landless or tenant farmers.
- Farmer bodies have been demanding that the state government should extend the agriculture assistance to tenant farmers as well. They have pointed out that those who work on lands taken on lease from landowners also need government assistance at the beginning of a crop season.
PLACES IN NEWS
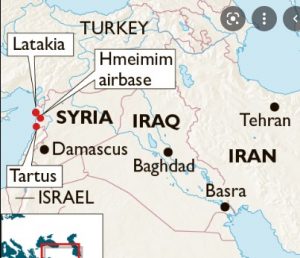
7. PORT OF LATAKIA
THE CONTEXT: An Israeli airstrike hit a shipment of Iranian weapons in the Syrian port of Latakia on 7th December 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
Port of Latakia:
- The Port of Latakia is a seaport, located on the Mediterranean Sea in the city of Latakia.
- Established in 1950, it has since served as Syria’s main seaport.
Significance:
- The repeated strikes are a flagrant violation of Syria’s sovereignty. Israel, which has hardly upheld international norms and laws when it comes to its security policies, is setting another bad precedent.
- Syria, devastated by the civil war, is emerging as a new front in the Israel-Iran tussle. In recent years, Israel has reportedly carried out sabotage activities inside Iran and assassinated Iranian nuclear scientists. Iran, in return, has attacked Israel-linked vessels in the Gulf and Mediterranean waters and enhanced supplies to Shia rebel groups in the region.
- Iran is preparing to take control of Syria’s main commercial port, advancing its plans to secure a trade route from Tehran to the Mediterranean and establishing a significant foothold on Israel’s doorstep.
- Russia, whose primary focus in Syria is on the survival of the Assad regime and the protection of its own troops and assets deployed there, has largely stayed away from the Iran-Israel cold war. This gives Israel a free hand in Syria to target the Iranian and Hezbollah shipments.
Major ports in Syria:
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTION
|
Q1. With reference to the history of ancient India, Bhavabhuti, Hastimalla andKshemeshvara were famous – a) Jain monks b) Playwrights c) temple architects d) philosophers ANSWER FOR 29THDECEMBER 2021 Answer: D EXPLANATION: ACE2: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the angiotensin-converting enzyme family of dipeptidyl carboxypeptidases and has considerable homology to the human angiotensin 1 converting enzyme. This secreted protein catalyzes the cleavage of angiotensin I into angiotensin 1-9, and angiotensin II into the vasodilator angiotensin1-7. ACE2 is known to be expressed in various human organs, and its organ- and cell-specific expression suggests that it may play a role in the regulation of cardiovascular and renal function, as well as fertility. In addition, the encoded protein is a functional receptor for the spike glycoprotein of the human coronavirus HCoV-NL63 and the human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses, SARS-CoVand SARS-CoV-2, the latter is the causative agent of coronavirus disease-2019(COVID-19). Multiple splice variants have been found for this gene and the dACE2(or MIRb-ACE2) splice variant has been found to be interferon inducible. |


