INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
1. DAIRY SAHAKAR SCHEME
THE CONTEXT: Union Minister of Home Affairs and Cooperation launched the “Dairy Sahakar” scheme at Anand, Gujarat, during the function organised by Amul for the celebration of the 75th Foundation Year of Amul.
ABOUT DAIRY SAHAKAR
- The Dairy Sahakar with a total investment of Rs 5000 crore will be implemented by NCDC under the Ministry of Cooperation, the Government of India to realize the vision, “from cooperation to prosperity”.
- Under Dairy Sahakar, financial support will be extended by NCDC to eligible cooperatives for activities such as bovine development, milk procurement, processing, quality assurance, value addition, branding, packaging, marketing, transportation and storage of milk and milk products, exports of dairy products within the overall objectives of “Doubling the farmer’s income” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- There will also be a convergence with various schemes of Government of India and/or of State Government/UT Administration/ Development agencies/ bilateral/multilateral assistance/ CSR mechanism is encouraged
SOURCE: PIB
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
2. G20 ENDS WITHOUT TIME-BOUND PROMISE ON CLIMATE CHANGE
THE CONTEXT: No time-bound agreements were reached as leaders of the world’s top economies ended the summit in Rome, recommitting to providing $100 billion a year to counter climate change, and pushing for greater vaccine equality to fight the COVID-19 pandemic.
THE EXPLANATION:
- G-20 countries also committed to ending international financing for all new coal plants by the end of 2021 but made no mention of domestic commitments on ending coal power generation.
- Amongst the other highlights of the statement was a decision to pursue the recognition of more vaccines by the World Health Organization under a “One Health approach” for the world and providing finances and technology for vaccine production at “mRNA Hubs” in South Africa, Brazil and Argentina, and to mobilize more international public-private financing for “green” projects.
- India pushed for “safeguarding the interests of the developing world” as Prime Minister Narendra Modi addressed the G20 summit at sessions on climate change and sustainable development.
SOURCE: TH
3. INDIAN DATABASE HIGHLIGHTS EMISSIONS GAP
THE CONTEXT: A day ahead of the commencement of COP 26, India has officially endorsed a website ‘Climate Equity Monitor’, made by Indian climate experts, that lists the historical carbon dioxide emissions of developed countries.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The database aims to highlight the disparity between the emissions of developed and developing countries with countries such as the United States, Canada, and Australia and those in Western Europe shown as having a net carbon debt while developing countries such as India and China have net credit.
- Its focus on equity & climate action from a data and evidence-based perspective will encourage vigorous discussion on the crucial issue and engage experts from all nations.
- It is aimed at monitoring the performance of Annex-I Parties under the UNFCCC (developed countries) based on the “foundational principles” of the Climate Convention.
- The performance and policies of the Non-Annex-I Parties (developing countries) will be provided for comparison.
- The website was conceptualised and developed by the Climate Change Group at the M.S. Swaminathan Research Foundation, Chennai, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Department at the National Institute of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru, with other independent researchers.
SOURCE: TH
4. PUNJAB BATS FOR CONSERVATION OF INDUS RIVER DOLPHIN
THE CONTEXT: The census of the Indus river dolphin (Platanista gangetica minor), a freshwater dolphin found in the Beas River, is slated to begin this winter as part of a Centre project. Punjab’s wildlife preservation wing, on the other hand, has gone above and above to conserve not only the dolphins but also their natural habitat.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Indus river dolphin is classified as endangered by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and, until recently, it was believed that these dolphins were endemic to Pakistan.
- But in 2007, a remnant but viable population of Indus dolphins were discovered in Punjab’s Harike wildlife sanctuary and in the lower Beas River.
- The Indus river dolphin was declared the State aquatic animal of Punjab in 2019.
- Alongside research, the importance will be on engaging the riparian communities by encouraging community-led biological monitoring.
- Villages around the hot spot sites of dolphin occurrence will be developed as models for community-led conservation.
- Extension programmes will be held to develop a group of dedicated individuals, called ‘Beas-Dolphin Mitras’ [friends and protectors] of the river Beas.
- The project also will embark on dolphin eco-tourism.
SOURCE: TH
INTERNAL SECURITY
5. NAVY TAKES DELIVERY OF GUIDED-MISSILE DESTROYER VISAKHAPATNAM
THE CONTEXT: The first ship of the four Project-15B state-of-the-art stealth guided-missile destroyers, Visakhapatnam, being built at the Mazgaon Docks Limited (MDL), was delivered to the Navy. Delayed by three years, the ships will be commissioned very soon.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The 163-metre-long warship has a full load displacement of 7,400 tonnes and a maximum speed of 30 knots. The overall indigenous content of the project is approximately 75%,” the Navy said
- The design of the ships has been developed in-house by the Directorate of Naval Design and are a follow on of the Kolkata class (Project 15A) destroyers.
- The four ships are named after major cities from all four corners of the country — Visakhapatnam, Mormugao, Imphal and Surat, the Navy said.
- These ships are equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles and long-range Surface-to-Air missiles (SAM).
- These ships are propelled by four gas turbines in Combined Gas and Gas (COGAG) configuration and have maximum endurance of 4000 nm at an economical speed of 14 knots.
SOURCE: TH
INDIAN ECONOMY
6. PROPOSED AMENDMENT TO ENERGY CONSERVATION ACT 2001
THE CONTEXT: Amidst the growing energy needs and changing global climate landscape, the Government of India has identified new areas to achieve higher levels of penetration of Renewable energy by proposing certain Amendments to Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The objective will be to enhance demand for renewable energy at the end-use sectors such as Industry, buildings, transport etc.
- Ministry of Power has prepared amendments, after consultations with stakeholders. The proposal includes defining the minimum share of renewable energy in the overall consumption by the industrial units or any establishment.
- There will be provision to incentivise efforts on using clean energy sources by means of a carbon saving certificate.
- The proposed amendments would facilitate the development of the Carbon market in India and prescribe minimum consumption of renewable energy either as direct consumption or indirect use through the grid. This will help in the reduction of fossil fuel-based energy consumption and carbon emission to the atmosphere.
- The proposed changes to the EC Act will boost the adoption of clean technologies in various sectors of the economy. The provisions would facilitate the promotion of green Hydrogen as an alternative to the existing fossil fuels used by the industries.
- The additional incentives in the form of Carbon credits against the deployment of clean technologies will result in private sector involvement in climate actions. The proposal also includes expanding the scope of the Act to include larger Residential buildings, with an aim to promote Sustainable Habitat.
SOURCE: PIB
7. GOI IS COMMITTED TO RELEASE FUNDS FOR THE MGNREGA SCHEME
THE CONTEXT: The government of India is committed to release funds for wage and material payments for proper implementation of the Mahatma Gandhi NREGA scheme.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Fund release towards wage and material is a continuous process. There has been increasing of more than 18% of funds allocated for the current financial year in comparison to the previous financial year as a budget estimate. During the current FY, so far more than Rs.63,793 crore funds have been released for the implementation of the scheme in the States/UTs. Currently Rs.8921 crore funds are available which can meet the wage liability equal to this current availability.
- Govt of India is committed to release funds for wage and material payments for proper implementation of the scheme, as per the provisions of the act and guidelines applicable for Central Government as well as State Governments.
- Whenever additional fund is required, the Ministry of Finance is requested to provide the funds. In the previous financial year, the Ministry of Finance allocated Rs.50,000 crore additional funds for the scheme over and above that of BE.
- The provision for unemployment allowances is applicable for the beneficiary who has demanded work and could not be offered the work within 15 days from the date of demand for work.
- All other demands for work where the beneficiary has already completed 100 days in the current financial year or the beneficiary who has demanded the work but died before 15 days of the date of the demand of work shall not be eligible for unemployment allowances.
- The category wise (SC, ST and Others) wage payment system, as made applicable from this current financial year, has been introduced to accurately reflect on the ground flow of funds to various population groups. Its further streamlining is being undertaken.
- According to its own financial statement, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) scheme shows a negative net balance of 8,686 crores.
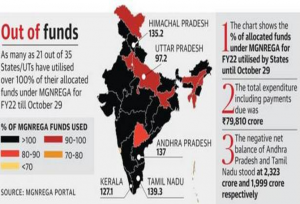
ABOUT MGNREGA
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (Mahatma Gandhi NREGA) provides the guarantee of at least 100 days of wage employment against the demand made by a household in a rural area.
- During the current financial year so far more than 222 crore person-days has been generated. A total of more than 6 crore households have got wage employment during the current financial year against their demand.
- Employment has been offered to 99.63% of the total demand of wage employment and against the offer of employment, a total of 87.35% of beneficiaries has turned up for work as per their will.
SOURCE: PIB
8. LAKHPATISHG WOMEN
THE CONTEXT: Ministry of Rural Development launched an initiative to enable rural SHG women to earn at least Rs.1 lakh per annum.
THE EXPLANATION:
- For the realization of this ambitious goal, the Ministry has envisioned livelihood support to 25 million rural SHG women in the next 2 years. Based on various models existing across the country.
- Over the years this money borrowed by SHGs through bank capitalization support is now being used for creating diversified livelihood opportunities. While all these efforts are yielding positive transformation, it is realized that for ensuring sustainable livelihoods and dignified life of women SHG members, there is a need to make a concerted effort for ensuring at least INR 1,00,000 income per annum for the household i.e. enabling them to become a Lakhpati. The figure of Rs 1 lakh is both aspirational and inspirational for rural SHG women.
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana is a flagship scheme of the Ministry of Rural Development organizing the rural poor into self-governed institutions with a focus on building capacity and creating diversified livelihood opportunities for Rural Poor Women.
- The mission has made successful strides through the Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana bringing focus on the role of women as farmers. Moving from the phase of community mobilization and building institutions of women, now the focus is on envisaging SHG women in higher-order economic activities through producer groups, FPOs and producer companies.
SOURCE: PIB
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
9. EX YUDH ABHYAS
THE CONTEXT: The 17th Edition of Indo-US joint exercise “Ex Yudh Abhyas 2021”, the joint military training between Indian and the US Armies concluded at Joint Base Elmendorf Richardson, Alaska on 29 October 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The aim of this 14-day exercise was to familiarise each other with operational procedures, combat drills and developing inter-operability.
- The Indian contingent comprised 350 personnel of an Infantry Battalion group of the MADRAS Regiment while the US contingent consisted of 300 soldiers of the First Squadron (Airborne) of the 40th Cavalry Regiment.
- The exercise was conducted in two phases. The first phase comprised combat conditioning and tactical training by both the contingents. Training received by both contingents in the first phase was put into practice in the validation stage.
- Both contingents jointly took part in the validation exercise which comprised combat shooting, rappelling and helicopter-based mobilization of quick response teams.
- The troops were organized into composite companies with mixed platoons of Indian and US Armies and the validation exercise culminated in a raid on an enemy position in mountainous terrain and securing of critical infrastructure.
- The two Armies have gained from each other’s expertise and experience in the conduct of platoon and company level operations. The exercise has strengthened mutual confidence, inter-operability and enabled sharing of best practices between the two contingents.
SOURCE: PIB
10. PRIME MINISTER’S MEETING WITH PRIME MINISTER OF SPAIN
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi met H.E. Mr. Pedro Sanchez, Prime Minister of Spain on the sidelines of the G20 Summit in Rome on 31 October 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The two leaders welcomed the growing bilateral trade and investment linkages including the recent signing of the contract to procure 56 C295 aircrafts from Airbus Spain, 40 of which will be ‘Made in India’ in collaboration with Tata Advanced Systems.
- They agreed to further expand bilateral cooperation in new areas like e-mobility, clean tech, advanced materials and deep sea exploration.
- PM Modi invited Spain to invest in various sectors including Green Hydrogen, infrastructure and defence manufacturing and further take advantage of India’s National Infrastructure Pipeline, Asset Monetization Plan and the Gati Shakti Plan.
- The two leaders discussed India-EU relations as well as cooperation on climate action and priorities at upcoming COP26.
- They also exchanged views on regional and global issues of mutual interest including Afghanistan and the Indo-Pacific.
- PM Modi looks forward to welcoming PM Sanchez to India next year.
SOURCE: PIB
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q1 Consider the following statements about the Indus dolphins:
- It is classified as endangered species by IUCN.
- It is found in India only in the Sutlej River.
- It is declared as the state aquatic animal of Punjab.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
ANSWER FOR OCTOBER 30, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q1. Answer: C
Explanation:
A conjugate vaccine is a type of vaccine which combines a weak antigen with a strong antigen as a carrier so that the immune system has a stronger response to the weak antigen.
Spread the Word
