INDIAN POLITY
1. SECTION 153A OF THE INDIAN PENAL CODE (IPC)
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II- POLITY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a Congress leader was booked under IPC sections including 153A, 505, and 295A.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Section 153A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC):
- Origin: In the pre-Independence Rangila Rasool case, the Punjab High Court had acquitted the Hindu publisher of a tract that had made disparaging remarks about the private life of the Prophet, and had been charged under Section 153A.
- Section 153A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) penalizes “promoting enmity between different groups on grounds of religion, race, place of birth, residence, language, etc., and doing acts prejudicial to maintenance of harmony”.
- This is punishable with imprisonment up to three years, with a fine, or with both.
- The provision was enacted in 1898 and was not in the original penal code.
- Section 505, penalizes “statements conducing to public mischief” .
- The data from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) show that the rate of conviction for Section 153A is very low.
- In 2020, the cases registered were six times higher than the cases in 2014.
- However, the conviction rate in 2020 was 20.2%, suggesting that the process often becomes the punishment.
Safeguards against misuse of Section 153 A:
- Sections 153A and 153B require prior sanction from the government for initiating prosecution.
- This is required before the trial begins, and not at the stage of preliminary investigation.
- To curb indiscriminate arrests, the Supreme Court laid down a set of guidelines in its 2014 ruling in Arnesh Kumar v State of Bihar.
- According to this, for offenses that carry a sentence of fewer than seven years, the police cannot automatically arrest an accused before investigation.
- In a 2021 ruling, the SC said that the state will have to prove intent for securing a conviction under Section 153A.
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. OLIVE RIDLEY TURTLES , RUSHIKULYA RIVER
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, experts reported that suitable climatic and beach conditions are the reasons for the early mass nesting of Olive Ridley turtles.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Olive Ridley turtles:
- The Olive ridley turtles are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in the world.
- They are found to be inhabiting the warm waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans.
- They are carnivores and feed mainly on jellyfish, shrimp, snails, crabs, molluscs, and a variety of fish and their eggs.
- The males and females grow to the same size.
- These turtles, along with their cousin the Kemps ridley turtle, are best known for their unique mass nesting called Arribada, where thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.
- The coast of Orissa in India is the largest mass nesting site for the Olive-ridley, followed by the coasts of Mexico and Costa Rica.
- The species is recognized as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red list.
- They lie in Scheduled 1 of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- They are in Appendix I of the CITES.
About Rushikulya river :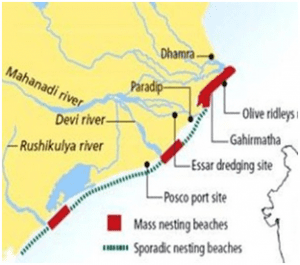
- It is one of the major rivers in Odisha and covers the entire catchment area in the districts of Kandhamal and Ganjam.
- The Rushikulya originates at an elevation of about 1000 meters from the Daringbadi hills of the Eastern Ghats.
- The tributaries of the Rushikulya River are Dhanei, Badanadi, and Baghua.
- It does not have any delta in its mouth region.
- This river is extremely rich in mineral wealth and some of the prime ones include-Lime stone, sand talc, grinding materials, black sand, and clay.
- This is one of the remote areas for mass nesting and is regarded as a site of Ridley Olive sea turtles.
3. BISPHENOL A
TAGS: TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: Recent studies have reported that ‘Bisphenol A’, may shorten the life cycle of a mosquito and lead to a population explosion.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Bisphenol A:
- Bisphenol A is a synthetically obtained colourless, crystalline organic compound that occurs in the solid phase belonging to the diphenylmethane group.
- It is soluble in organic solvents but poorly dissolves in water
- It is also used as eyewear glasses. It is a chemical is widely used to soften plastics, paints, and other products.
- It is known to impair reproduction and development in aquatic organisms.
- Its exposure is delayed larval development and pupation time in common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster).
Uses of Bisphenol A :
- BPA polycarbonate plastics are very sturdy in nature and are used to make large variants of microwave-proof utensils.
- It is used as a material for safety glasses, bulletproof windows and helmets.
- Bisphenol A acts as a component in epoxy resins that are very good coating agents and therefore is used for the protective coating of pipelines and to cover the inner surface of food cans.
- It is used in many medical devices such as heart-lung machines, incubators, artificial kidneys, dental fillers, and sealants.
- It is also used as eyewear glasses , due to their optical clarity.
Environmental impacts of Bisphenol A:
- BPA can enter the environment directly through the leaching of chemicals or degradation of materials containing bisphenol A and may render the land unfertile and barren making it unsuitable for agriculture.
- It affects the growth and reproduction of marine life.
- It causes endocrine effects in fish, amphibians, and reptiles.
Adverse effects of Bisphenol A on human health:
- When ingested, the chemical disrupts the endocrine system by interfering with the hormones and affecting the brain and prostate gland of foetuses, infants, and children.
- It can cause high blood pressure, diabetes and cardiovascular disease in adults.
- BPA is a xenoestrogen and mimics estrogen present in the body, thus exhibiting hormone-like properties.
- It can indirectly aid in the spread of vector-borne diseases in humans and animals.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. CAVEAT
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the CJI reprimanded a student for filing a caveat in a petition seeking menstrual leave.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Caveat
- A caveat refers to a “formal notice requesting the court to refrain from taking some specified action without giving prior notice to the person lodging the caveat.”
- The person lodging the caveat is called a “caveator”.
- The term “caveat” is not expressly defined anywhere except in the Calcutta High Court’s 1978 ruling in the “Nirmal Chandra Dutta vs Girindra Narayan Roy” case.
- It is a precautionary measure taken against the grant of probate or letters of administration, as the case may be, by the person lodging the caveat.
- Section 148A of the Civil Procedure Code (CPC) , elaborating upon a caveat was inserted by the Amendment Act of 1976, after the Law Commission’s recommendation.
- Any person can lodge a caveat in a Court.
- The caveator or the person lodging is also required to serve a notice of the caveat by “registered post” to the person on whose plea they are lodging the application
- It was recently used in the “Shailendra Mani Tripathi v. Union of India & Others”, a petition seeking menstrual leave for female students and working women across Indian institutions.
5. BORTHEKERA
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: In recent studies, the medicinal plant commonly called Borthekera in Assamese was found to have cardioprotective potential.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Garcinia pedunculata, commonly called ‘Borthekera’ is a medicinal plant found in Assam.
- The tree is endemic to the south-eastern regions of Asia such as parts of Myanmar and north-eastern parts of India.
- It is traditionally forbidden for raw consumption.
- It has been found to protect from heart diseases.

Uses of Borthekera :
- The administration of the dried pulp of its ripe fruit reduces cardiac hypertrophy indicators, oxidative stress, and heart inflammation.
- The sun-dried slices of the ripe fruit are used for culinary and medicinal purposes and are known to have therapeutic properties like anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, antibacterial, antifungal, antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, nephroprotective, and even neuroprotective activity.
- Borthekera is a rich source of antioxidants.
- In Assam, such slices are used for preparing delicacies like “tengadiyamasor jol” meaning Assamese sour fish curry.


