INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. WINDSOR FRAMEWORK
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-II-INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT:Recently, the United Kingdom and the European Union struck a deal regarding post-Brexit trade rules for Northern Ireland, with a view to remove the border between Britain and Northern Ireland running through the Irish Sea.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The fact that the Republic of Ireland remained with the EU after Brexit led to complications on the trade front, a wrinkle that the U. K.’s conservative government ironed out with the Northern Ireland Protocol.
- However, the Protocol, which allowed EU customs rules to apply across Northern Ireland, led to tensions in the province. The Windsor framework is the latest attempt at a remedy to the political complexities that have impacted trade and sentiments in the area.
- The ‘Windsor Framework’ will replace the Northern Ireland Protocol, which had proved to be among the thorniest of Brexit fall-outs, creating problems both economic and political.
What are the salient features of the Framework:
The framework has two crucial aspects:
- Introduction of a green lane and red lane system – For goods that will stay in Northern Ireland and those that will go to the EU respectively.
- The Stormont Brake – it allows Northern Ireland lawmakers and London to veto any EU regulation they believe affects the region adversely.
- The two-lane system– British goods meant for Northern Ireland will use the green lane at the ports and will be allowed to pass with minimal paperwork and checks.
- Physical checks will be conducted if the goods are deemed suspicious, in place of the routine checks now.
- Goods destined for Ireland or the rest of the EU will have to take the red lane, with the attendant customs and other checks.
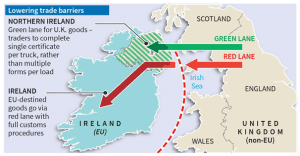
The Northern Ireland Protocol:
- The Northern Ireland Protocol is a trading agreement that was negotiated in 2020 between the U.K. and the E.U.
- Under the protocol, both the U.K. and E.U. agreed that the inspection of goods would be conducted between Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
- Northern Ireland remained in the EU single market, and trade-and-customs inspections of goods coming from Great Britain took place at its ports along the Irish Sea.
Issues related to the Northern Ireland Protocol :
- The protocol has led to political division in Northern Ireland.
- The checks made trade between Great Britain and Northern Ireland cumbersome, with food products, especially, losing out on shelf life while they waited for clearance. Some taxation and spending policies of the UK government could not be implemented in Northern Ireland because of EU rules.
- The sale of medicines, too, was caught between different British and EU rules.
2. RAISINA DIALOGUE
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-II-INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT:Prime Minister recently inaugurated the eighth edition of the Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi. Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni is the Chief Guest of the three-day Dialogue.
THE EXPLANATION:
The theme of the 2023 Edition is “Provocation, Uncertainty, Turbulence: Lighthouse in the Tempest.”
About Raisina Dialogue:
- The Raisina Dialogue is a multilateral conference held annually in New Delhi, India. Since its inception in 2016, the conference has emerged as India’s flagship conference on geopolitics and geo-economics. The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation, an independent think tank, in collaboration with the Ministry of External Affairs of India.
- The conference is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving a variety of global policymakers including heads of states, cabinet ministers and local government officials. In addition, the Dialogue also welcomes major private sector executives, as well as members of the media and academia. It is designed on the lines of Singapore’s Shangri-La Dialogue.
- The name “Raisina Dialogue” comes from Raisina Hill, an elevation in New Delhi, seat of the Government of India, as well as the Presidential Palace of India, Rashtrapati Bhavan.

3. PROTON BEAM THERAPY
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT:Cancer patients in India face twin challenges when it comes to accessing proton beam therapy (PBT): there are not enough facilities offering the treatment, and the cost can run into tens of lakhs of rupees.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The PBT is considered a viable alternative to radiation for treating solid tumours, especially for head and neck cancers.
- According to hospitals, that it has treated up to 900 patients in its Chennai-based Proton Cancer Centre, of which 47% of cases are brain tumours. Patients with cancers of the prostate, ovaries, breast, lungs, bones and soft tissues have also seen promising results in terms of recovery through proton beam therapy.
ABOUT PROTON BEAM THERAPY:
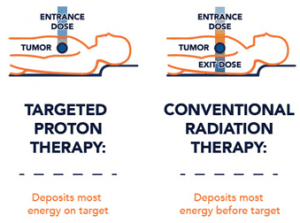
- Proton beam therapy, is a type of radiation therapy. It uses protons rather than x-rays to treat cancer.
- A proton is a positively charged particle. At high energy, protons can destroy cancer cells. Doctors may use proton therapy alone. They may also combine it with x-ray radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, and/or immunotherapy.
- Unlike radiation which uses X-rays, PBT uses protons to tackle cancer. While radiation can prove toxic to the whole body, protons can destroy cancer cells precisely by targeting tumours, thus saving adjoining organs.
4. INDIA’S FIRST PROSPECTIVE DNA VACCINE
TAGS: PRELIMS-GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT:In a significant development in DNA vaccination research, India’s first and only DNA vaccine candidate for dengue has shown promising results.
THE EXPLANATION:
- In preliminary trials on mice, the candidate generated a robust immune response and improved survival rates after exposure to the disease.
- According to researchers, the world’s first DNA vaccine—ZyCoV-D, developed by Ahmedabad-based pharmaceutical firm Zydus Cadila—was approved in 2021 for emergency use against COVID-19. Globally, DNA vaccines are being developed for diseases like tuberculosis and chikungunya. Some 19 DNA dengue vaccines are being evaluated, but yet to reach final clinical trials.
What is DNA Vaccine?
- A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
- DNA vaccines work by injecting genetically engineered plasmid containing the DNA sequence encoding the antigen(s) against which an immune response is sought, so the cells directly produce the antigen, thus causing a protective immunological response.
- DNA vaccines have theoretical advantages over conventional vaccines, including the “ability to induce a wider range of types of immune response”.Several DNA vaccines have been tested for veterinary use.
- In some cases, protection from disease in animals has been obtained, in others not. Research is ongoing over the approach for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases in humans, as well as for cancers.
- In August 2021, Indian authorities gave emergency approval to ZyCoV-D. Developed by Cadila Healthcare, it is the first DNA vaccine approved for humans.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. UNITED NATIONS COMMITTEE ON ECONOMIC, SOCIAL, AND CULTURAL RIGHTS
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: The representatives of fugitive ‘godman’ Nithyananda’s self-proclaimed country, the United States of Kailasa (USK), attended a discussion conducted by the United Nations Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR) recently.
THE EXPLANATION:
About United Nations Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights:
- The Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (CESCR) is the body of 18 independent experts that monitors the implementation of the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights by its States parties.
- It was established under ECOSOC Resolution 1985/17 in 1985.
- All States parties are obliged to submit regular reports to the Committee on how economic, social, and cultural rights are being implemented.
- States must report initially within two years of accepting the Covenant and thereafter every five years.
- The Committee examines each report and addresses its concerns and recommendations to the State party in the form of “concluding observations”.
- The Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, which entered into force in 2013, gives the Committee competence to receive and consider communications from individuals claiming that their rights under the Covenant have been violated.
- The Committee meets in Geneva and normally holds two sessions per year.
Objectives :
- to carry out the monitoring functions assigned to the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) in Part IV of the Covenant.
- Drawing on the legal and practical expertise of its members.
- It also helps States in fulfilling their obligations under the Covenant by issuing specific legislative, policy, and other recommendations so that economic, social, and cultural rights are better protected.
It seeks to:
- develop a constructive dialogue with State parties
- determine whether the Covenant’s norms are being applied in State parties
- assess how the implementation and enforcement of the Covenant could be improved


