TAG: GS-2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
CONTEXT: The Indian Prime Minister proposed seven key pillars to strengthen ties between India and CARICOM during talks with Caribbean partner countries on November 20, 2024, focusing on trade, technology and tourism.
EXPLANATION:
About CARICOM (Caribbean Community):
-
- CARICOM, which stands for Caribbean Community, is the oldest surviving integration movement in the developing world.
- It is an organization of Caribbean countries and dependencies originally established as the Caribbean Community and Commons Market in 1973 by the Treaty of Chaguaramas.
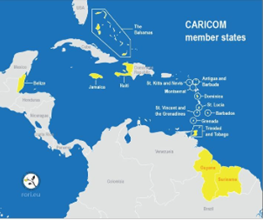
- It has 15 members Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago.
-
-
- Anguilla, Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, and the Turks and Caicos Islands have associate member status, and Aruba, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Venezuela maintain observer status.
-
-
- The Chairmanship of the Community is rotated every six months among the member countries’ Heads.
- The CARICOM Secretariat in Georgetown, Guyana, is the principal administrative organ of the Community and is headed by a Secretary General who is the Chief Executive Officer of the Community.
- In 2007, CARICOM officially inaugurated the Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ), which serves as the final court of appeal for CARICOM members and also handles regional trade disputes.
The Prime Minister of India proposed a seven-pillar framework to enhance cooperation between India and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). These pillars, forming the acronym “C.A.R.I.C.O.M.,” are:
-
- Capacity Building: Enhancing skills and capabilities through training and education initiatives.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Collaborating to improve agricultural practices and ensure food security.
- Renewable Energy and Climate Change: Joint efforts to promote sustainable energy solutions and address climate change challenges.
- Innovation, Technology, and Trade: Fostering innovation, technological advancement, and trade relations.
- Cricket and Culture: Strengthening cultural ties and promoting cricket as a shared passion.
- Ocean Economy: Leveraging marine resources for economic development.
- Medicine and Healthcare: Collaborating to improve healthcare systems and medical services.
Key Agreements and Cooperation
-
- Digital Payments: India’s UPI system will be introduced in Guyana, fostering financial inclusion and technological collaboration.
- Defense: India provided two Dornier aircraft and pledged continued support for military capacity building through scholarships and training.
- Agriculture: India supplied millet seeds to Guyana, aiding food security, and agreed to establish a Jan Ausadhi Kendra to improve access to affordable medicines.
Significance
-
- The visit underscored India’s commitment to deepening ties with South America, with Guyana emerging as a pivotal partner in energy and economic collaboration. The agreements signify a shared focus on mutual growth and strategic cooperation.
Source:
Spread the Word



