GEOGRAPHY
1. INDIA’S IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY IS CAPABLE OF EMITTING LESS AND PRODUCING MORE: CSE
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-I- GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT:India’s iron and steel sector can produce less emissions and increase its output at the same time, according to a new analysis released by Delhi-based non-profit, Centre for Science and Environment (CSE).
THE EXPLANATION:
- The iron and steel industry is an emission-intensive sector. According to the new study shows it is possible to bring down carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from our iron and steel sector drastically by 2030, while more than doubling India’s output of steel. We can emit even less than what we do today. But this will need planning, technology and adequate funds.
- The analysis also gave a number of recommendations to achieve these twin goals. These included switching over to cleaner fuels, increasing the use of steel scrap, implementing carbon capture utilisation and storage (CCUS) and organising finance for a switchover to new fuels and technologies.
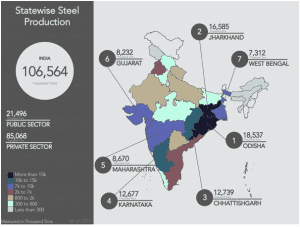
- The iron and steel sector is a hard-to-abate sector in terms of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions; at the same time, it is a critical contributor to the economic development of the country. Globally, the sector accounts for some 7 per cent of total GHG emissions; in India, the sector’s share is 5 per cent (as per the latest Biennial Update Report (BUR) submitted to UNFCCC in 2016).
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE:
2. HEATWAVES LIKELY FROM MARCH TO MAY: IMD FORECAST
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-I- GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: According to India Meteorological Department (IMD),Heatwaves during March-May are likely in most parts of India, except for the northeastern States, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala and coastal Karnataka.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The study also shows, accentuating the heat is the lack of rainfall. “Below normal rainfall is most likely over most areas of northwest India, west central India and some parts of east & northeast India. Normal to above normal rainfall is likely over most parts of peninsular India, east central India and some isolated pockets of northeast India”.
- February temperature hit record levels, with many parts of north and western India reporting 35-39 degree Celsius, or about 3-5 degrees above what is normal for this time of the year, and the IMD’s latest advisory suggests that these conditions are likely to persist over the coming months.
- Currently, La Nina conditions— or below normal temperatures— are prevailing over the equatorial Pacific region. The La Nina is likely to weaken and turn to El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO), ‘neutral conditions’ during the pre-monsoon season, the IMD forecast noted. La Nina conditions are associated with better monsoon rains with El Nino conditions linked to reduced monsoon rains, particularly in northwest India.
- La Nina conditions have persisted for nearly three years leading to above normal rains in India since 2019. La Nina and El Nino conditions are cyclical in nature and while El Nino conditions are expected to emerge, a full picture can emerge only after March when global climate models can better capture such changes.
- The elevated temperatures threaten wheat yields with the IMD last week issuing advisories to farmers to either irrigate or initiate soil treatment to conserve moisture.
VALUE ADDITION:
What is La Nina?
- La Niña is a climate pattern that describes the cooling of surface-ocean waters along the tropical west coast of South America. La Niña is considered to be the counterpart to El Niño, which is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the equatorial region of the Pacific Ocean.
- Together, La Niña and El Niño are the “cold” (La Niña) and “warm” (El Niño) phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). ENSO is series of linked weather- and ocean-related phenomena. Besides unusually warm or cool sea-surface temperatures, ENSO is also characterized by changes in atmospheric pressure.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
3. FATF SUSPENDS RUSSIA’S MEMBERSHIP OVER UKRAINE WAR
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II- INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the global anti-money laundering watchdog the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has suspended Russia’s membership over the Ukraine war.
THE EXPLANATION:
About FATF:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog. The inter-governmental body sets international standards that aim to prevent these illegal activities and the harm they cause to society. As a policy-making body, the FATF works to generate the necessary political will to bring about national legislative and regulatory reforms in these areas.
- The 39-member body sets international standards to ensure national authorities can effectively go after illicit funds linked to drugs trafficking, the illicit arms trade, cyber fraud and other serious crimes.
- The FATF was created in 1989 at the behest of the G7 and is headquartered in Paris.
- In total, more than 200 countries and jurisdictions have committed to implement the FATF’s Standards as part of a co-ordinated global response to preventing organised crime, corruption and terrorism.
- On June 25, 2010 India was taken in as the 34th country member of FATF. Therefore, India is not founding member of FATF.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
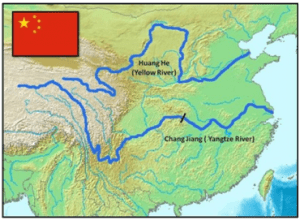
4. YELLOW RIVER
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: A recent study has noted that the Chinese practice of building embankments is one of the reasons to blame for the devastating floods occurring in the “Yellow river”.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Yellow River:
- The Yellow River (Huang He) is the second longest river in China (after the Yangtze).
- It’s the fifth-longest river in the world.
- Source: The Bayankala Mountains on the Plateau of Tibet in western central China.
- Mouth: southern Bohai Sea
- Claims to fame: world’s muddiest major river, “China’s cradle (of civilization)”
- Provinces flowed through: Qinghai, Sichuan, Gansu, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, and Shandong
- Tributaries: Black River, White River, Tao River, Huangshui, Fen River, Luo River, Wei River.
- The name “Yellow River” comes from the huge amounts of “yellow” loess sediment it carries, which are eroded when it flows through the Loess Plateau.
- Hukou Waterfall on it is the second-largest waterfall in China.
5. EXERCISE DESERT FLAG
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II- INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: For the first time, India’s indigenously made light combat aircraft Tejas is participating in an international multilateral air exercise – Exercise Desert Flag VIll – in the UAE, reflecting India’s increasing efforts at showcasing the jet on the world stage.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Exercise Desert Flag:
- Exercise Desert Flag is a Multilateral air exercise which will see participation from the air forces of the UAE, France, Kuwait, Australia, the UK, Bahrain, Morocco, Spain, the Republic of Korea, and the US.
- The objectives for the exercise were to expose coalition participating forces to large force employment, sharpen tactical capabilities, and enhance interoperability along with fostering closer relations between the participating forces.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) participated in the exercise for the first time in Exercise Desert Flag-VI (2021).




