International Developments
Chemical Weapons Convention:
-
- Context: Ricin poison being used as chemical weapon.
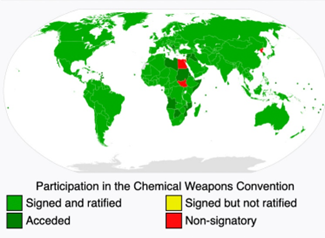
- The Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) is an arms control treaty that prohibits the development, production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons.
- It came into force in 1997 and is implemented by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), headquartered in The Hague, Netherlands.
- India is a signatory and one of the first countries to ratify the CWC in 1996.
- The CWC mandates the destruction of existing chemical weapon stockpiles and verification of compliance through inspections.
- It is the only multilateral disarmament treaty that provides for elimination of an entire category of weapons of mass destruction under international verification.
(IE)
Economy
GI tag:
-
- Context:The application fee for the Geographical Indications (GI) tag had been reduced to ₹1,000 from ₹5,000.
- GI tag certificates being distributed for crafts and products such as Kannadippaya (bamboo mat) of Kerala, Apatani textile of Arunachal Pradesh, Marthandam honey of Tamil Nadu, Lepcha Tungbuk of Sikkim, Bodo Aronai of Assam, Ambaji white marble of Gujarat, and Bedu and Badri cow ghee of Uttarakhand.
- GI (Geographical Indication) is a form of intellectual property right (IPR) that identifies goods as originating from a specific place, possessing qualities or reputation due to that origin.
- Governed by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 — effective from 2003.
- Administered by the Geographical Indications Registry, Chennai (under DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry).
- Validity: 10 years, renewable indefinitely.
- Examples: Darjeeling Tea (first GI in India, 2004), Kandhamal Haldi, Mysore Silk, Basmati Rice.
- Promotes rural economic growth, cultural heritage, and export potential while preventing misuse of regional product names.
- Context:The application fee for the Geographical Indications (GI) tag had been reduced to ₹1,000 from ₹5,000.

(TH)
Science & Technology
Ricin poison:
-
- Context: the Gujarat ATS arrested three men, including a ‘doctor’, for trying to produce ricin.
- Ricin is a protein toxin extracted from castor-bean seeds; even a few milligrams can kill an adult.
- It works by entering cells and binding ribosomes, halting protein synthesis and causing multi-organ failure.
- Symptoms vary by exposure route: ingestion causes vomiting, bloody diarrhoea, low blood pressure; inhalation causes breathing trouble; injection leads to organ collapse.
- There is no antidote; treatment is symptomatic, often limited because the toxin acts fast and is rare, so diagnosis may be delayed.
- Ricin has been considered for use as a chemical weapon (listed under Schedule 1 of the Chemical Weapons Convention, adopted in 1993 and entering into force in 1997) and has featured in terror/poison-plots due to ease of extraction from widely grown castor plants.

(IE)
Government Schemes
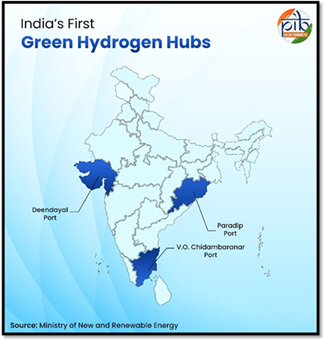
Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) scheme:
-
- It is under India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission.

-
- Designed to catalyse the green hydrogen ecosystem in India by providing incentives for both manufacturing of electrolysers and production of green hydrogen (and derivatives).
- It is structured with two major components:
- Incentive scheme for electrolyser manufacturing (domestic value-addition, efficiency targets); approx ₹ 4,440 crore from FY 2025-26 to FY 2029-30.
- Incentive scheme for green hydrogen production (competitive bids, fixed incentives per kg for first few years); approx ₹ 13,050 crore over same period.
- Combined mission budget around ₹ 17,490 crore (or approx ₹ 19,744 crore including other elements) for SIGHT.
- Objectives / outcomes:
- To make India a global hub for production, usage, export of green hydrogen & derivatives.
- To reduce cost of hydrogen production, increase domestic manufacturing / value-addition, and reduce dependency on fossil-fuel imports.
- To support decarbonisation of “hard-to-abate” sectors (like steel, shipping, mobility) via pilot projects under SIGHT/mission.
- Implementation & governance: The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) is the nodal ministry; Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) acts as the implementing agency for the competitive-bidding/selection, monitoring and verification.
(PIB)
Important data/facts
Society & Social Justice
Health:
-
- Tuberculosis incidence falling in India by 21% a year: WHO report
(TH)
Geography & Environment
-
- At least three out of four Indians believe that climate change is affecting the area they live in and is harming them. Most were willing to make lifestyle changes to help reduce its impact, according to a Pew survey.
- India is one of the few countries where the willingness to make changes was uniformly high across all age groups. Over 75% of Indians across all age groups (18-34, 35-49 and 50+) were willing to make a lot of lifestyle changes or some lifestyle changes.
(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Consider the following statements regarding the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM):
1. The Mission aims to make India a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of green hydrogen and its derivatives.
2. The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme is a key component of the Mission, providing incentives for electrolyser manufacturing and green hydrogen production.
3. The Ministry of Power is the nodal ministry for the implementation of the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- The National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM), launched in 2023, seeks to make India a global hub for green hydrogen production, usage, and export.
- The SIGHT programme under the Mission provides incentives for electrolyser manufacturing and green hydrogen production.
- However, the nodal ministry for implementation is the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), not the Ministry of Power.
Q2. Consider the following statements regarding Ricin toxin:
1. It is a synthetic chemical developed in laboratories for use in biochemical research.
2. It is listed under Schedule 1 of the Chemical Weapons Convention due to its potential use as a biological weapon.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Ricin is not synthetic; it is a naturally occurring protein toxin obtained from the seeds of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis). It is highly lethal, with no antidote, and death results from organ failure due to inhibition of protein synthesis.
- It is a highly potent toxin recognized under Schedule 1 of the Chemical Weapons Convention. It disrupts protein synthesis in cells, leading to multi-organ failure and death, depending on the route of exposure.
Q3. Consider the following statements regarding Geographical Indications (GI Tags) in India:
1. GI Tags are a form of intellectual property right that indicate goods as originating from a specific geographical location.
2. The registration and protection of GI Tags in India are governed by an Act administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
3. The first product to receive a GI Tag in India was Basmati Rice.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999, under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, governs GI Tags in India.
- The first GI granted was Darjeeling Tea (2004), not Basmati Rice.
Q4. Consider the following statements regarding the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC):
1. The CWC is the only multilateral disarmament treaty that bans an entire category of weapons of mass destruction.
2. The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), headquartered in Geneva, is responsible for implementing the Convention.
3. India is a signatory to the CWC and has destroyed all its declared chemical weapon stockpiles under OPCW verification.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
-
- The CWC (1997) prohibits the production, use, and stockpiling of chemical weapons.
- It is implemented by the OPCW, headquartered in The Hague, not Geneva.
- India ratified the Convention in 1996 and became the first country to completely destroy its declared chemical weapons stockpile under OPCW supervision.




