ART, CULTURE AND HISTORY
RAJA MAHENDRA PRATAP SINGH
THE CONTEXT: Two years after Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister said Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh had not received the recognition due to him for having donated land for Aligarh Muslim University (AMU) and promised to construct a university in the same city in his name, Prime Minister laid the foundation stone of the university.
ABOUT RAJA MAHENDRA PRATAP SINGH
- Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh was a freedom fighter, revolutionary, writer, social reformer, and internationalist who entered Lok Sabha as an Independent candidate from Mathura in 1957, in an election in which Atal Bihari Vajpayee of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh came fourth.
- Mahendra Pratap established a “Provisional Government of India” in Kabul in the middle of World War I in 1915 and, as the British government targeted him for his activities, based himself in Japan. In 1932, he was nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize.
- The Raja finally returned to India a year before Independence, and immediately began work with Mahatma Gandhi. In free India, he diligently pursued his ideal of Panchayati raj.
- Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh was born into the ruling Jat family of Mursan estate in Hathras in 1886. In 1907, the young Raja proceeded on a world tour with his wife, who was Sikh.
- On his return, the Raja gave up his own residence in Mathura to be converted into a technical school named Prem Mahavidyalaya in 1909. It is said to have been the country’s first polytechnic.
- After studying at the Government School in Aligarh, Raja Mahendra Pratap went to the Muhammadan Anglo-Oriental College in Aligarh, which later came to be called Aligarh Muslim University.
- Although he was unable to complete his graduation from the institution, Raja Mahendra Pratap’s name is counted among the prominent alumni of the university.
- As prominent notables of the area, Mahendra Pratap’s father and grandfather were close to the educationist and reformer Sir Syed Ahmad Khan, the founder of Aligarh Muslim University.
SOURCE: IE
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
DATA ON FARMERS SELLING THEIR PRODUCE IN APMC MANDIS, OPEN MARKET, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
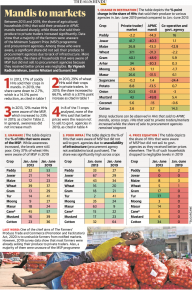
THE CONTEXT: Between 2013 and 2019, the share of agricultural households (HHs) that sold their produce in APMC mandis reduced sharply, while those that sold their produce to private traders increased significantly. Data show that a majority of the farmers were unaware of the Minimum Support Price (MSP) programme and procurement agencies.
SOURCE: TH
INDIAN ECONOMY
FUEL PRICES QUICKEN WPI INFLATION TO 11.39% IN AUGUST
THE CONTEXT: Inflation in wholesale prices resurged to 11.39% in August, staying in the double digits for the fifth month in a row.
ANALYSIS:
- Inflation in manufactured products escalated for the fourth month in a row to 11.4%, as second-order effects of high fuel prices kicked in.
- Fuel and power inflation firmed up to 26.1% in August after a dip in July, even though food price inflation moderated to 3.43% from 4.46%.
- High fuel inflation tends to transmit across sectors as they push up transport, input and wage costs.
- Core WPI inflation, which leaves out fuel and food, hit an all-time high of 11.1%.
ABOUT WHOLESALE PRICE INDEX (WPI)
- Measures inflation at the first stage of transaction i.e. wholesale prices.
- Compiled by: The Office of Economic Advisor, Ministry of Commerce & Industry
- The Wholesale Price Index measures inflation on a year-on-year basis.
- It consists of 3 major groups as below:
| Group | Number of Commodities | Weight |
|
Primary Articles |
117 | 22.62 |
| Fuel & Power | 16 | 13.15 |
| Manufactured Products | 564 | 64.23 |
| TOTAL | 697 | 100 |
SOURCE: TH
GST COUNCIL MAY CONSIDER BRINGING PETROL, DIESEL UNDER GST
THE CONTEXT: The GST Council might consider taxing petrol, diesel and other petroleum products under the single national GST regime, a move that may require huge compromises by both central and state governments on taxing these products.
ANALYSIS:
- GST is being thought to be a solution for the problem of near-record high petrol and diesel rates in the country, as it would end the cascading effect of tax on tax (state VAT being levied not just on the cost of production but also on the excise duty charged by the Centre on such output).
- In June, the Kerala High Court, based on a writ petition, had asked the GST Council to decide on bringing petrol and diesel within the goods and services tax (GST) ambit.
- The sources said bringing petrol and diesel within GST would be placed before the Council for discussion in the light of the court asking the Council to do so.
- When a national GST subsumed central taxes such as excise duty and state levies like VAT on July 1, 2017, five petroleum goods – petrol, diesel, ATF, natural gas and crude oil – were kept out of its purview for the time being.
- This is because both central and state government finances relied heavily on taxes on these products.
- Since GST is a consumption-based tax, bringing petro products under the regime would have mean states where these products are sold get the revenue and not ones that currently derive the most benefit out of them because of they being the production centre.
- Simply put, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar with their huge population and a resultant high consumption would get more revenues at the cost of states like Gujarat.
SOURCE: TH
GLITCHES REMAIN ON THE I-T PORTAL
THE CONTEXT: The Income Tax portal remains a festering worry for taxpayers scrambling to file their returns, ahead of the September 15 deadline set by the Union Finance Minister for the portal’s tech developer, Infosys, to resolve glitches.
ANALYSIS:
- Tax practitioners said a slew of problems still abounds in the return filing modules of the portal. Even routine tasks like seeking an adjournment in ongoing assessments, complying with the ‘Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme and uploading a digital signature, are proving to be a challenge.
- Although the government has extended the deadline for individual taxpayers to file an income tax returns (ITR) till December 31, it is levying a 1% interest for each month of delay beyond the original July 31 deadline, prompting questions about the exchequer penalising them for administrative failures.
- Some glitches still remain to be sorted out even as there has been some ‘gradual improvement’ in the portal’s interface.
- On August 23, after summoning Infosys CEO Salil Parekh, FM had conveyed the government’s ‘deep disappointment with the firm’s handling of the IT portal that has been ineffective and ridden with problems ever since its launch on June 7.
- FM had ‘demanded’ that the issues pertaining to the ‘current functionalities of the portal be resolved by September 15 so that taxpayers and professionals can work seamlessly on the portal.
SOURCE: TH
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
PROPOSED FTA BETWEEN INDIA & UK
THE CONTEXT: India and UK are aiming to launch the negotiations on FTA by November 2021. Two sides looking for an Interim Agreement as a priority and later a Comprehensive Agreement.
ANALYSIS:
- The proposed FTA between India & UK is expected to unlock extraordinary business opportunities and generate jobs. Both sides have renewed their commitment to boosting trade in a manner that benefits all.
- India is committed to the early conclusion of an ambitious, comprehensive and mutually beneficial India UK FTA with an early harvest agreement within an expedited timeframe.
- Interim Agreement to allow both the countries to harvest early gains in some select commodities and services
SOURCE: PIB
Prelim Practice Question
Q1. Consider the following statements about the Wholesale Price Index (WPI):
- It is compiled by National Statistical Office (NSO).
- It calculates the changes in prices of goods and services at the producer level.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR SEPTEMBER 14, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER TO RELEVANT ARTICLES)
Answer: d)
Explanation:
Types of CPI:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW): Compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL): Compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- CPI for Rural Labourer (RL): Compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined): Compiled by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.




