Indian Polity
How a Bill becomes an Act:
-
- A Bill is a draft law presented for deliberation in Parliament.
- Becomes an Act after approval by both Houses of Parliament and the President’s assent.
- Types of Bills:
- Ordinary Bill: Can be introduced in either House (except Money Bills).
- Money Bill: Related to taxes, expenditure, borrowing; can only be introduced in Lok Sabha.
- Financial Bill: Related to revenue/expenditure but not fully a Money Bill.
- Constitution Amendment Bill: Alters Constitution provisions; requires special majority.
- Introduction (First Reading):
- Member introduces the Bill in Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha.
- Title is read, copies circulated, and Bill published in Gazette.
- Notice of motion is required for private member bills; government bills are scheduled by the Ministry.
- Consideration (Second Reading):
- Detailed discussion of principles and clauses.
- Can be sent to Parliamentary Committee for scrutiny.
- Committee reports presented and debated.
- Passing (Third Reading):
- House votes clause-by-clause or full Bill.
- If passed, Bill moves to other House for similar procedure.
- Special Procedures:
- Money Bill: Rajya Sabha can recommend amendments within 14 days; Lok Sabha can accept/reject.
- Constitution Amendment Bill: Requires 2/3rd majority of members present & voting + majority of total membership.
- President’s Assent:
- Bill sent to President for approval.
- President can give assent, withhold, or return (ordinary Bills only).
- After assent, Bill becomes an Act and is published in Gazette.
- Private Member Bill: Rarely becomes law; discussed on Fridays.
- Money Bill cannot be introduced in Rajya Sabha.
- Joint Sitting: If ordinary bill is rejected or amended differently, Lok Sabha prevails (Lok Sabha has greater strength).
(TH)
International Developments
Biological Weapons Convention (BWC):
-
- Context: bioweapons development.
- BWC is the first multilateral disarmament treaty banning an entire category of weapons: biological and toxin weapons.
- Adopted: 10 April 1972; Entered into force: 26 March 1975.
- Objective: Prohibit the development, production, stockpiling, and use of biological and toxin weapons.
- India is a signatory and ratified it in 1974.
- Verification: No formal verification mechanism exists; confidence-building measures (CBMs) are used.
- Linked to UN Security Council Resolution 1540 (non-proliferation of WMDs).
(TH)
Economy
Trade Deficit:
-
- Context: Trade deficit falls to $6.6 bn. in Nov. due to merchandise export growth
- Trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed its exports of goods.
- It is a component of the Current Account Deficit (CAD) of the Balance of Payments.
- India’s trade deficit is driven mainly by crude oil, gold, electronics and chemicals imports.
- A persistent trade deficit can put pressure on the exchange rate and foreign exchange reserves.
- Depreciation of domestic currency may reduce trade deficit in the long run (via J-curve effect).
- Trade deficit is not inherently bad if financed by stable capital inflows and productive imports.
(TH)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Kandhamal district in Odisha:
-
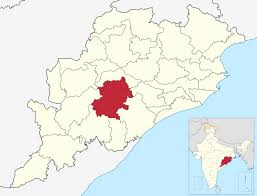
- Kandhamal district is located in central Odisha, in the Eastern Ghats region.
- It is predominantly a Scheduled Tribe–dominated district, with a large Kondh (Khond) tribal population.
- Known for turmeric cultivation; “Kandhamal Haldi” has Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
- The district has significant forest cover and forms part of Eastern Ghats biodiversity landscape.
- It has been in news for tribal welfare, forest rights, and agro-based livelihoods.
-
- Kandhamal Turmeric:
- Kandhamal Turmeric (Kandhamal Haldi) is a GI-tagged agricultural product from Kandhamal district, Odisha.
- Known for high curcumin content, strong aroma, and deep yellow colour.
- Cultivated largely by tribal farmers (Kondh tribe) using traditional, low-chemical practices.
- Grown in Eastern Ghats agro-climatic conditions with forest-based, rainfed farming.
- GI tagging helps in price premium, export potential, and livelihood security for tribals.
- Kandhamal Turmeric:

(TH)
Bondi Beach (Sydney, Australia):
-
- Context: Recent shooting killing 15 people.
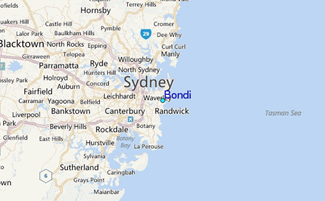
- Bondi Beach is a world-famous urban beach located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia.
- Famous for surfing, tourism, and beach culture.
- Located about 7 km east of Sydney’s central business district (CBD).
- It is part of the Bondi to Coogee coastal walk, highlighting coastal biodiversity and scenic views.
- Recognized globally as a major tourist attraction and hosts annual events like the City to Surf marathon.
(TH)
Donetsk and Luhansk Regions:
-
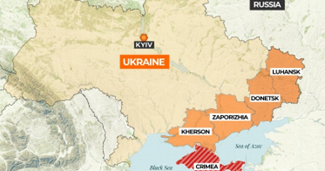
- Donetsk and Luhansk are regions in eastern Ukraine, collectively called the Donbas region.
- They are industrial and coal-rich regions, historically significant for heavy industry and mining.
- In 2014, pro-Russian separatists declared independence in both regions, leading to conflict with Ukraine.
- Recognized globally as part of Ukraine, but Russia has claimed and annexed these regions in 2022, escalating geopolitical tensions.
- Key in global security, energy, and geopolitical studies due to:
- NATO–Russia tensions
- European energy supply (coal and gas transit)
- Impact on Ukraine’s territorial integrity
(TH)
History, Art & Culture
Angkor Wat:
-
- Context: Thailand’s air strikes hit home province of heritage temples.
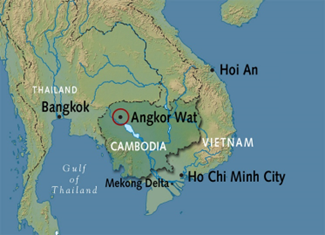
- Angkor Wat is a temple complex located in Siem Reap, Cambodia.
- Built in the early 12th century by King Suryavarman II of the Khmer Empire.
- Originally dedicated to Hindu god Vishnu, later transformed into a Buddhist temple.
- It is the largest religious monument in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Architectural significance: classical Khmer architecture, extensive bas-reliefs, symbolic representation of Mount Meru.
- Major tourism and cultural symbol of Cambodia, appearing on the national flag.

(TH)
Terms in news
Biosecurity:
-
- Biosecurity refers to measures to prevent the introduction, spread or misuse of harmful biological agents affecting humans, animals, plants or ecosystems.
- It covers natural outbreaks, accidental releases, and deliberate misuse (bioterrorism).
- Key components: biosafety, bio-surveillance, border quarantine, and early warning systems.
- In India, biosecurity is relevant to public health, agriculture, livestock, and invasive alien species control.
- Internationally linked with Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) and One Health approach.
- Biosecurity differs slightly from biosafety, which is a set of practices meant to prevent the accidental leakage of pathogens. A robust biosafety protocol feeds into biosecurity.
(TH)
Miscellaneous
International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP):
-
- The 2025 ICTP Prize has been awarded to Titas Chanda of IIT-Madras and Sthitadhi Roy of the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences, Bengaluru.
- For exceptional and original contributions to the theory of quantum many-body systems, at the interface of condensed matter and quantum information science.
- The ICTP Prize is an annual affair and has been awarded since 1982 to young scientists from developing countries. It carries a certificate and a cash component.
- Past winners from India include Mohit Kumar Jolly, Narendra Ojha, Aninda Sinha, Shiraz Minwalla, Ashoke Sen, and G. Baskaran.
- The ICTP was founded by Pakistani physicist and Nobel laureate Abdus Salam in 1964 to support scientists from developing countries.
(TH)
Spread the Word
