THE CONTEXT: The 15th BRICS summit was hosted by South Africa in Johannesburg on August 22–24, 2023. The summit was held against the backdrop of geopolitical changes and changing global economic dynamics. The summit also marked the first in-person meeting of BRICS leaders since 2019. In this article, we will analyze the various dimensions of the summit from the UPSC CSE perspective.
THE OUTCOMES OF THE SUMMIT
- The theme for the 15th BRICS Summit was “BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development and Inclusive Multilateralism”.
- The 26-page Johannesburg declaration adopted at the conclusion of the Summit reflected the issues of global economic, financial, and political importance.
Some of the major joint statements released during the summit are:
- Opposition to Unilateral Measures:The summit condemned unilateral coercive actions, advocated inclusive multilateralism, and upheld international law.
- Agriculture and Food Security:The summit strived for fair agricultural trade, ending hunger, sustainable agriculture, and resilient practices.
- UN Reform: The summitsupported comprehensive UN reform, including the Security Council, for enhanced democracy, effectiveness, and developing country representation.
- Anti-Corruption: The summit also reiterated the importance of uplifting and strengthening anti-corruption practices. It has led an initiative to combat corruption practices by educating the masses and leading numerous programs.
- Protecting Customers in the e-Commerce Era: The summit acknowledged the need to safeguard customers in the era of e-commerce which has led to the establishment of the Digital Economy Working Group.
- Strengthening Trade: The summit supported and decided that there will be a surge in the collaboration pertaining to trade activities. As prescribed by the BRICS Framework for Cooperation on Trade in Services, there will be a collaboration of the BRICS business council with the BRICS national focal points.
BRICS EXPANSION
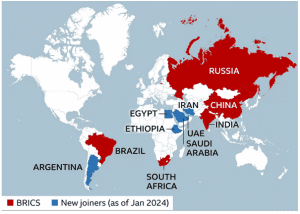
- The major highlight of the fifteenth summit was the agreement to admit six new member countries: Argentina, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, who will officially join the group in January 2024.
- BRICS currently consists of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
COUNTER-TERRORISM
- It also calls for expeditious finalization and early adoption of the India initiated Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) within the UN Framework, while maintaining that ‘terrorism should not be related to any religion, nationality, civilization or ethnic group’.
- The declaration also called for peaceful resolution of global conflicts, including in Niger and a ceasefire in Sudan.
DE- DOLLARISATION
- It emphasized need for BRICS to conduct trade and financial transactions in their own currencies, rather than the US dollar. The notion of de-dollarization of the global economy is, however, unlikely to materialize, not at least in the next 10-15 years, as currently over 50% of global trade is in US dollars (while the Chinese renminbi accounts for just 3-4%).
- It was agreed at the Summit to work towards this issue and the BRICS Finance Ministers and Central bank Governors were tasked with considering the modalities of trading in local currencies and payment platforms and report to the next Summit.
INTRA-BRICS COOPERATION
- It focuses on intra-BRICS cooperation and outreach to other developing countries.
- The Declaration also reflects the shared views of its members on several political issues in a bid to strengthen the bloc as an alternative to the U.S.-led liberal international order.
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE SUMMIT
- This is the first in-person summit since 2019 and the COVID-19 pandemic. This is also the first in-person meeting since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, an event that has cast a long shadow not only over global stability, but food, fertilizer and energy security.
- Generally, BRICS is essentially a movement of “emerging economies”, and thus gives importance mainly to economic issues, but given the geopolitical flux especially after the war in Ukraine, this BRICS summit takes on a new importance in geopolitical issues.
- At the Summit along with critical geopolitical concerns, economic cooperation and the constantly increasing multilateral trade and development were discussed.
EXPANSION OF THE BRICS
- The summit’s most notable outcome was the admission of six new members.
- Among these, Iran stands out as particularly contentious and in direct opposition to the U.S. whereas Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates will bring substantial financial resources, while Argentina will bolster South American representation.
- Egypt and Ethiopia will enhance the African presence within the organization.
ECONOMIC AND GROWTH ASPECTS
- The countries discussed global trade, investment and economic growth in general, as the nations of this intergovernmental organisation comprise of almost one third of the world’s GDP and in world trade, these countries have about 17% share.
- The new members are economically strong as India, Iran, and Russia are already developing the International North-South Transport Corridor. Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, two of the world’s largest oil and gas exporters
- The New group incorporates major global oil producers near crucial trade chokepoints, such as the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz and Bab-al Mandab Strait.
- Egypt and Ethiopia are an important presence in the strategically important Horn of Africa and the Red Sea. Argentina is the second largest economy in Latin America.
CLIMATE CHANGE
- BRICS members agreed to address the challenges posed by climate change while also ensuring a just, affordable and sustainable transition to a low-carbon and low-emission economy.
- The five nations called on developed countries to lead by example and support developing countries towards such transitions.
- BRICS nations opposed trade barriers imposed by certain developed countries under the pretext of tackling climate change.
MULTILATERALISM
- BRICS has always been understood as a constructive platform to contribute to the reform of multilateral institutions.
- The growing weight of the BRICS members merits demands for a larger role in economic governance reforms.
- The BRICS countries want more power in multilateral decisions that guarantee a greater degree of domestic autonomy or flexibility in their respective development agendas.
- The decision to invite new members is a choice of development model for the next stage and will foster collective influence in global partnerships for multilateralism.
REFORM OF EXISTING GLOBAL INSTITUTIONS
- This brand-new BRICS policy document emphasised on reform of existing global institutions including the United Nations, World Bank, IMF, WTO, WHO and others.
- BRICS can deal with this via a democratic platform within the UN. As with the new BRICS expansion, the members have quite specific trade influence.
SECURITY
- Apart from world trade and global economic growth, another key area of discussion was the world security.
- The BRICS nations vowed to work towards confronting the menace including cross-border movement of terrorists and terror financing networks.
THE IMPLICATIONS OF THE EXPANSION OF THE BRICS
- The implications of this expanding BRICS have very specific and wide-ranging implications in both positive and negative terms.
- First, there is considerable anti-US sentiment in the world, and all these countries are looking for a grouping where they can use that sentiment to gather together. Second, there is a lot of appetite for multipolarity, for a platform where countries of the Global South can express their solidarity.
GROWING INCLUSIVITY
- The expansion signifies a growing alignment of geopolitical and economic agendas within the BRICS which indicates towards inclusivity with incorporating of countries with varied interests.
- With the inclusion of two African countries, it strengthened efforts to promote integration, development, and growth through the African continent as well.
ALTERNATIVE WORLD ORDER
- The expansion of the BRICS to a BRICS+ format and the adoption of guiding principles, standards, and procedures for the same, have potentially made the BRICS a more attractive institution for consensus-building and dialogue in the developing world.
- If not a new world order, the BRICS expansion is certainly an attempt at an alternative world order, one with a more sympathetic ear for the developing many versus the developed few.
SPOKESPERSON OF THE DEVELOPING WORLD
- Adding new members strengthens the group’s heft as a spokesperson of the developing world. BRICS currently represents around 40% of the world’s population and more than a quarter of the world’s GDP.
- With the additions, it will represent almost half the world’s population, which will increases its say in the global multilateral forums.
DIFFICULT TO BUILD CONSENSUS
- Apart from above mentioned positive implication, there is challenges and opportunities as well because of expansion that will test the BRICS’ cohesion and effectiveness.
- Its ability to remain a credible force for reshaping global governance will depend on its capacity to forge consensus among its diverse members.
- However, a larger membership also means greater challenges to reaching consensus and adds new layers of complexity.
BALANCING THE GROUP
- There is major challenge in front of institution and India to not portrait the grouping as anti-west.
- The incorporation of U.S. allies such as the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia alongside countries ambivalent or opposed to the United States could frustrate efforts at deepening cooperation between member-states.
- Members would need to decide if BRICS is to be a bloc of emerging economies seeking to promote their interests in a multipolar world order or adopt a more explicitly anti-West orientation, the latter of which is preferred by China and Russia.
- The most controversial issue for BRICS however, is the defense of nonalignment and neutrality in tensions between the United States and China and in the war in Ukraine.
THE ISSUES THAT BRICS SUMMIT DID NOT ADDRESS
BRICS as a forum was expected to address the few prominent geopolitical issues that it failed to address:
UKRAINE WAR
- BRICS should have acted as a summit to taking up the issues of Ukraine War and complaints against the West for its responsibility for crises and wars and its inability to even control the consequences of these events.
- Though Russian President and BRICS addressed the matter that they are ready to join efforts to seek an immediate ceasefire in Ukraine but not any fruitful conversation or action took place.
ISSUE OF CONSENSUS
- BRICS is being called a negative coalition of states that cannot agree on a common position.
- They can create a consensus on what they oppose to avoid sanctions and protectionist measures but cannot build consensus over important issues because of differing viewpoints within the grouping.
BRICS NATIONS FAILED TO REBUILD THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL ORDER
- There are issues pertaining to the New Development Bank (NDB) which was not addressed.
- Less than a quarter of disbursements made by the BRICS Bank last year were in local currency and the vast bulk of that was denominated in Chinese renminbi and, more recently, South African rand.
- Despite initially inspiring language around equality, transparency and accountability, NDB’s decision-making process probably much more opaque than other banks.
CURRENCY
- BRICS leaders are also expected to take forward earlier talks on intra-BRICS trading in national currencies, although plan for pushing for a “BRICS currency” to challenge the dollar appear to be on the agenda.
- But the hype about a common BRICS currency might be impractical and premature, but trading in national currencies is needed in a reality. The recent rupee-designated oil transaction between India and the United Arab Emirates is not merely a swipe at the petrodollar arrangement that has prevailed since 1973. It is also a signal that the world’s major commodity exporters and importers can try to reduce their dependence on the dollar by trading in local currencies.
INDIA AND THE BRICS SUMMIT 2023
At the Summit, India called for a strengthened BRICS that will be.
(B) Breaking barriers
(R) Revitalizing economies
(I) Inspiring innovation
(C) Creating opportunities
(S) Shaping the future
India’s initiatives at the summit:
- Called for reform of Multilateral Financial Institutions and WTO
- Called for setting defined timelines for UNSC reforms.
- Urged BRICS to send a global message of unity and not polarization.
- Proposed creation of a BRICS Space Exploration Consortium
- Offered Indian Digital Public Infrastructure – the Indian stack to BRICS partners.
- Proposed undertaking skill mapping, skilling and promoting mobility among BRICSs countries
- Proposed joint efforts of BRICS countries for protection of Big Cats under International Big Cat Alliance
- Proposed establishing a repository of traditional medicine among BRICS countries
- Called upon BRICS partners to support AU’s permanent membership of the G20
India participated at BRICS-Africa Outreach and BRICS Plus dialogue session and invited the participant countries to join International Solar Alliance, One Sun, One World, One Grid; Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure; One Earth, One Health; Big Cat Alliance and Global Centre for Traditional Medicine. India initiated Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) within the UN Framework to openly discuss the problem of terrorism and build deliberations with the BRICS nations. India supported expansion of the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) grouping. India took the lead in forging consensus on membership criteria and selection of new members. India suggested measures in areas of railway research networks, and cooperation among MSMEs and start-ups.
THE WAY FORWARD
- Expansion should be fast tracked: Expansion of BRICS has further boosted its influence as now the group represents a significant portion of the world’s population, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), global trade, and energy production. In this respect, there is need to fast track the expansion mechanism by building consensus.
- Permanent secretariat: With its expanded membership and relevant portfolio, BRICS should consider setting up a permanent secretariat, which it does not have yet.
- Promote globalization and multilateralism: As we enter a multipolar era, it becomes imperative to acknowledge new players and the reality that the global landscape will not be characterized by harmonized systems, but rather a rich variety of approaches. This is the role BRICS, a platform should play that contributes to globalization, multipolarity and multilateralism.
- Prioritize Cooperative mechanism: There is need of cooperative mechanisms for energy transition, technology transfer, financing the New Development Bank, resumption of the World Trade Organization dispute settlement mechanism, and UN Security Council reform.
- Global Governance: There is a need to make global governance more representative and inclusive by igniting a genuine conversation. In global governance, more imperfect institutions reflecting the realities of today are better than one imperfect institutional structure that is alien to the world of today. In this context BRICS should work towards equity, inclusion and representation.
- International stability: BRICS nations should strive for peaceful and diplomatic settlement of crisis and conflict in various regions of the world. BRICS, being one of the pillars of the emerging polycentric world order, plays an important stabilising role in global affairs. In the context, BRICS can contribute significantly in maintaining international stability and ensuring global economic growth.
THE CONCLUSION: The 15th BRICS Summit represented a significant moment in the evolution of this alliance. As BRICS continues to grow and evolve, it holds the promise of promoting cooperation, stability, and development on a global scale. In this respect, it is needed that BRICS should promote comprehensive development of all states both big and small and enhanced mutually beneficial cooperation among them on the basis of shared interests.
MAINS QUESTIONS
- The Fifteenth BRICS summit has sent a strong signal that the post–World War II order should accept the multipolar reality and change with the times.
- “With the expansion of BRICS grouping, it can strengthen its claim of being the voice of the Global South”. Analyse.

