Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Sokoto (North-Western State of Nigeria):
-
- Location & geography:
- Situated in north-western Nigeria, bordering Niger Republic
- Lies in the Sudano-Sahelian zone; semi-arid climate
- Drained mainly by the Sokoto–Rima river system (tributary of Niger River)
- Historical significance:
- Core area of the Sokoto Caliphate founded by Usman dan Fodio (1804)
- Major centre of Islamic reform and scholarship in West Africa
- Political & administrative status:
- One of Nigeria’s 36 states; capital: Sokoto city
- Ruled traditionally by the Sultan of Sokoto, a key Islamic authority
- Socio-economic features:
- Economy based on subsistence agriculture and livestock
- Key crops: millet, sorghum, rice
- Low industrialisation: human development indicators remain weak
- Security situation:
- Affected by banditry, kidnapping and armed violence in NW Nigeria
- Part of wider Sahelian insecurity spillover impacting governance
- Environmental issues:
- Facing desertification, land degradation and water stress
- Climate change intensifying Sahel expansion southwards
- Location & geography:
(TH)
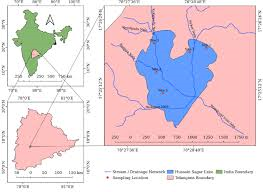
Hussain Sagar Lake (Hyderabad):
-
- Location:
- Artificial lake located between Hyderabad and Secunderabad
- Lies on the Musi River basin (tributary of Krishna)
- Origin & history:
- Constructed in 1563 by Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah
- Built primarily for water supply to Golconda
- Physical nature:
- Artificial lake, not natural
- One of Asia’s largest artificial lakes by surface area
- Cultural landmark:
- Hosts the Buddha Statue of Hyderabad at its centre
- Important urban heritage and tourism site
- Ecological status:
- Declared a National Lake under NLCP (National Lake Conservation Plan)
- Suffers from eutrophication, sewage inflow and industrial pollution
- Environmental concerns:
- Frequent fish deaths due to low dissolved oxygen
- Linked to urbanisation, untreated sewage and nutrient loading
- Administrative efforts:
- Managed by Telangana State Government with central support
- Pollution control via STPs, lake rejuvenation projects
- Location:
(TH)
Defence & Security
INSV KAUNDINYA:
-
- The Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Kaundinya commenced its maiden overseas voyage from Porbandar (Gujarat) to Muscat (Oman) on 29 December 2025.

-
- Constructed by & nature:
- INSV Kaundinya is an indigenously built traditional stitched sailing vessel of the Indian Navy.
- It employs traditional shipbuilding techniques using natural materials, inspired by historical maritime practices.
- Flag-off & diplomatic presence:
- The vessel was formally flagged off by Vice Admiral Krishna Swaminathan, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Western Naval Command.
- The Ambassador of the Sultanate of Oman to India was present, highlighting the event’s diplomatic significance.
- Historical maritime heritage:
- The voyage retraces ancient maritime routes that historically connected the western coast of India with the Arabian Peninsula — facilitating trade, cultural exchange and civilisational interaction.
- Strategic & Cultural Significance:
- Maritime Diplomacy: Reinforces India–Oman relations and enhances people-to-people ties.
- Heritage Revival: Showcases India’s maritime heritage, indigenous seamanship and traditional navigation skills.
- Naval Outreach: Demonstrates the Indian Navy’s role in cultural diplomacy and regional cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Constructed by & nature:
(PIB)
Pinaka Long Range Guided Rocket:
-
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) conducted the maiden flight test of the Pinaka Long Range Guided Rocket (LRGR 120) on 29 December 2025 at the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The rocket successfully demonstrated all planned in-flight manoeuvres and hit the target with textbook precision.
- Key features & technology:
- Indigenously Developed: Designed by the Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in collaboration with:
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL)
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL)
- Research Centre Imarat (RCI)
- Flight trial was coordinated by ITR and Proof & Experimental Establishment.
- Range & Capabilities:
- Maximum range: ~120 km
- Demonstrated precision guidance and control in flight.
- Launched from the existing Pinaka launcher, showcasing multi-range capability from a common platform.
- Strategic significance:
- Boosts India’s rocket artillery and guided munitions capabilities.
- Enhances accuracy and lethality of the Pinaka system, a critical element of Army artillery modernization.
- Adds to networked and precision strike capability under modern battlefield requirements.
- Policy & defence impact:
- Supports Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat goals in defence technology.
- Reinforces indigenous defence research strength and reduces dependency on foreign suppliers.
- Viewed as a game-changer by Raksha Mantri for augmenting battlefield effectiveness.

(PIB)
Spread the Word



