THE INDIAN HISTORY
1. EXPLAINED: RECALLING ‘QUIT INDIA’, WHEN ORDINARY INDIANS TOOK TO THE STREETS WITH A VOW TO ‘DO OR DIE’
THE CONTEXT: On this day 80 years ago — on August 9, 1942 — the people of India launched the decisive final phase of the struggle for independence. It was a mass upsurge against colonial rule on a scale not seen earlier, and it sent out the unmistakable message that the sun was about to set on the British Empire in India.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Quit India Movement:
• The call for Quit India Movement was given on August 8, 1942 by Mahatma Gandhi in a bid to end the British rule in India. the movement was launched at Mumbai session of the All-India Congress Committee. In the speech at August Kranti Maidan (Gowalia Tank maidan) in Mumbai, Mahatma Gandhi made a called for “Do or Die for Independence”.
• During the movement, Aruna Asaf Ali hoisted the Indian flag at the August Kranti Maidan. Yusuf Meherally is also associated with the Movement, who gave the slogan of “Quit India” and “Simon Go Back”. This movement aimed at asking the British to grant Independence to India.
Immediate cause of Quit India Movement
• Immediate cause for Quit India failure of Cripps Mission, that was sent under Stafford Cripps to resolve the Indian question regarding new constitution and self-government. Cripps Mission failed because it did not offer complete freedom to India. It was for ‘Dominion Status to India’ along with partition.
Failure of the Quit India Movement
• The Quit India Movement was supposed to be a peaceful and non-violent movement. But it witnessed violence at some places. Furthermore, Muslim League, Hindu Mahasabha and the Communist Party of India did not extended support to it. As a result, movement was suppressed by British, violently.
Gandhi’s address: Do or Die
• On August 8, 1942, Gandhi addressed the people in the Gowalia Tank maidan in Bombay (Mumbai). “Here is a mantra, a short one, that I give you. Imprint it on your hearts, so that in every breath you give expression to it,” he said.
• “The mantra is: ‘Do or Die’. We shall either free India or die trying; we shall not live to see the perpetuation of our slavery,” Gandhi said. Aruna Asaf Ali hoisted the Tricolour on the ground. The Quit India movement had been officially announced.
THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
2. MANIPUR’S NRC EXERCISE
THE CONTEXT: On July 5, the 60-member Manipur Assembly resolved to implement the National Register of Citizens (NRC) and establish a State Population Commission (SPC).
THE EXPLANATION:
• The approval to a couple of private member resolutions moved by Janata Dal (United) MLA, came after more than two dozen organizations, most of them tribal, demanded an Assam-like NRC to protect the indigenous people from a perceived demographic invasion by “non-local residents”.
• The National Register of Citizens (NRC) is a register of all Indian citizens whose creation is mandated by the 2003 amendment of the Citizenship Act, 1955.
• The register was first prepared after the 1951 Census of India.
• Its purpose is to document all the legal citizens of India so that the illegal immigrants can be identified and deported.
• It has been implemented for the state of Assam starting in 2013–2014.
• The GoI announced plans to implement it for the rest of the country in 2021, but it has not yet been implemented.

NRC and Assam
• Assam, being a border state with unique problems of illegal immigration, had a register of citizens created for it in 1951 based on the 1951 census data.
• However, it was not maintained afterwards.
• For decades, the presence of migrants, often called “bahiragat” or outsiders, has been a loaded issue here.
• The Illegal Migrants (Determination by Tribunal) Act, 1983 was then passed by the Parliament, creating a separate tribunal process for identifying illegal migrants in Assam.
• The Supreme Court struck it down as unconstitutional in 2005, after which the Centre agreed to update the Assam NRC.
Who is a Foreigner in Assam?
• The National Register of Citizens now takes its definition of illegal immigrants from the Assam Accord – anyone who cannot prove that they or their ancestors entered the country before the midnight of March 24, 1971, would be declared a foreigner and face deportation.
• Those who entered on or after March 25, 1971, the eve of the Bangladesh War, would be declared foreigners and deported.
• This means you could be born in India in 1971 to parents who crossed the border in that year, and still be termed an illegal immigrant at the age of 48.
CAA and NRC protests
• These were a series of protests in India against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 which was enacted into law on December 12, 2019, and against the nationwide implementation of the NRC.
• Protesters in all regions are concerned that the upcoming compilation of the National Register of Citizens might be used to deprive a community of its Indian citizenship.
VALUE ADDITION:
National Population Register (NPR)
• The NPR is a database containing a list of all usual residents of the country.
• Its objective is to have a comprehensive identity database of people residing in the country.
• It is generated through house-to-house enumeration during the “house-listing” phase of the census, which is held once in 10 years.
• A usual resident for the purposes of NPR is a person who has resided in a place for six months or more, and intends to reside there for another six months or more.
• Once the basic details of the head of the family are taken by the enumerator, an acknowledgement slip will be issued. This slip may be required for enrolment in NPR, whenever that process begins.
• And, once the details are recorded in every local (village or ward), sub-district (tehsil or taluk), district and State level, there will be a population register at each of these levels.
• Together, they constitute the National Population Register.
3. NITI AAYOG GOVERNING COUNCIL MEETING
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the 7th Governing Council meeting was held at Rashtrapati Bhawan Cultural Centre in New Delhi. It was chaired by Prime Minister. It was the first in-person meeting of the council since July 2019.
THE EXPLANATION:
Agenda of the NITI Aayog meeting were;
• To achieve self-sufficiency in pulses, oilseeds & other agri-communities.
• Issues of crop diversification and National Education Policy were also discussed, besides the Urban Governance.
• States’ interventions were moderated by Defence Minister.
• External Affairs Minister gave presentation on India’s G20 presidency from December 1, 2022, to November 30, 2023.
• Discussions on ‘ongoing controversy related to freebies’ could not held.
• Many states raised concerns on Minimum support price for farmers, review of GST, shortage of IAS officers, and increased allocation of funds for states.
• NITI Aayog will increase its outreach to states on how it could collaborate with them further.
• They discussed on how to lower down dependence imported edible oils, from 50 % to 25% in coming years.
• During the meeting, PM note that, every state played a significant role in fight against Covid-19. India’s federal structure and cooperative federalism have become a model for the world during covid pandemic.
NITI Aayog’s Governing Council:
Members of the Governing Council of NITI Aayog include-
• Prime Minister of India
• Chief Ministers of all States and Union Territories with legislature
• Ex-Officio Members
• Lt Governors of Union Territories
• Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog
• Full-Time Members of NITI Aayog and
• Special Invitees.
THE SECURITY AFFAIRS
4. INDIAN ARMY ‘SKYLIGHT’ MEGA- EXERCISE
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Army recently conducted “Skylight Mega-Exercise”, to enhance its space domain capabilities. It was first of its kind large-scale exercise. Skylight exercise was aimed at testing operational readiness of satellite communication assets and giving training to personnel manning these assets.
THE EXPLANATION:
• Skylight Mega-Exercise was pan-India exercise, covering Lakshadweep and Andaman Islands. It also covered high reaches of India’s northern borders where Indian Army had activated all satellite communication assets from July 25-29, 2022.
• During the exercise, several technical and operational scenarios in space domain were pointed up.
• The exercise witnessed the participation of ISRO and other agencies responsible for space & ground segments.
• More than 280 platforms were checked in field formations.
• Indian Army makes use of services of a number of satellites by ISRO. These satellites are used to connect multiple communication terminals of different types, including transportable vehicle mounted terminals, static terminals, small form factor etc.
Communication Satellite of Indian Army:
Satellite communication networks are being used by The Indian Army across some of the remote border areas. On the other hand, Navy and Air Force have satellite of their own. Thus, Indian Army is also working to have its own communication satellite, called GSAT-7B, by 2025. Indian Army got the nod from Defence Acquisition Council to work on Satellite GSAT-7B in March 2022.
About GSAT-7B Satellite:
The GSAT-7B satellite is an indigenous multiband satellite, that has been designed with advanced security features. Satellite will extend support to tactical communication needs of the troops deployed on the ground as well remotely piloted air defence weapons, aircraft, & other mission.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
5. THE PARVAZ MARKET LINKAGE SCHEME
THE CONTEXT: Government of Jammu & Kashmir launched the “PARVAZ Market Linkage Scheme” recently. This is an innovative Market Linkage scheme, having tremendous potential to uplift the economic conditions of farmers across Jammu and Kashmir.
THE EXPLANATION:
About PARVAZ Market Linkage Scheme:
• The PARVAZ scheme was launched with the aim of creating market linkage support for shipment of Agriculture & Horticulture perishables from Jammu and Kashmir.
• Under the scheme, government will provide a subsidy of 25% on freight charges, in a bid to carry perishable fruits through Air Cargo. Subsidy will be provided to farmers through Direct Benefit Transfer mode.
• Scheme is being implemented by Jammu & Kashmir Horticultural Produce Marketing and Processing Corporation (JKHPMC).
• JKHPMC is spreading awareness among farmers regarding the significance of PARVAZ scheme so that they could benefit from it.
Significance of the Scheme:
Government has made the documentation work related to scheme simple and easy. Farmers will get the subsidy on time, under the scheme. This scheme seeks to benefit the farmers in doubling their income. Thus, it will ensure economic and social welfare of the farmers. They will receive the price of their produce directly in bank account and no intermediary will get involved.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6. AUGUST 7: NATIONAL HANDLOOM DAY
THE CONTEXT: National Handloom Day is celebrated in India on August 7, every year. The day highlights the contribution of handloom industry in socio-economic development of India. It also raises awareness among people regarding the handloom industry. Ministry of Textile is the nodal agency of the celebration.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Indian handloom Industry:
• Handloom Industry is the largest industry in India.
• Products manufactured by weaving community of this sector are popular worldwide.
• It is a significant employment source across rural areas of India.
• This sector is an important player in women empowerment. 70% of all weavers and allied workers are women.
• Indian handloom sector exports its products to more than 20 countries worldwide, like the UK, the USA, France, Germany, and South Africa.
HISTORY OF THE DAY
• India’s handloom industry played a significant role in Swadeshi Movement, which was launched on August 7, 1905.
• Swadeshi movement was aimed at curbing dependency on foreign goods and boosting domestic production.
• As a part of the movement, production of khadi started in almost every household.
• When India got independence, Indian flag made of Khadi was unfurled near India Gate.
• Thus, the National Handloom Day is celebrated on August 7, the same day when Swadeshi Movement was started.
• First National Handloom Day was celebrated on August 7, 2015; in Chennai.
• National Handloom Day is observed in the honour handloom weaving community. The day highlights the contribution weaving community across several sectors of India, including rural employment. The day also seeks to protect the rich handloom heritage of India as well as to empower handloom community by providing better opportunities.
THE NEWS IN NUMBERS
7. INFRA ASSETS MONETISED
1.62 In ₹ lakh crore, the worth of infrastructure assets expected to be monetised during FY22-23. The government had last year announced a ₹6 lakh crore National Monetisation Pipeline to unlock value in infrastructure assets across sectors till 2025. Minister of State for Finance said about ₹97,000 crore worth of public assets were monetised in the last fiscal. The proposed transactions include highway TOT bundles and InvIT future rounds, redevelopment of sports stadia etc.
8. SCHEME FOR BEEDI WORKERS
49.82 In lakh, the number of ‘beedi’ workers and their families in India, for whom the Centre is running a labour welfare scheme, according to Union Labour and Employment Minister . He said the scheme envisages health care facilities, scholarships and housing for the workers. He added that under the scheme, health care facility is provided to ‘beedi’ workers and their families within a network of 285 dispensaries and 10 hospitals across the country.
9. INSOLVENCY CASES
1,999 The number of cases of corporate insolvency resolution processes (CIRP) going on under the insolvency law as of June this year out of which only 436 are in the real estate sector. These resolutions are done under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code which provides for resolutions through a market-driven process. The Minister of State for Corporate Affairs said that the time taken for CIRP depended on factors such as market sentiments, marketing efforts and so on.
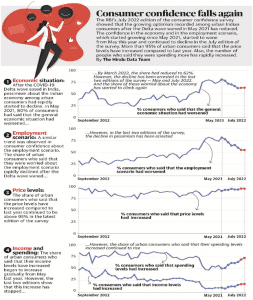
GRAPHICALLY SPEAKING: CONSUMER CONFIDENCE SURVEY 2022