INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
50,000 RUPEES FOR EACH COVID-19 DEATH
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Home Affairs informed the Supreme Court that the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has recommended the payment of 50,000 Rupees each as ex gratia assistance to the next kin of those who died of COVID-19, including those who succumbed to the virus while involved in relief operations and preparedness activities.
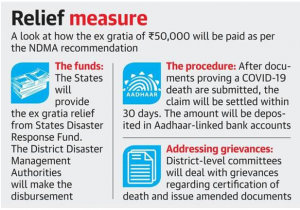
SOURCE: TH
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
WORLD RHINO DAY
THE CONTEXT: The “world’s largest stockpile” of rhino horns was consigned to flames in eastern Assam’s Bokakhat, the headquarters of the Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve, amid Vedic rituals. The event timed with World Rhino Day was aimed at dispelling myths that have driven the illegal horn trade and the poaching of the animal.
ANALYSIS:
-
- Wildlife officials said 2,479 of the 2,623 horns stored in 12 district treasuries since 1979 were burnt in six large iron pyres placed at a stadium in Bokakhat, about 240 km east of Guwahati. These were lit remotely through drones.
INDIAN RHINO VISION 2020 (IRV 2020)
-
- Launched in 2005.
- The initiative was led by the Forest Department, Government of Assam, in partnership with WWF India, International Rhino Foundation.
- The goal of IRV2020 was to increase the rhino population in Assam to 3,000 by establishing populations in new areas.
- Rhinos are now found in four Protected Areas in Assam: Pabitora Wildlife Reserve, Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, Kaziranga National Park, and Manas National Park.
ONE-HORNED RHINOS
-
- Only the Great One-Horned Rhino is found in India.
- Also known as the Indian rhino, it is the largest of the rhino species.
- It is identified by a single black horn and grey-brown hide with skin folds.
- They primarily graze, with a diet consisting almost entirely of grasses as well as leaves, branches of shrubs and trees, fruit, and aquatic plants.
- Conservation status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- CITES Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I.
SOURCE: TH
WHO TIGHTENS GLOBAL AIR QUALITY NORMS
THE CONTEXT: The World Health Organisation (WHO), in its first-ever update since 2005, has tightened global air pollution standards.
ANALYSIS:
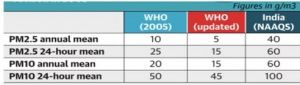
- The move does not have an immediate effect in India as the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) do not meet the WHO’s existing standards.
- The government has a dedicated National Clean Air Programme (launched in 2019) that aims for a 20% to 30% reduction in particulate matter concentrations by 2024 in 122 cities, keeping 2017 as the base year for the comparison of concentration.
- These are cities that do not meet the NAAQS when calculated from 2011 to 2015.
- Every year, exposure to air pollution is estimated to cause 7 million premature deaths.
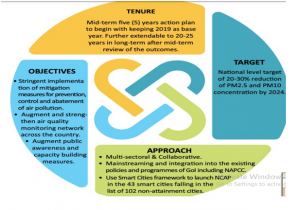
NATIONAL CLEAN AIR PROGRAMME (NCAP)
- The initiatives under NCAP are:
- The National Air Quality Monitoring Network will be augmented.
- Air Quality Management Plan for the cities chosen.
- Indoor Air Pollution Monitoring & Management.
- National Emission Inventory – this is an inventory of the quantity of pollutants discharged into the air.
- Network of Technical Institutions
- Technology Assessment Cell
- International cooperation including the sharing of best practices with respect to the abatement of air pollution.
SOURCE: TH
POSSIBLY EXTINCT
THE CONTEXT: A number of animals and plants have been listed as ‘possibly extinct in the latest edition of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List of Threatened Species. The latest edition of the Red List was released at the recently-concluded World Conservation Congress organised by the IUCN at Marseille, France.
ANALYSIS:
- Among animals, there is the coconut crab, the largest terrestrial arthropod in the world. There are also fish species such as bovany barb, native to the Cauvery river system.
- Other fish that have been declared as possibly extinct include the Deolali minnow, the Deccan barb and the Nilgiri mystus, all of which are found in the Deccan.
- Birds include the Pink-headed duck, which has been feared to be extinct since the 1950s, the Siberian crane, which once famously drew crowds to Keoladeo National Park as well as the Buffy fish-owl or Malay owl.
- The Tentacled butterfly ray, a type of ray and the Dwarf sawfish are two other animal species that are feared to be possibly extinct.
- The Millepora boschmaior fire coral is also possibly extinct.
- There are also species that have been marked as ‘Extinct Post-1500’. The term is taken as a marker to estimate after when the presence/population of the species has declined. Species marked thus have been last assessed in the 1900s post which their presence and updates to their population has not been found.
SOURCE: DTE
INDIAN ECONOMY
INCREASED FDI INFLOWS
THE CONTEXT: FDI Inflows grow 62% during the first four months of the current Financial Year over the corresponding period last year.
ANALYSIS:
- India has attracted a total FDI inflow of US$ 27.37 billion during the first four months of F.Y. 2021-22 which is 62% higher as compared to the corresponding period of F.Y. 2020-21 (US$ 16.92 billion).
- FDI equity inflow grew by 112% in the first four months of F.Y. 2021-22 (US$ 20.42 billion) compared to the year-ago period (US$ 9.61 billion).
- ‘Automobile Industry’ has emerged as the top sector during the first four months of F.Y. 2021-22 with 23% share of the total FDI Equity inflow followed by Computer Software & Hardware (18%) and Services Sector (10%) respectively.
- Under the sector `Automobile Industry’, the majority of FDI Equity inflow (87%) was reported in the state of Karnataka during the first four months of the current financial year (2021-22).
- Karnataka is the top recipient state during the F.Y. 2021-22 (up to July 2021) with a 45% share of the total FDI equity inflows followed by Maharashtra (23%) and Delhi (12%).
SOURCE: PIB
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
MISSION DEPLOYED
THE CONTEXT: Towards enhancing military cooperation with friendly nations, Indian Naval Ship INS Tabar was mission-deployed in international waters for over three months from 13 June 21.
ANALYSIS:
- During the deployment, she made 11 port calls in nine countries of Europe and Africa, traversing nearly 20,000 nautical miles. In all ports, the ship received a warm reception from local officials and was visited by several local dignitaries.
- The ship’s port visits saw various social and professional interactions conducted with the host countries.
- The ship also undertook twelve maritime partnership exercises with foreign navies at sea. These also included prominent bilateral exercises such as Exercise Konkan 21 with the Royal Navy and Exercise Indra-Navy 21 with the Russian Navy.
- These exercises involved wide-ranging and multi-dimensional evolutions covering a diverse range of naval operations. The exercises are deemed to have enhanced interoperability among participating navies and increased the ease with which they can operate together to address shared maritime concerns and threats if required.
- A few of these exercises were maiden engagements, such as that with the Royal Norwegian Navy, the Algerian Navy and the Sudanese Navy.
SOURCE: PIB
COVISHIELD FINE, BUT NOT INDIAN CERTIFICATION: U.K.
THE CONTEXT: In an unexpected move, the United Kingdom added Indian-made Covishield to its list of recognised vaccines, but refused to recognise vaccine certificates given to those administered the vaccine in India.
ANALYSIS:
- The decision, which means Indian travellers to the U.K. will still be subject to 10-day quarantine rules, is expected to further fuel the rift between both countries over what India has called a “discriminatory practice”, and had threatened reciprocal measures against.
SOURCE: TH
THE SAARC MEETING CANCELLED
THE CONTEXT:A meeting of foreign ministers from the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) countries, which was set to be held in New York, has been cancelled. The member states were unable to agree upon the participation of Afghanistan, with Pakistan and India in particular at loggerheads over the issue.
ANALYSIS:
- After Pakistan objected to the participation of any official from the previous Ghani administration, SAARC members reportedly agreed to keep an “empty chair” as a symbolic representation of Afghanistan.
- However, Islamabad later insisted that the Taliban be allowed to send its representative to the summit, a notion that all of the other member states rejected.
- After no consensus could be formed, Nepal, the ‘host’ of the summit, officially cancelled the meeting.
SOURCE: TH
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Which of the following species of rhino are critically endangered?
- Javan rhino
- Sumatran rhino
- One-horned rhino
- Black rhino
- White rhino
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2 and 4 only
d)1, 4 and 5 only
ANSWER FOR SEPTEMBER 22, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT TO ARTICLE)
ANSWER: C
Explanation:
The reproduction number, or R, refers to how many persons an infected person infects on average. In other words, it shows how ‘efficiently’ a virus is spreading
Spread the Word

