1. UNFPA’S STATE OF WORLD POPULATION (SOWP) REPORT
TAGS:GS-II- SOCIAL ISSUES
THE CONTEXT: According to the latest edition of the UNFPA’s State of World Population (SOWP) report, India’s population has grown by 1.56 per cent in the past year and is estimated to be 1,428,600,000 million (142.86 crore), and more than two-thirds of its population or 68 per cent comprises people between the ages of 15 and 64, considered the working population of a country.
THE EXPLANATION:
- China has a population of 142.57 crore, according to the UN world population dashboard. The United States is a distant third, with an estimated population of 340 million.
- The population demographics of India vary from state to state. Kerala and Punjab have an ageing population while Bihar and Uttar Pradesh have a young population.
- The latest report also shows that India’s total fertility rate (births per woman in the reproductive age) is estimated at 2.0. The average life expectancy for an Indian male stands at 71 and for females at 74, states the report which has been published annually since 1978.
- The report also states that 44 per cent of partnered women and girls in 68 reporting countries do not have the right to make informed decisions about their bodies when it comes to having sex, using contraception and seeking health care. An estimated 257 million women worldwide have an unmet need for safe, reliable contraception, it states.
- Although India and China will account for more than one-third of the estimated global population of 8.045 billion, the population growth in both Asian giants has been slowing, at a much faster pace in China than in India.
- Last year, China’s population fell for the first time in six decades, a historic turn that is expected to mark the start of a long period of decline in its citizen numbers with profound implications for its economy and the world.
- India’s annual population growth has averaged 1.2% since 2011, compared with 1.7% in the 10 years previously, according to government data.
VALUE ADDITION:
- The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, is a UN agency aimed at improving reproductive and maternal health worldwide.
- Its work includes developing national healthcare strategies and protocols, increasing access to birth control, and leading campaigns against child marriage, gender-based violence, obstetric fistula, and female genital mutilation.
- Headquarters: New York City, United States
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. SEA CUCUMBER
TAGS: GS-III- ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT:Recently, 105 kilograms of sea cucumber was seized by the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) near Attangarai in Ramanathapuram district.
About Sea Cucumber:
- They are marine invertebrates that live on the seafloor found generally in tropical regions. They’re named for their unusual oblong shape that resembles a fat cucumber.
- They act like garbage collectors of the ocean world, and they recycle nutrients, thus playing an important role in keeping coral reefs in good condition.
- They are an important constituent of the marine ecosystem as they play an important role in maintaining the health of the ecosystem.
- It has no limbs or eyes, or blood.
- In India is treated as an endangered species listed under schedule I of Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- As per IUCN Red List Brown Sea Cucumber has been listed as
- Demand: Sea cucumbers are in high demand in China and Southeast Asia, where they are consumed as food and used in medicine.
- This endangered species is primarily smuggled from Tamil Nadu to Sri Lanka.
- Recently, Lakshadweep has created the world’s first conservation area for sea cucumbers.
3. ONE WORD A DAY: MAGNAPORTHE ORYZAE
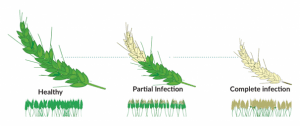
THE CONTEXT: Scientists have warned that the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, which is destroying South American wheat crops, could spread worldwide. The pathogen affects the crop in a disease known as ‘wheat blast’.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The seriousness of the disease is indicated by the fact that crops are burnt to avoid this disease. Magnaporthe oryzae originated in South America, but cases of infection have also been reported in Asia in 2016 and Africa in 2018.
- Genomic analysis of fungus samples from all three continents showed that these fungi are part of the same family.
- Wheat crops around the world are susceptible to the fungus. pathogen is also resistant to fungicides. The biggest concern is that this fungus has the potential to affect not only wheat but also other major food crops.
How wheat blast destroys crops
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
4. WHAT IS SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE?
TAGS:GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT:Recently, researchers from IIT Madras come up with the best way to neutralise carbon dioxide emissions in depleted oil and gas reservoirs.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Researchers found that supercritical carbon dioxide can be a good agent for simultaneous carbon dioxide sequestration and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) from depleted reservoirs when the gas is used along with surfactants in a ‘surfactant-alternating gas (SAG) injection’ approach.
What is Supercritical carbon dioxide?
· Supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) is a fluid state of CO2 where it is heated and held at or above its critical temperature and pressure. In this supercritical phase, CO2 exhibits properties and behaviors between that of a liquid and a gas. In particular, supercritical CO2 possesses liquid-like densities with gas-like diffusivity, surface tension and viscosity.
· When CO2 exceeds temperatures of 87.9°F (31.1°C) and is subjected to pressures above 1071 psi (7.39 MPa), it enters the supercritical phase. This phase of CO2 is commonly used as a solvent in chemical extraction processes due to its high solubility, low toxicity and minimal net effect on the environment.
- In this process, carbon dioxide gas is injected in the reservoir, where it becomes supercritical, followed by injection of water or surfactant solution.
- The study shows that the use of supercritical carbon dioxide for EOR resulted in greater storage of carbon dioxide for both water-alternating gas (WAG) and SAG approaches.
- However, SAG performed better at all pressures and temperatures as surfactant solution alters the interfacial tension between the oil and water phases, leading to a higher oil recovery percentage and more effective storage of carbon dioxide. The researchers also found that the reservoir pressure and temperature had a strong effect on the flow dynamics.
- This method not only promises improved recovery of oil but also safe, enhanced, and permanent storage of carbon dioxide gas emitted from human and other anthropological activities, for both WAG and SAG approaches.
- The use of supercritical carbon dioxide reduces oil viscosity, induces in situ swelling of the oil, and reduces the interfacial tension of the in-situ fluid system.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
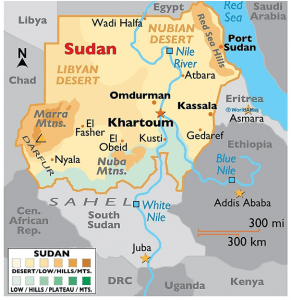
5. SUDAN‘S CONFLICT
TAGS: PRELIMS -PLACES IN NEWS
THE CONTEXT: Amid the intensified fighting between the army and paramilitaries in Sudan has killed around 200 people and wounded 1,800, damaging hospitals and hampering aid after three days of urban warfare.
Background:
- A weeks-long power struggle exploded into deadly violence between the forces of two generals who seized power in a 2021 coup: Sudan’s army chief Abdel Fattah al-Burhan and his deputy, Mohamed Hamdan Daglo, who commands the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
In this context from Prelims point of view, we may expect a Map based question on Sudan bordering countries.
Prelims Perspective:
- Sudan is a country in North Africa. It is bounded on the north by Egypt, on the east by the Red Sea, Eritrea, and Ethiopia, on the south by South Sudan, on the west by the Central African Republic and Chad, and on the northwest by Libya.
- Sudan’s capital Khartoum, which is located in the central part of the country where the White Nile and the Blue Nile rivers meet.
- The country is mainly composed of vast plains and plateaus that are drained by Nile river and its tributaries.
- Deriba Caldera is part of the volcanoes of the Marra mountains. It is considered to be the highest point in the whole of Sudan.
- Also, Sudan is part of the Great Green Wall Project, along with Burkina Faso, Chad, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria and Senegal.