THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. THE CHINESE PROJECT AT BALOCHISTAN PORT
THE CONTEXT: Amid continuous protests in Gwadar, Balochistan against mega development plans of the port city as part of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Despite the severe conservatism of Balochistan, women protesters have come out in large numbers.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Balochistan is among the least developed even though the most resource-rich of Pakistan’s four provinces. The main means of livelihood for people in the region is Balochistan has the lowest access to drinking water, electricity, and even the gas that is the main resource of the region.
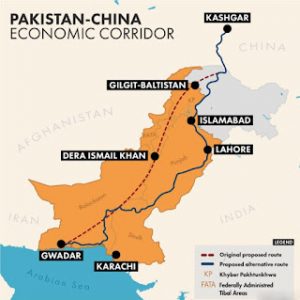
- The port development at Gwadar is perhaps the single most strategically important project of the CPEC, and Chinese involvement there predates the CPEC by at least a decade.
- Protesters pointed out that while Gwadar fishermen had given up their fishing spots for development of the port after assurances that it would greatly improve their economic condition, their existing condition was only worsening because of the unequal competition with the Chinese fishing vessels, which were also harming the eco-system.
- Work there began during the 10-year rule of General Pervez Musharraf, who pitched it as a strategic energy corridor that would provide the Chinese an alternative to the sea route for its oil imports from the middle east. Now it is integral to the Chinese President’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Ever since, Baloch nationalists have been angry at their exclusion, and separatist insurgent groups like the Baloch Liberation Army and others have targeted Chinese interests in and around Gwadar. The attacks have only risen after the CPEC took off. An attack on the Serena in 2019 took place during a visit by an official Chinese delegation. In response, more Pakistani troops have flooded the port city. One of the protesters’ demands is a reduction in the number of checkpoints.
Concerns of India, West
India has been concerned that Gwadar, which gives China strategic access to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, is not just being developed as a trade entrepot but as a dual-purpose port for use by PLAN (the Chinese Navy) and is intended to expand Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean Region alongside Kyaukpyu in Myanmar and Hambantota in Sri Lanka. With vital military interests in West Asia, the US too is concerned about the Chinese presence in Gwadar.
About CPEC:
- Launched in 2015, the CPEC is the flagship project of the multi-billion-dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a pet project of Chinese President, aimed at enhancing Beijing’s influence around the world through China-funded infrastructure projects.
- The 3,000 km-long China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) consists of highways, railways, and pipelines.
- CPEC eventually aims at linking the city of Gwadar in South Western Pakistan to China’s North Western region Xinjiang through a vast network of highways and railways.
- The proposed project will be financed by heavily-subsidised loans, that will be disbursed to the Government of Pakistan by Chinese banks.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. THE DECLINE OF DRAGONFLY POPULATION
THE CONTEXT: According to the update of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, the number of species is at risk of extinction on the Red List has exceeded 40,000 for the first time. The destruction of wetlands is leading to the decline of dragonflies worldwide.
THE EXPLANATION:
- “Dragonflies are highly sensitive indicators of the state of freshwater ecosystems, and this first global assessment finally reveals the scale of their decline. It also provides an essential baseline we can use to measure the impact of conservation efforts.
- Their decline is symptomatic of the widespread loss of the marshes, swamps, and free-flowing rivers they breed in, mostly driven by the expansion o
 f unsustainable agriculture and urbanization around the world. The IUCN Red List now includes 142,577 species of which 40,084 are threatened with extinction.
f unsustainable agriculture and urbanization around the world. The IUCN Red List now includes 142,577 species of which 40,084 are threatened with extinction.
- “Marshes and other wetlands may seem unproductive and inhospitable to humans, but in fact, they provide us with essential services. They store carbon, give us clean water and food, protect us from floods, as well as offer habitats for one in ten of the world’s known species.”
- To conserve these beautiful insects, it is critical that governments, agriculture, and industry consider the protection of wetland ecosystems in development projects, for example by protecting key habitats and dedicating space to urban wetlands.”
PYRENEAN DESMAN
- The Pyrenean desman (Galemyspyrenaicus), a semiaquatic mammal found only in rivers in Andorra, France, Portugal, and Spain, has moved from Vulnerable to Endangered. This unusual species is related to moles and has a long, sensitive nose and large webbed feet. It is among the last of its evolutionary line; one of only two remaining desman species in the world.

- The Pyrenean desman population has declined throughout its range by as much as 50% since 2011, largely due to human impacts on its habitats.
- Disruption to river flow and reduced water levels as a result of the hydropower plant, dam and reservoir construction, and water extraction for agriculture make significant areas inhospitable to the desman, isolate populations, and markedly reduce desman prey and shelter.
Threats:
- Invasive alien species, illegal fishing using poison, nets, and explosives, increasing droughts due to climate change, excavation of riverbeds and banks, and water pollution further threaten the desman.
- Preserving and restoring the natural flow of rivers and surrounding vegetation, controlling invasive alien species, and tackling climate change are key for this species to recover.
3. THE RADIOACTIVE POLLUTION IN WATER
THE CONTEXT: Radioactive pollution of water is newly emerging but is of grave concern for water pollution and human health. Recently, radioactive contamination and associated health impacts have been reported in many parts of the globe.
What is Radioactive Pollution?
- The radioactive pollution is defined as the physical pollution of living organisms and their environment as a result of release of radioactive substances into the environment during nuclear explosions and testing of nuclear weapons, nuclear weapon production and decommissioning, mining of radioactive ores, handling and disposal of radioactive waste, and accidents at nuclear power plants.The proportion of radioactive pollution is 15% of the total energy of the explosion.
- Radioactivity is the phenomenon of spontaneous emission of particles or waves from the
- unstable nuclei of some elements. There are three types of radioactive emissions: Alpha, Beta and Gamma.
- Alpha particles are positively charged He atoms, beta particles are negatively charged electrons and gamma rays are neutral electromagnetic radiations. Radioactive elements are naturally found in the earth’s crust.
Radioactive pollution in water:
Percolation of naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) from the soil sediments to the aquifer causes groundwater contamination. In anthropogenic sources of radioactive pollution, nuclear weapon investigation, nuclear calamities, nuclear power houses and dumping of radioactive waste are major sources of contamination, while application of radioisotopes in industries and scientific laboratories are the minor sources.
- Radioactive contamination is more prevalent in groundwater as compared to surface water since it is much exposed to radioactive elements found in the rocks. Sometimes, magma also releases radioactive gases into the environment.
- The deposition of these radioactive gases in waterbodies also cause radioactive contamination. Atmospheric deposition (both dry and wet) of cosmogenic radionuclides also add radioactive nuclei in the surface water.
- A number of radionuclides are found in surface and subsurface waters, among which 3H, 14C, 40K, 210Pb, 210Po, 222Rn, 226Ra, 228Ra, 232Th and 234,235,238U are common. Uranium, thorium and actinium are three NORM series that contaminate water resources.
- Radium, a descendant of the NORM series, is one of the decidedly radiotoxic elements found in aquatic systems and can be penetrated into groundwater via
- aquifer rock dissolution
- decaying of 238U and 232Th,
- desorption processes.
- Nuclear reactors and nuclear warhead experiments are the key sources of human-induced radionuclides discharge. Nuclear reactors produce radioisotopes (Cobalt-60, Iridium-192, etc) that hand out as sources of gamma radiation in radiotherapy and numerous industrial appliances.
- Oceans and seas are the natural repositories of naturally occurring uranium. Where it is found in the form of uranyl carbonate ion. A significant concentration of uranium is supposed to be found in the greater salinity of the marine water. 40K is also found in considerable concentration in the marine environment.
- Nuclear power plants placed at the coastal regions add to the radiological contaminants in the marine water by releasing atomic wastes. Water is also used as coolants in these powerhouses, which also get contaminated.
Example:
- Nuclear submarines cause radioactive contamination in the marine environment. Radioactive pollution due to submarine accidents and sinking have been reported. The Rocky Flats plant in Colorado, Fukushima and the Chernobyl nuclear disaster are some examples of such nuclear accidents.
Radioactivity is measured in Becquerel (SI unit) or in Curie. Energy absorbed per unit mass is measured by Gray, while the unit Sievert measures the quantity of radiation absorbed by human tissues.
A small amount of radiation is found in all types of water but the extended amount of radiation is harmful to human health. Radioactivity in drinking water can be determined by a gross alpha test.
The World Health Organization set guidelines for drinking water quality and a permissible limit of reference dose level of 0.1 micro-sieverts per year. The United States Environmental Protection Agency released guidelines known as ‘radionuclides rule’. This rule recognised standards of:
|
- Radioactive elements have an effect on the environment and can cause a risk to human healthiness if inhaled, injected or exposed.
- Human tissues absorb radiation through polluted water and foodstuff, which can cause serious health risks. High doses of radiation can cause acute radiation syndrome or cutaneous radiation injury.
- Exposure to radiation causes various disorders in human physiology, including cancer, leukaemia, genetic mutations, osteonecrosis, cataracts and chromosomal disruption.
The harmful impacts of nuclear radiation are:
- Immediate, recoverable consequences distressing skin, lungs, genitals, and causing hair fall.
- Long-standing, permanent outcomes such as various infections like radiation damage, bone marrow fatality, cataract initiation, cancer stimulation, cholera, dysentery, tuberculosis and pneumonia. Sometimes, these outcomes may be fatal also.
- Genetic effects ionizing radiation induces mutations in germ cells (male sperm cells and female egg cells) or germ cells, resulting in structural alteration in germ cell DNA that are passed on to offsprings. Hereditary disorders can lead to premature death and severe mental illness.
Nowadays, proper analysis and monitoring of radioactive pollutants are also required for a safe water supply. Prevention and precaution measures can check the anthropogenic sources of radioactive contamination in water resources.
Various treatment methods like aeration, reverse osmosis, ion exchange and granule carbon adsorption are effective remedial measures for treating the radioactive contaminated water.
4. WORLD’S COLDEST REGIONS HAVE BEEN ON FIRE
THE CONTEXT: According to the European Union’s Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service, some of the coldest regions of the world have been on fire in 2021, some even through the winter months, indicating an influence of a changing climate. Wildfires around the world emitted 1.76 billion tonnes of carbon in 2021 (till November 30, 2021 ).
THE EXPLANATION:
- The wildfires mostly occurred in Siberia, North America, North Africa and the Mediterranean.
- This is the equivalent of 6.45 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide and was 148 per cent more than the total fossil fuel emissions of the European Union.
- This was mainly due to dry and hot conditions in the regions, Mark Parrington, a senior scientist with Copernicus, pointed out.
- Globally, even though the carbon emissions from wildfires was not the maximum recorded by Copernicus, the EU agency said such emissions would increase in a world reeling under climate change.
- Wildfires in Siberia affected the western part of the region, around Omsk and Tyumen in the early part of the year. By summer, the eastern part of the region started feeling the heat of the wildfires, especially the Sakha Republic in the northeast.
- The Mediterranean was also affected by wildfires during the same period, leading to an increase in the PM 2.5 levels in the region. Turkey was the worst-affected country but there were fires from Tunisia in North Africa to Italy in Europe.
Impacts on India
- Fires were a major concern in India. The report highlighted the seasonal stubble burning in northwest India as the major cause of fires in October and November 2021
- Neighbouring Pakistan also witnessed an increase in fire activity. This increased the particulate matter pollution across the Indo-Gangetic plains, from Pakistan till Bangladesh.
- Earlier, Odisha had reported 51,968 forest fires from November 2020 to June 2021 — the highest in India for the period, according to the Ministry of Environment, forest and climate change.
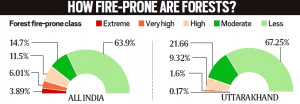
- A total of 345,989 forest fires were recorded across the country. The other states with huge losses due to forest fires were Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Mizoram, Assam and Manipur.
- Forest fires had ravaged Uttarakhand in the early part of the year. The fires had been going on continuously for six months.
- There were 989 fire incidents in the forests of the state, which would have ignited multiple forest fires, from October 1, 2020, to April 4, 2021, according to forest department figures. Some 1,297.43 hectares of forest got burned down in the fires, as per estimates.
- The important thing to note here is that Uttarakhand is a mountain state and the fires were burning through the entire winter season.
- The current outlook for the winter season released by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) for the state also does not look promising as temperatures are going to be higher than normal.
Significance of Forests:
- Forests play an important role in mitigation and adaptation to climate change.
- They act as a sink, reservoir and source of carbon.
- A healthy forest stores and sequesters more carbon than any other terrestrial ecosystem.
- In India, with 1.70 lakh villages in close proximity to forests (Census 2011), the livelihood of several crores of people is dependent on fuelwood, bamboo, fodder, and small timber.
Efforts to Mitigate Forest Fires:
- Since 2004, the FSI (Forest Survey of India) developed the Forest Fire Alert System to monitor forest fires in real time.
- In its advanced version launched in January 2019, the system now uses satellite information gathered from NASA and ISRO.
- National Action Plan on Forest Fires (NAPFF) 2018 and Forest Fire Prevention and Management Scheme.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5. NASA’S IXPE MISSION
THE CONTEXT: NASA launched a new mission named Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer or IXPE. Onboard SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, it was sent to its orbit from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
THE EXPLANATION:
- IXPE observatory is a joint effort of NASA and the Italian Space Agency. The mission will study “the most extreme and mysterious objects in the universe – supernova remnants, supermassive black holes, and dozens of other high-energy objects.”
- The mission’s primary length is two years and the observatory will be at 600 kilometers altitude, orbiting around Earth’s equator. IXPE is expected to study about 40 celestial objects in its first year in space.
What are the instruments onboard?
- IXPE carries three state-of-the-art space telescopes. Each of the three identical telescopes hosts one light-weight X-ray mirror and one detector unit. These will help observe polarized X-rays from neutron stars and supermassive black holes. By measuring the polarization of these X-rays, we can study where the light came from and understand the geometry and inner workings of the light source.
- This new mission will complement other X-ray telescopes such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the European Space Agency’s X-ray observatory, XMM-Newton.
Why is it important?
According to NASA, IXPE’s polarization measurements will help scientists answer questions such as:
- How do black holes spin?
- Was the black hole at the center of the Milky Way actively feeding on surrounding material in the past?
- How do pulsars shine so brightly in X-rays?
- What powers the jets of energetic particles that are ejected from the region around the supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies?
THE MISCELLANEOUS
6. INDIA SKILLS REPORT 2022
THE CONTEXT: India Skills Report 2022 was released by Wheebox, a talent assessment platform, with AICTE, Association of Indian Universities, Confederation of Indian Industries, and other agencies.
THE EXPLANATION:
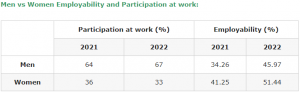
- According to the report, 51% Indian women will be employable in 2022, compared to 46% men.
- The theme of ISR 2021; “Reengineering Education and skilling-building for future of work’.
- States with Maximum hiring Activity: Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu are the 3 states that have a higher job demand.
- Pune, Maharashtra is the list with the most highly employable resources with 78% of the test takers above 60 percent.
Analysis of the report:
- This year’s report is based on responses gathered from an assessment of 3 lakh candidates across India who took part in the Wheebox National Eligibility Test (WNET), and a report from the India Hiring Intent Survey that covered 150 corporations spanning more than 15 industries and sectors.
- It also says that the sectors in which the most hiring will take place are IT, pharmaceutical, e-commerce, and banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI). These sectors are expected to hire 20 per cent more fresh graduates in 2022 than in 2021.
- The annual report examines hiring patterns and skill distribution in the country with an eye on the future. It uses an aptitude test to measure the employability of Indian youth.
- It says the pool of employable women is steadily increasing. This stands at 51.44 per cent for 2022, compared to 41.25 per cent in 2021. The 2022 figure for men is 45.97 per cent, against 34.26 per cent in 2021.
- According to the 2022 report, 2 per cent of skilled youth overall were found to be highly employable, compared to 45.97 per cent in 2021.
- In a new trend that has emerged this year, 6 per cent of graduates were found to be seeking internship positions within organisations.
THE PRELIM PRACTICE QUESTION
Q1. Consider the following statements about International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- It was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- Its headquarter is located in Gurugram, Haryana.
- Countries that do not fall within the Tropics can not join the alliance.
Which of the statements are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 10TH DECEMBER 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Answer: a)
Explanation:
- Hurricane – Atlantic Ocean
- Willy Willy – Western Australia
- Typhoons – South China Sea and Western Pacific Ocean
- Cyclone – Indian Ocean

 f unsustainable agriculture and urbanization around the world. The IUCN Red List now includes 142,577 species of which 40,084 are threatened with extinction.
f unsustainable agriculture and urbanization around the world. The IUCN Red List now includes 142,577 species of which 40,084 are threatened with extinction.


