INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
e-SANJEEVANI
THE CONTEXT: eSanjeevani, Government of India’s National Telemedicine Service, has completed 1.2 crores (120 lakh) consultations rapidly shaping into the country’s most popular and the largest telemedicine service.
ANALYSIS:
- Currently, the National Telemedicine Service is serving daily around 90,000 patients across the country signalling wide adoption by patients as well as doctors, and specialists across the country.
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare’s National Telemedicine Service eSanjeevani is operational through two modes viz. – eSanjeevani AB-HWC (doctor to doctor telemedicine platform) that is based on a hub and spoke model and eSanjeevaniOPD – (patient to doctor telemedicine platform) which provides outpatient services to the citizens in the confines of their homes.
- Andhra Pradesh was the first state to roll out eSanjeevaniAB-HWC services.
ABOUT e-SANJEEVANI
- of India’s eSanjeevani – National Telemedicine Service is plugging the digital health divide that exists in urban and rural India.
- It is addressing the shortage of doctors and specialists at the ground level while reducing the burden on secondary and tertiary level hospitals.
- In line with the National Digital Health Mission, this digital initiative is also boosting the digital health ecosystem in the country.
- It is an indigenous telemedicine technology developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in Mohali. The C-DAC team in Mohali is providing end to end services.
SOURCE: PIB
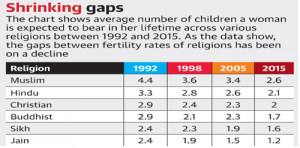
FERTILITY RATES OF HINDUS AND MUSLIMS CONVERGING
THE CONTEXT: According to a new study published by the Pew Research Center, the religious composition of India’s population since Partition has remained largely stable, with both Hindus and Muslims, the two largest religious groups, showing not only a marked decline but also a convergence in fertility rates.
ANALYSIS:
- From 1992 to 2015, the total fertility rates of Muslims declined from 4.4 to 2.6, while that of Hindus declined from 3.3 to 2.1, indicating that the gaps in childbearing between India’s religious groups are much smaller than they used to be.
- The average fertility rate in India today was 2.2, which was higher than the rates in economically advanced countries such as the U.S. (1.6), but much lower than what it was in 1992 (3.4) or 1951 (5.9).
- In terms of absolute numbers, every major religion in India saw its numbers rise. The sole exception to this trend are Parsis, whose number halved between 1951 and 2011, from 110,000 to 60,000.
- More than 99% of people who live in India were also born in India, and migrants leaving India outnumber immigrants three-to-one.
- Religious conversion has also had a negligible impact on India’s overall composition, with 98% of Indian adults still identifying with the religion in which they were raised.
SOURCE: TH
KASTURIRANGAN TO LEAD SYLLABUS PANEL
THE CONTEXT: The Centre has started the process to revise school textbooks by appointing former Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Chairman K. Kasturirangan as the head of a 12-member steering committee responsible for developing a new National Curriculum Framework (NCF).
ANALYSIS:
- Kasturirangan also chaired the drafting committee for the National Education Policy, 2020 which recommended the development of a new NCF.
- The steering committee has been given tenure of three years to complete its task.
- The last such framework was developed in 2005. It is meant to be a guiding document for the development of textbooks, syllabi and teaching practices in schools across the country.
- The subsequent revision of textbooks by the National Council of Educational Research and Training will draw from the new NCF.
- The steering committee will develop four such frameworks, one each to guide the curriculum of school education, teacher education, early childhood education and adult education.
SOURCE: TH
R-VALUE DROPPED BELOW ONE IN MID-SEPTEMBER
THE CONTEXT: According to experts, the R-value, dropped to 0.92 by mid-September after spiralling over one in August-end.
ANALYSIS:
- However, the R-values in certain major cities — Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai and Bengaluru — remained over one. The R-value in Delhi and Pune were below one.
- According to the data, the R-value of Mumbai stood at 1.09, Chennai was 1.11, Kolkata was 1.04, and Bengaluru was 1.06.
- The R-values in Maharashtra and Kerala were below one, giving much-needed relief to these two states with the highest number of active cases.
- The R-value was 1.17 at the end of August. It had declined to 1.11 between September 4 and 7. Since then, it has remained under one.
- The reproduction number or R refers to how many persons an infected person infects on average. In other words, it shows how ‘efficiently’ a virus is spreading.
- According to the Health Ministry, the recovery rate currently stood at 97.75%. The weekly positivity rate (2.08%) had been less than 3% for the last 88 days.
SOURCE: TH
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
22% RISE IN EXPORT OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS
THE CONTEXT: According to the Quick Estimates released by the Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCI&S), the overall export of Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) products has witnessed 21.8 per cent growth in terms of USD during April-August 2021 over the same period of the previous year.
ANALYSIS:
- The huge jump in exports of agricultural and processed food products during the first five months of the current fiscal is in continuation of growth in exports witnessed in the financial year 2020-21.
- According to WTO’s trade map, with the total agri-exports of USD 37 billion in the year 2019, India is ranked at 9th position in the world ranking.
- The export of rice, which recorded a positive growth of 13.7 per cent, increased from USD 3359 million in April-August 2020 to USD 3820 million in April-August 2021.
- As per the Quick Estimates, the exports of fresh fruits & vegetables registered a 6.1 per cent growth in terms of USD, while shipment of processed food products like cereals preparations and miscellaneous processed items reported a growth of 41.9 per cent.
- In April-August 2020-21, fresh fruits and vegetables were exported to the tune of USD 1013 million which rose to USD 1075 million in April-August 2021-22.
- India reported a significant 142.1 per cent jump in the export of other cereals while the export of meat, dairy & poultry products witnessed an increase of 31.1 per cent in the first five months of the current fiscal (2021-22).
- The export of other cereals increased from USD 157 million in April-August 2020 to USD 379 million in April-August 2021 and the export of meat, dairy and poultry products increased from USD 1185 million in April-August 2020 to USD 1554 million in April-August 2021.
- The cashew export witnessed a growth of 28.5 per cent in April-August 2021 as the export of cashew rose from USD 144 million in April-August 2020 to USD 185 million in April-August 2021.
- The rise in export of agricultural and processed food products is because of APEDA’s various initiatives taken for the export promotion of agricultural and processed food products.
SOURCE: PIB
INDIA NOW HAS 10 BLUE FLAG BEACHES
THE CONTEXT: The coveted International eco-label “Blue Flag”, has accorded the Blue Flag Certification for 2 new beaches–Kovalam in Tamil Nadu and Eden in Puducherry beaches.
ABOUT BLUE FLAG CERTIFICATION
- The Blue Flag is one of the world’s most recognised voluntary eco-labels awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators.
- In order to qualify for the Blue Flag, a series of stringent environmental, educational, safety, and accessibility criteria must be met and maintained.
- The Blue Flag Programme for beaches and marinas is run by the international, non-governmental, non-profit organisation FEE (the Foundation for Environmental Education).
- FEE (the Foundation for Environmental Education) was established in France in 1985.
- On the lines of Blue Flag certification, India has also launched its own eco-label BEAMS.
ABOUT BEAMS
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in its pursuit of “Sustainable Development” of the coastal regions of India embarked upon a highly acclaimed & flagship program Beach Environment & Aesthetics Management Services (BEAMS) which is one of the initiatives under the ICZM approach that the MoEF&CC has undertaken for the sustainable development of coastal regions of India, with a prime objective to protect and conserve the pristine coastal and marine ecosystems through holistic management of the resources.
- This was aimed at achieving the globally recognized and coveted International eco-label “Blue Flag”, accorded by the International Jury comprising of members from IUCN, UNWTO, UNEP, UNESCO etc.
- FEE Denmark conducts regular monitoring & audits for strict compliance with the 33 criteria at all times. A waving “Blue Flag” is an indication of 100% compliance to these 33 stringent criteria and sound health of the beach.
- The objective of the BEAMS program is to abate pollution in coastal waters, promote sustainable development of beach facilities, protect & conserve coastal ecosystems & natural resources, and seriously challenge local authorities & stakeholders to strive and maintain high standards of cleanliness, hygiene & safety for beachgoers in accordance with coastal environment & regulations.
SOURCE: PIB
SUPER-HYDROPHOBIC COTTON FOR OIL-SPILL CLEANUP
THE CONTEXT: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Guwahati, have developed a new class of super-hydrophobic cotton composite with Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) that promise marine oil-spill clean-up in near future.
ANALYSIS:
- This is a novel, highly porous and water-repellent super-hydrophobic cotton composite material containing MOF, which can absorb oil selectively from an oil-water mixture.
- The MOF composite has great capability for selective separation of the oils from oil/water mixtures and the separation efficiency lies between 95 per cent and 98 per cent, irrespective of the chemical composition and density of the oils.
- Besides, the MOF composite is also able to absorb large volumes of oils and can be reused a minimum of 10 times so that the sorbents can provide more recovery of the spilt oil.
- The practical applications of this research include cleaning the spilt oil from environmental water (river, sea or ocean water) during oil transportation with high efficiency and large absorption capacity, thus reducing environmental water pollution.
- Both heavy and light oils can be effectively absorbed by the material, which is easy to prepare, cost-effective and recyclable.
- MOFs are a class of compounds containing metal ions coordinated to organic ligands to form 3D structures, with the special feature that they are often highly porous materials that act like a sponge.
SOURCE: DTE
SUPER-HYDROPHOBIC COTTON FOR OIL-SPILL CLEANUP
THE CONTEXT: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Guwahati, have developed a new class of super-hydrophobic cotton composite with Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) that promise marine oil-spill clean-up in near future.
ANALYSIS:
- This is a novel, highly porous and water-repellent super-hydrophobic cotton composite material containing MOF, which can absorb oil selectively from an oil-water mixture.
- The MOF composite has great capability for selective separation of the oils from oil/water mixtures and the separation efficiency lies between 95 per cent and 98 per cent, irrespective of the chemical composition and density of the oils.
- Besides, the MOF composite is also able to absorb large volumes of oils and can be reused a minimum of 10 times so that the sorbents can provide more recovery of the spilt oil.
- The practical applications of this research include cleaning the spilt oil from environmental water (river, sea or ocean water) during oil transportation with high efficiency and large absorption capacity, thus reducing environmental water pollution.
- Both heavy and light oils can be effectively absorbed by the material, which is easy to prepare, cost-effective and recyclable.
- MOFs are a class of compounds containing metal ions coordinated to organic ligands to form 3D structures, with the special feature that they are often highly porous materials that act like a sponge.
SOURCE: DTE
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
INDIA CONSIDERS RECIPROCAL STEPS TO U.K.’S QUARANTINE RULES
THE CONTEXT: India could impose “reciprocal measures” on the United Kingdom if London maintained the current quarantine policy that subjected Indian travellers “irrespective of vaccination status” to a quarantine period lasting 10 days.
ANALYSIS:
- The U.K.’s policy to impose 10 days’ quarantine on people vaccinated with Covishield revealed a gap in that country’s policy regarding vaccines made in India.
- The basic issue is that there is a vaccine, Covishield, which is a licensed product of a U.K. company, manufactured in India.
- The U.K moved India to the ‘Amber list’, taking it away from the ‘Red list’. This opened the British “Visit visas” to Indian travellers “irrespective of vaccination status”.
- However, India has kept tourist visas suspended, which is preventing vaccinated British tourists from entering India.
SOURCE: TH
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
In the terminology related to the COVID-19 pandemic, which of the following best explains the ‘R’ value?
a) How many infected persons have recovered in one-day
b) How many persons are re-infected by the COVID-19 virus on average
c) How many persons an infected person infects on average.
d) How many persons are vaccinated in one day
ANSWER FOR SEPTEMBER 21, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER
RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Answer: C
Explanation:
COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access, abbreviated as COVAX, is a worldwide initiative aimed at equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines directed by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance (Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization, or GAVI), the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Spread the Word



