Economy
National Milk Day:
-
- Observed on 26 November to honour Verghese Kurien, architect of the White Revolution.
- India is the world’s largest milk producer, contributing ~25% of global output.
- Dairy sector: 5% of national economy, livelihood for 8+ crore farmers, strong women participation.
- Operation Flood (1970) and the Amul cooperative model transformed India from milk-deficit to self-sufficient.
- Milk production increased from 146.3 MT (2014–15) to 239.3 MT (2023–24).
- Key schemes: Rashtriya Gokul Mission, National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD).
- Government support includes dairy infrastructure, breed improvement, cooperatives expansion, and GST rationalisation for dairy products.
- Moving toward “White Revolution 2.0” with focus on sustainability, women-led cooperatives, and improving procurement & processing capacity.

(PIB)
Currency Depreciation:
-
- Currency depreciation is a fall in the value of a country’s currency relative to foreign currencies, typically in a floating exchange rate system.
- Causes:
- Trade deficit – imports exceed exports.
- Capital outflows – foreign investors withdraw funds.
- Inflation differential – higher domestic inflation reduces currency value.
- Monetary policy – low interest rates relative to other countries.
- Global factors – USD strength, geopolitical tensions, or oil price shocks.
- Effects:
- Positive: Exports become cheaper → can improve trade balance.
- Negative: Imports costlier → inflationary pressure (imported inflation), higher foreign debt servicing cost.
- Policy Response:
- RBI intervention – buying/selling foreign exchange.
- Monetary measures – interest rate adjustments.
- Structural reforms – boost exports, reduce fiscal deficit.
(IE)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Cuban gar:
-
- Origin & Habitat: Endemic to Cuba; freshwater rivers and lakes.
- Status: Critically Endangered (IUCN Red List) due to habitat loss, overfishing, and invasive species.
- Biology: Large predatory freshwater fish; can survive in low-oxygen water due to a vascularized swim bladder (air-breathing organ).
- Ecological Role: Apex predator in freshwater ecosystems; helps maintain ecological balance.
- Conservation: Protected under CITES Appendix I; conservation programs focus on habitat restoration, captive breeding, and controlling invasive species.

(TH)
African walking catfish:
-
- Origin & Invasion: Native to Africa and Southeast Asia; invasive species in India, especially in Kerala and northeastern states.
- Habitat: Freshwater: rivers, ponds, rice paddies; can survive in low-oxygen water.
- Unique Feature: Can “walk” short distances on land using pectoral fins to move between water bodies.
- Threat to Ecosystem: Highly predatory; competes with native fish species; alters local aquatic biodiversity.
- Reproduction: Rapid breeder; high resilience to harsh conditions; makes it a successful invasive species.
- Conservation/Management: Listed as invasive alien species; controlled through monitoring and preventing introduction into new water bodies.

(TH)
Yonaguni Island:
-
- Location: Southernmost of the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, close to Taiwan; in the East China Sea.
- Significance: Known for the underwater “Yonaguni Monument”, a submerged rock formation resembling terraces and steps, sometimes referred to as a “lost city.”

-
- Debate: Scientists debate whether it is natural or man-made.
- Cultural / Historical Relevance: If man-made, could date back to prehistoric Japan (~10,000 years ago); attracts archaeologists and divers.
- Tourism & Research: Popular diving site; studied for marine geology, plate tectonics, and archaeology.
- Geopolitical Note: Strategic location near Japan-Taiwan maritime boundaries, part of Ryukyu chain which is historically significant in East Asia.
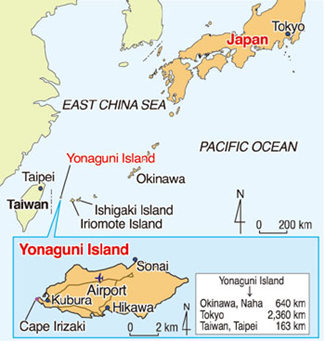
(TH)
Science & Technology
BharatGen:
-
- India’s first sovereign, multilingual & multimodal AI Large Language Model (LLM).
- Scope & capability: It supports 22+ Indian languages and integrates text, speech and document-vision modalities, enabling it to understand, generate, and interpret information in the way Indians communicate.
- Funding & backing: The project has received ₹1,293 crore in government support.
- It is part of the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber‑Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- It involves top institutions including IIT Bombay, IIT Madras, IIT Kanpur, IIIT Hyderabad, IIT Mandi, IIT Hyderabad, IIM Indore, IIT Kharagpur, and IIIT Delhi.
- Digital sovereignty & inclusion: It is designed to build a “truly Indian” AI stack, capturing India’s linguistic, cultural and social diversity.
- Its ambition is to give Indians control over their digital knowledge resources and reduce dependence on foreign AI models.
- Strategic significance: The initiative aligns with India’s push for “home-grown deep-tech” and could play a key role in governance, education, health, agriculture, commerce and digital inclusion, marking a step forward in national technological self-reliance.

(TH)
Defence & Security
EXERCISE SURYAKIRAN XIX – 2025:
-
- Joint military exercise between Indian Army and Nepal Army.
- 19ᵗʰ edition commenced on 25 November 2025 at Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand; scheduled to continue until 8 December 2025.
- Participants: 334 personnel each — Indian side predominantly from ASSAM Regiment; Nepal side chiefly from Devi Datta Regiment.
- Objectives & Scope:
- Practice sub-conventional operations under Chapter VII of UN mandate.
- Strengthen battalion-level coordination in jungle/mountain warfare, counter-terrorism in mountainous terrain, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR), medical response, environmental conservation, and ground-aviation integrated operations.
- New Focus (2025 edition): Integration of emerging technologies, unmanned aerial systems (UAS/drones), drone-based ISR (intelligence, surveillance & reconnaissance), AI-enabled decision-support tools, unmanned logistic vehicles, armoured protection platforms, to update tactics, techniques and procedures as per evolving counter-terrorism and modern warfare challenges.
- Wider Significance: Enhances interoperability between Indian and Nepal armies; strengthens bilateral defence cooperation; helps both militaries adapt to modern security demands and contribute to UN peace-keeping readiness.

(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Exercise SURYAKIRAN XIX, recently in news, is a joint military exercise between:
a) India and Sri Lanka
b) India and Bangladesh
c) India and Nepal
d) India and Bhutan
Answer: C
Explanation:
Exercise SURYAKIRAN is a bilateral military exercise between India and Nepal, aimed at enhancing interoperability in counter-terrorism, jungle and mountain warfare, humanitarian assistance, and disaster relief. The 19th edition (2025) was held in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand.
Q2. Consider the following statements regarding India’s dairy sector and National Milk Day:
1. National Milk Day is observed on 26 November to commemorate the birth anniversary of Verghese Kurien.
2. Operation Flood (1970) was implemented by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
3. Rashtriya Gokul Mission focuses on improving indigenous bovine breeds, while the National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) mainly aims at infrastructure development and milk procurement enhancement.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All three
Answer: D
Explanation:
-
- National Milk Day is on 26 November to honour Dr. Verghese Kurien.
- Operation Flood (1970) by NDDB transformed India from milk-deficit to milk-surplus.
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission improves indigenous breeds; NPDD focuses on milk procurement, processing, infrastructure, and cooperative strengthening.
Q3. Consider the following statements regarding the African Walking Catfish:
1. It is an invasive species in India, originally from Africa and Southeast Asia.
2. It can survive in low-oxygen water and move over land using its fins.
3. It plays a significant role in enhancing native fish biodiversity in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) All three
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- African Walking Catfish is non-native to India and invasive.
- It can “walk” short distances and survive in hypoxic water.
- It is predatory and harmful to native fish, reducing biodiversity, not enhancing it.
Q4. BharatGen, recently in news, is best described as:
a) India’s first quantum-enabled supercomputer
b) India’s sovereign multilingual and multimodal AI Large Language Model
c) A national platform for cybersecurity threat monitoring
d) A unified digital ID system for government welfare schemes
Answer: B
Explanation:
BharatGen is India’s first sovereign AI Large Language Model (LLM) developed to support 22+ Indian languages and multiple modalities such as text, speech, and document-vision. It is part of India’s effort to build an indigenous AI ecosystem and reduce dependence on foreign AI models.
Q5. Yonaguni Island, sometimes in news for its underwater monument, is located:
a) Near Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India
b) In the East China Sea, part of the Ryukyu Islands, Japan
c) Off the coast of Taiwan, part of the Philippines
d) In the Sea of Japan, near Hokkaido
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Yonaguni Island is the southernmost island of the Ryukyu chain, Japan, close to Taiwan.
- Famous for the Yonaguni Monument, its submerged rock formations attract archaeological and marine-geological interest.
- Not part of India, Taiwan, or Hokkaido regions.
Q6. Consider the following statements regarding the Cuban Gar:
1. It is endemic to Cuba and inhabits freshwater ecosystems.
2. It is listed as Critically Endangered in the IUCN Red List.
3. It is primarily a marine fish that migrates to freshwater for spawning.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All three
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Cuban Gar is endemic to freshwater rivers and lakes in Cuba.
- it is Critically Endangered due to overfishing and habitat degradation.
- Cuban Gar is a strictly freshwater species, not marine.
Q7. Consider the following statements regarding currency depreciation:
1. Currency depreciation improves export competitiveness but may increase the cost of imports.
2. Depreciation always occurs in a fixed exchange rate system.
3. Factors like capital outflows, high domestic inflation, and strong USD can contribute to currency depreciation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) All three
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Depreciation makes exports cheaper and imports costlier.
- In a fixed exchange rate system, depreciation does not occur automatically; the central bank maintains the rate.
- Capital outflows, higher domestic inflation, and USD appreciation are common causes.

