Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Cyclone Ditwah:
-
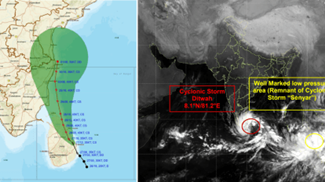
- It formed from a low‑pressure area over the southwest Bay of Bengal / adjoining southeast Sri Lanka — depression on 26 November 2025, became a cyclonic storm by 27 November 2025.
- The name “Ditwah” was contributed by Yemen; it refers to the “Detwah Lagoon” on Socotra Island.
- It threatened Sri Lanka first (heavy rain, floods, landslides), causing extensive damage, deaths and displacement.
- It moved north-northwest towards Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and south Andhra Pradesh coasts, prompting alerts (yellow/orange/red) by India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Forecast impact in India included strong winds (65–70 kmph, gusts up to 90–100 kmph), heavy to very heavy rainfall, rough seas and high waves (up to ~5m) — danger to coastal zones, fishermen, transportation, potential flooding.
- Authorities issued advisories: fishermen to avoid sea area; preparation and evacuation readiness in coastal districts; schools/transport may be suspended depending on severity.
(TH)
Science & Technology
Skyroot Aerospace’s “Vikram-I”:
-
- Context: Narendra Modi inaugurates private‑sector rocket launch — Skyroot Aerospace’s “Vikram-I” becomes India’s first privately developed orbital rocket.
- Significance
- India’s first privately developed orbital-class rocket.
- Marks privatisation of India’s space sector, complementing ISRO.
- Targets small-satellite market, enhancing India’s global competitiveness.
- Technical Features
- Four-stage rocket: 3 solid + 1 liquid stage for precise orbital insertion.
- Height: ~20 m, Diameter: ~1.7 m, Payload: 350 kg to LEO.
- Uses carbon composites & 3D-printed engines → lightweight & rapid launch readiness (~24 hrs).
- Policy & Strategic Implications
- Boosts domestic space industry & economy.
- Strengthens strategic autonomy & private-public synergy in space sector.
- Supports satellite deployment for communication, earth observation, and development goals.

(IE+TOI)
S-400 system:
-
- S‑400 Triumf is a long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed by Russia’s Almaz-Antey.
- Capable of targeting aircraft, UAVs, cruise missiles, and ballistic missiles up to 400 km range and altitudes of 30 km.
- Uses multiple missile types for layered air defense.
- India signed a deal with Russia in 2018 for 5 S‑400 regiments (~$5.43 billion); deliveries expected to be completed by 2025–26.
- The system is India-Russia joint defence cooperation, part of strategic modernization of Indian Air Defence.
- Strategic Importance
- Strengthens air defence & strategic deterrence of India against adversaries like China and Pakistan.
- Integrates with India’s command and control network, improving surveillance, early warning, and neutralization capability.
- Considered one of the most advanced SAM systems globally, creating a credible area denial shield.
(TH)
Samudrayaan:
-
- India’s first human–occupied deep-sea mission under the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM).
- Aims to send humans to 6,000 metres inside the ocean.
- The Vehicle – Matsya-6000
- A 3-person crewed submersible developed by NIOT (National Institute of Ocean Technology), Chennai.
- Capable of deep underwater exploration, high pressure endurance, and 12-hour life support.
- Objectives
- Exploration of polymetallic nodules in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB).
- Study of hydrothermal vents, biodiversity, and deep-sea ecosystems.
- Boosts India’s capability in blue economy, seabed mining, and marine research.
- Nodal Ministry
- Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Importance
- Makes India one of the few nations with deep-sea human submersible capability (others: US, Russia, China, France, Japan).
- Supports strategic resource security—manganese, nickel, cobalt nodules.
- Promotes indigenous technology development in extreme-environment engineering.

(TH)
Defence & Security
Operation Sagar Bandhu:
-
- Operation Sagar Bandhu is a Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR) mission launched by India to assist neighbouring countries in times of natural disaster or crisis.
- It was activated in late November 2025 after Cyclone Ditwah devastated parts of Sri Lanka — causing floods, landslides, widespread damage, casualties and displacement.
- Agencies involved: The mission is coordinated by the Indian Navy and the Indian Air Force (IAF), with support from disaster-relief agencies.
- Relief materials — including dry & fresh rations, ready-to-eat meals, tents, tarpaulins, blankets, hygiene kits — along with rescue equipment and personnel.
- Scale & speed: Within 24–48 hours of launch, IAF aircraft (C-130J, IL-76) air-lifted hundreds of tonnes (first 12–21 tonnes; more followed) to Sri Lanka’s Colombo port/airport. Naval ships (including INS Vikrant and INS Udaygiri) already present in Colombo diverted to deliver essential supplies.
- Policy & strategic significance:
- Reflects India’s “Neighbourhood First” doctrine and its regional maritime cooperation framework Vision MAHASAGAR — reinforcing India as first responder in Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Enhances India’s soft-power and diplomatic goodwill: humanitarian gesture strengthens bilateral ties (in this case with Sri Lanka) during crisis.
- Demonstrates India’s growing HADR logistics & operational capability (naval + air + relief + coordination) — a capacity increasingly relevant given climate-linked disasters and regional vulnerabilities.

(TH+TOI)
PRACTICE MCQS
Q1. Consider the following statements about Skyroot Aerospace’s Vikram‑I rocket:
1. It is India’s first privately developed orbital-class rocket.
2. Vikram‑I has a four-stage configuration: three liquid stages and one solid stage.
3. Its primary target is launching small satellites into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
4. The rocket uses carbon composites and 3D-printed engines to reduce weight and enable rapid launch.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 1, 3 and 4 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) All of the above
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Vikram‑I is India’s first privately developed orbital rocket.
- It has three solid stages and one liquid stage, not the other way around.
- Primarily for small satellites to LEO.
- Uses carbon composites & 3D printing for lightweight and rapid assembly.
Q2. Consider the following statements:
1. Ditwah was named by Yemen after a lagoon on Socotra Island.
2. Ditwah became a cyclonic storm on 26 November 2025.
3. IMD issued alerts for Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and south Andhra Pradesh coasts when Ditwah approached Indian shores.
4. Maximum sustained winds associated with Ditwah were forecast at 150–160 kmph near landfall.
Which of the following statements about Cyclone Ditwah are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 1, 2 and 3 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: A
Explanation: Statement 1 is correct, 3 is correct. It became a storm on 27 November 2025 (not 26). Forecast winds were ~65–70 kmph (gusts 90–100 kmph), not 150 – 160.
Q3. Consider the following statements:
1. The deal was signed in 2018 with Russia.
2. India plans to procure 5 regiments of S‑400 systems.
3. S‑400 can target ballistic missiles, aircraft, and drones.
4. The system is fully indigenous and developed in India.
Which of the following statements about India’s S‑400 deal are correct?
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 1, 3 and 4 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation: 4 is incorrect — S‑400 is imported from Russia, not developed indigenously.
Q4. Match the following Indian operations with the countries/regions where they were conducted:
List–I: Operations List–II: Countries / Locations
A. Operation Sagar Bandhu – 1. Maldives
B. Operation Raahat – 2. Yemen
C. Operation Sankat Mochan – 3. South Sudan
D. Operation Samudra Setu – 4. Multiple countries (Evacuation from Gulf/Indian Ocean during COVID-19)
Select the correct code:
a) A–1, B–2, C–3, D–4
b) A–3, B–1, C–4, D–2
c) A–2, B–3, C–1, D–4
d) A–4, B–2, C–3, D–1
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Operation Sagar Bandhu – India assisting Maldives during floods/cyclone.
- Operation Raahat – Evacuation of Indians from Yemen (2015).
- Operation Sankat Mochan – Evacuation from South Sudan (civil war).
- Operation Samudra Setu – Indian Navy mission for repatriating Indians from various countries during COVID-19.
Q5. With reference to “Samudrayaan”, which of the following statements are correct?
1. It is India’s first manned deep-ocean mission.
2. Its submersible, Matsya-6000, has a maximum operational depth of 6 km.
3. The project is implemented by the National Institute of Ocean Technology.
4. The mission aims primarily at exploring hydrocarbon reserves under the seabed.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 1 and 4 only
c) 2, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 4 is incorrect → The mission focuses on polymetallic nodules and deep-sea ecology, not hydrocarbons.
Spread the Word



