International Developments
African Union:
-
- Context: The African Union said it was suspending Madagascar “with immediate effect” after a coup saw an elite Army unit seize power following President Andry Rajoelina’s impeachment.
- The African Union (AU) is a continental organization established in 2002, replacing the Organization of African Unity (OAU), and includes all 55 countries of the African continent.
- Its primary aims are to promote unity, solidarity, and cooperation among African states; defend their sovereignty and territorial integrity; advance economic and political integration; and represent African interests on the global stage.
- Key objectives include promoting peace, security, and stability, encouraging democracy and good governance, protecting human rights, advancing sustainable development, and fostering science, technology, and innovation across Africa.
- The institutional structure of the AU comprises:
- Assembly of Heads of State and Government (supreme decision-making body)
- Executive Council (Foreign Ministers)
- Permanent Representatives Committee
- Peace and Security Council
- AU Commission (Secretariat)
- Pan-African Parliament
- It also has judicial and advisory bodies, such as the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights, the AU Advisory Board on Corruption, and the African Commission on International Law.
- It promotes citizen participation and civil society engagement through the Pan-African Parliament and the Economic, Social and Cultural Council (ECOSOCC).
- The headquarters of the AU are in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- The AU’s long-term vision, Agenda 2063, seeks to build an integrated, peaceful, and prosperous Africa, driven by its own citizens.
- Plans for continental financial institutions include the establishment of an African Central Bank, African Investment Bank, and African Monetary Fund.
- The Regional Economic Communities (RECs) and the African Peer Review Mechanism (APRM) form integral components of the AU’s governance and integration framework.
(TH)
India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
-
- It was announced in September 2023 during the G20 Summit in New Delhi, with various leaders of the EU, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia etc. endorsing the initiative.
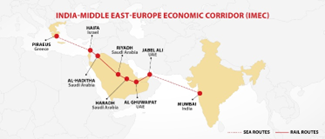
- The IMEC visualises the upgradation of maritime connectivity between India and the Arabian Peninsula, as well as high-speed trains running from the ports in the UAE to the Haifa port in Israel through Saudi Arabia and Jordan.
- The goods transported on these networks would be shipped to and from European countries.
- Additionally, the IMEC seeks to build a clean hydrogen pipeline, an electricity cable, a high-speed undersea digital cable and consolidate existing infrastructure such as ports.
- Members: India, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Jordan, Israel, and the European Union (including key European nations like Italy, France, and Germany).
- Purpose: To enhance connectivity and trade between India, the Middle East, and Europe through multimodal transport (ship–rail–road link).
- Structure:
- Eastern Corridor: Connects India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connects the Arabian Gulf to Europe.
- Objective: Promote economic integration, reduce transit time, strengthen energy and digital connectivity, and counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Key Components:
- Rail and shipping networks
- Energy pipelines (including green hydrogen)
- Digital and data connectivity infrastructure
- Strategic Importance: Strengthens India’s role in global supply chains and enhances strategic cooperation with the Middle East and Europe.
(TH)
Defence & Security
FIFTH EDITION OF EXERCISE ‘SAMUDRA SHAKTI’ – 2025:
-
- Indian Navy is hosting the fifth edition of the Indo-Indonesian Joint Bilateral Maritime Exercise, ‘Samudra Shakti – 2025’ , at Visakhapatnam from 14 – 17 Oct 2025.
- The participating units include INS Kavaratti, an Anti-Submarine Warfare Corvette of Eastern Fleet under the aegis of Eastern Naval Command (ENC) and the Indonesian Navy Ship KRI John Lie, a Corvette (with an integral helicopter).
- Exercise ‘Samudra Shakti’ is a key bilateral engagement aimed at enhancing interoperability, strengthening mutual understanding, and sharing best practices between the two navies. The exercise highlights shared commitment of both nations towards maintaining stability and peace in the Indo-Pacific region.
(PIB)
India’s legal provisions on refugees and infiltration:
-
- Till the end of March 2025, apart from the Citizenship Act 1955 and the Passports Act 1967, three laws (the Foreigners Act, 1946, the Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939 and the Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920) were applied to deal with foreign nationals, including refuge seekers.
- From April, the Immigration and Foreigners Act replaced the three pre-Independence laws and subsumed the Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000.
(PIB)
Captions and Quotations
Ethics:
-
- When loyalty is transferred from ideas to personalities, democracy weakens and authoritarianism strengthens.
- R. Ambedkar, in his historic speech to the Constituent Assembly on November 25, 1949. – “The second thing we must do is to observe the caution which John Stuart Mill has given to all who are interested in the maintenance of democracy, namely, not ‘to lay their liberties at the feet of even a great man, or to trust him with power which enable him to subvert their institutions.’
- Bhakti in religion may be a road to the salvation of the soul. But in politics, Bhakti or hero-worship is a sure road to degradation and to eventual dictatorship.”
- Merciless criticism and independent thinking are the two necessary traits of revolutionary thinking.
- Leaders can and should be admired for their vision, their achievements, and their service. But admiration must not curdle into devotion. The republic’s health depends on the vigilance of its citizens and the strength of its institutions.
(TH)
Polity:
-
- Urban India generates nearly two-thirds of the national GDP, yet its municipalities control less than one per cent of the country’s tax revenue.
- Municipalities in India shows a peculiar inversion of democracy — where power is centralised and responsibility decentralised.
- India must democratise the fiscal contract.
(TH)
Geography:
-
- India’s ambition to be a global leader in clean energy and sustainable growth depends on securing critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt and Rare Earth Elements (REEs).
(TH)
Important data/facts
Economy
-
- In 2022, mining contributed just 2.5% to India’s GDP, compared to 13.6% in Australia.
- India generates close to four million metric tonnes of e-waste annually, yet only 10% is formally recycled.
(TH)
Defence & Security
-
- At the end of June 2023, the population of refugees or persons of concern in India was over 2.11 lakh (also counting those from Myanmar, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Africa and West Asia).
(TH)
Miscellaneous
Sports:
-
- Commonwealth Games: The Executive Board (EB) of Commonwealth Sport on Wednesday recommended Ahmedabad as the proposed host city for the 2030 Centenary Commonwealth Games.
- Ahmedabad, which is also in the race to bid for the 2036 Olympics, and Nigerian capital Abuja had submitted their proposals to host the 2030 Games.
(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. With reference to the Commonwealth Games, consider the following statements:
1. The first Commonwealth Games were held in Hamilton, Canada in 1930.
2. India has hosted the Commonwealth Games only once since its inception.
3. The Commonwealth Games are held every four years and involve only countries that were formerly part of the British Empire.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – The first Commonwealth Games (then called the British Empire Games) were held in Hamilton, Canada in 1930.
Statement 2 is correct – India has hosted the Games only once, in 2010 (New Delhi).
Statement 3 is incorrect – The Games are held every four years, but participation is not limited to countries formerly under the British Empire; it includes all Commonwealth member nations, some of which were not part of the Empire.
Q2. With reference to the African Union (AU), consider the following statements:
1. The African Union replaced the Organization of African Unity (OAU) in 2002.
2. The headquarters of the African Union are located in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
3. The Pan-African Parliament serves as the AU’s principal judicial body.
4. Agenda 2063 is the AU’s long-term vision for an integrated and prosperous Africa.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2 and 4 only
c) 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: AU was established in 2002, replacing the OAU.
Statement 2 is correct: The headquarters are in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Pan-African Parliament is a deliberative body, not a judicial one; the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights serves the judicial function.
Statement 4 is correct: Agenda 2063 outlines the AU’s development blueprint for a peaceful and prosperous Africa.
Q3. With reference to the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), consider the following statements:
1. The IMEC was announced during the 2023 G20 Summit held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
2. The Corridor aims to connect India with Europe through multimodal transport including rail, road, and shipping links.
3. One of the key objectives of IMEC is to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
4. The Eastern Corridor of IMEC connects the Arabian Gulf to Europe.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) Only three
d) All four
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: IMEC was announced at the G20 Summit in New Delhi (2023), not Riyadh.
Statement 2 is correct: The project indeed seeks multimodal connectivity between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Statement 3 is correct: A major strategic aim is to counter China’s BRI influence.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The Eastern Corridor connects India to the Arabian Gulf, while the Northern Corridor connects the Arabian Gulf to Europe
Q4. Recently, Executive Board (EB) of Commonwealth Sport recommended which of the following cities as host city for the 2030 Centenary Commonwealth Games?
a) Delhi
b) Ahmedabad
c) Kolkata
d) Hyderabad
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Executive Board (EB) of Commonwealth Sport recommended Ahmedabad as the proposed host city for the 2030 Centenary Commonwealth Games. Ahmedabad is also in the race to bid for the 2036 Olympics.
Q5. recently, the Exercise ‘Samudra Shakti’ – 2025 was held at Visakhapatnam between Naval forces of –
a) India and Indonesia
b) India and Singapore
c) India and Sri Lanka
d) India and Bangladesh
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Indian Navy is hosting the fifth edition of the Indo-Indonesian Joint Bilateral Maritime Exercise, ‘Samudra Shakti – 2025’, at Visakhapatnam from 14 – 17 Oct 2025.
- The participating units include INS Kavaratti, an Anti-Submarine Warfare Corvette of Eastern Fleet under the aegis of Eastern Naval Command (ENC) and the Indonesian Navy Ship KRI John Lie, a Corvette (with an integral helicopter).
- Exercise ‘Samudra Shakti’ is a key bilateral engagement aimed at enhancing interoperability, strengthening mutual understanding, and sharing best practices between the two navies. The exercise highlights shared commitment of both nations towards maintaining stability and peace in the Indo-Pacific region.




