International Developments
Second World Summit for Social Development in Doha (4–6 Nov 2025):
-
- First held in Copenhagen, Denmark (1995), organized by the United Nations.
- Focuses on three core goals:
1. Eradication of poverty,
2. Full and productive employment, and
3. Social integration/inclusion.
-
- It led to the Copenhagen Declaration and Programme of Action, forming the global framework for social development.
- Since 2011, India has lifted around 248 million people out of multidimensional poverty, reducing the share of people below the international poverty line to 2.3% in 2022-23.
- India’s social security coverage has increased from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, covering over 940 million citizens, aided by the JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile) architecture.
- During the summit, India will host a side-event through NITI Aayog on “Pathways Out of Poverty: India’s Experience in Empowering the Last Mile”.
- On the sidelines, bilateral meetings will be held with ministers from Qatar, Romania, Mauritius, the EU and with the International Labour Organization Director-General to strengthen cooperation on labour mobility, skilling, employment and social protection.
(TH)
High Seas Treaty (UN Treaty on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction – BBNJ):
-
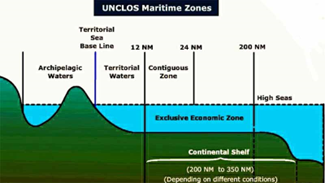
- Officially called the United Nations Treaty on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ).
- Adopted in 2023 under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Aims to protect biodiversity in the high seas (areas beyond national jurisdiction, covering about 60% of the ocean).
- The “common heritage principle” supports equitable access and benefit-sharing of marine resources for all.
-
- Focuses on marine genetic resources, area-based management tools (e.g., marine protected areas), environmental impact assessments, and capacity-building & technology transfer.
- Seeks to balance conservation and sustainable use while ensuring equitable sharing of benefits from marine resources.
- India is a signatory and actively supports sustainable high seas governance in line with its maritime interests.
(TH)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
International Day for Biosphere Reserves:
-
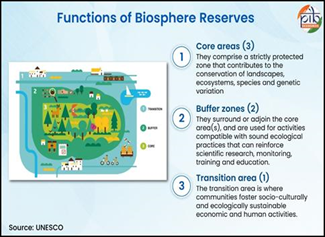
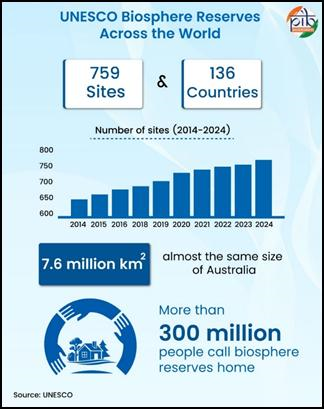
- Context: On November 3, the world observes the International Day for Biosphere Reserves. Designated by UNESCO.
-
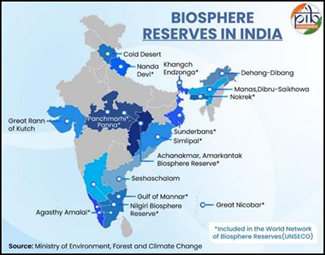
- India has 18 notified Biosphere Reserves covering around 91,425 sq km; out of these, 13 are recognised by UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
- The scheme for these reserves is implemented by Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change under a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with cost-sharing: 60: 40 (Centre: States) generally, and 90:10 for North-Eastern & Himalayan states.
- The budget for biodiversity conservation under this scheme has doubled from ₹5 crore in 2024-25 to ₹10 crore in 2025-26, indicating increased focus.
- India ranks 9th globally in total forest area and 3rd in annual forest gain according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) 2025 assessment.
- The reserves serve as “living laboratories” where biodiversity conservation is linked with community welfare, sustainable livelihoods, and integration with national initiatives like Project Tiger, Project Elephant and the Green India Mission.
- In 2025, India’s new addition to the network: the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve (Himachal Pradesh) got included in UNESCO’s WNBR, highlighting India’s enhanced global role in conservation.
(TH)
Science & Technology
NITI Aayog Unveils ‘Reimagining Agriculture: A Roadmap for Frontier Technology Led Transformation’”:
-
- NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub launched a roadmap called “Reimagining Agriculture: A Roadmap for Frontier Technology Led Transformation” in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- The roadmap aims to harness frontier technologies such as climate-resilient seeds, digital twins, precision agriculture, agentic AI, and advanced mechanisation, to enhance productivity, sustainability and incomes in agriculture.
- Farmers are segmented into three archetypes: “Aspiring”, “Transitioning”, and “Advanced”, so that solutions can be tailored to their specific needs (from smallholders to commercial cultivators).
- The vision links this transformation with the broader ambition of achieving a “Viksit Bharat by 2047”.
- The roadmap was developed in collaboration with knowledge-partners like Boston Consulting Group (BCG), Google and Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), and with inputs from industry and academia.
(TH)
History, Art & Culture
Ramman:
-
- Context: President Murmu presented with a Ramman mask.
- Ramman is a traditional festival held annually in late April (during Baisakhi) in the twin villages of Saloor-Dungra in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli district.
- It is dedicated to the local deity Bhumiyal Devta, whose temple is central to the celebrations.
- The festival features theatrical enactments (including portions of the Ramayana and local legends), masked dances (18 distinct Himalayan birch/Bhojpatra masks), songs, and rituals.
- In 2009, UNESCO recognized Ramman as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, noting how it combines theatre, music, myth and community identity.
- The origin is medieval, drawing on Vaishnavite traditions, and over time it has incorporated local folklore (e.g., dances depicting buffalo-herders’ journeys, trader-couple episodes) beyond the purely Ramayana narrative.
- The performance also reflects local social hierarchies and connections between nature, community and the divine (for example, offering sprouted seeds as part of ritual for prosperity of agriculture and forest produce)

(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. With reference to the Ramman Festival, consider the following statements:
1. It is celebrated in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
2. The festival has been inscribed by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
3. Both men and women perform the ritual dances wearing Bhojpatra (Himalayan birch) masks.
How many of the above statements are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) All three
d) None
Answer: B
Explanation: Only 1 and 2 are correct. The dances are performed by men, not women, and the masks are traditionally worn by male performers from specific castes.
Q2. With reference to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR), consider the following statements:
1. It is a UNESCO‑led initiative under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
2. India has 18 notified Biosphere Reserves all of which are recognized under the WNBR.
3. The Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in Himachal Pradesh is the latest Indian addition to the UNESCO WNBR.
4. Biosphere Reserves serve as “living laboratories” linking biodiversity conservation with community welfare and sustainable livelihoods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B
Explanation: Not all Indian Biosphere Reserves are recognized by UNESCO; currently, 13 out of 18 are part of the WNBR. The Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve is the latest addition.
Q3. Consider the following statements regarding the World Summit for Social Development:
1. It is a United Nations initiative aimed at promoting poverty eradication, full employment, and social integration globally.
2. Doha hosted the first World Summit for Social Development in 1995.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Explanation: The first summit was held in Copenhagen, Denmark (1995).
Q4. Which of the following statements are correct with reference to the High Seas Treaty (BBNJ)?
1. It was adopted under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
2. The treaty focuses on marine genetic resources and area-based management tools.
3. The treaty applies only to coastal waters under national jurisdiction.
4. India is not a signatory.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2, 3, and 4 only
c) 1, 2 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A
Explanation: The treaty does not apply to waters under national jurisdiction, it only governs areas beyond national jurisdiction (high seas). India is a signatory.
Spread the Word



