Economy
Samudra se Samriddhi:
-
- Prime Minister inaugurated and laid the foundation stone for development projects in Bhavnagar, Gujarat, focusing heavily on maritime and port-led infrastructure.
- Major highlights include the inauguration of Mumbai International Cruise Terminal, expansion projects at key ports (Kolkata, Paradip, Kandla, Ennore, Chennai, Car Nicobar), and new ship repair facilities, all forming part of national maritime advancement.
- A historic policy reform was announced: large ships have been granted infrastructure status, enabling shipbuilding companies to access easier financing and reduced interest rates, strengthening India’s competitiveness in global shipping.
- PM emphasized reducing India’s dependence on foreign shipping; currently, 95% of India’s trade is conducted via foreign ships, with around $75 billion paid annually for shipping services, nearly equal to India’s defence budget.
- He stated that a robust ship-breaking ecosystem is emerging in the region, with the Alang Ship Breaking Yard serving as a prime example.
- Next-generation reforms in the maritime sector will establish ‘One Nation, One Document’ and ‘One Nation, One Port’ processes, simplifying procedures and port governance nationwide.
- India aims to triple its share in global sea trade by 2047; port capacity has doubled in the past decade, and deep-water container trans-shipment ports and the mega Vadhavan Port project are driving this expansion.
Vadhavan Port Project is an upcoming deep-draft, greenfield port near Dahanu, Maharashtra, designed to become one of the world’s top ports, significantly increasing India’s container handling capacity by 23.2 million TEUs and boosting its maritime trade. Jointly developed by the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and the Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB) under PM Gati Shakti program and Sagarmala program, it is a key initiative for India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
-
- A world-class maritime museum is under development at Lothal to celebrate India’s ancient maritime heritage.
- PM stressed the need for ‘Atmanirbharta’ (self-reliance) across sectors, urging that “both chips and ships are to be made in India for future prosperity”.
(PIB)
Launch of LEADS 2025:
-
- Government launched Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2025 in New Delhi to benchmark logistics performance across Indian States and Union Territories, supporting the Make in India initiative.
- LEADS 2025 introduces performance assessments of key transport corridors and API-enabled evaluation of section-wise road speeds, enabling sharper analysis for logistics improvements.
- The initiative aims to reduce logistics costs, strengthen infrastructure, and boost India’s global manufacturing competitiveness, advancing the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat and Viksit Bharat by 2047.
(PIB)
Launch of the Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) 3.0:
-
- Government launched IPRS 3.0 to benchmark and improve industrial parks, strengthening the Make in India initiative.
- IPRS 3.0 features an expanded framework with new parameters, including sustainability, green infrastructure, logistics connectivity, digitalization, skill linkages, and tenant feedback.
- Industrial parks will be rated as Leaders, Challengers, or Aspirers, helping investors with credible information and promoting healthy competition among States and Union Territories.
- It aims to attract investments, generate employment, and position India as a more sustainable and globally competitive destination for industry.
(PIB)
Polity
Article 200 of the Constitution:
-
- It lays down that when a Bill, passed by a State Legislature, is presented to the Governor for his/her assent, he/she has four alternatives:
a). may give assent to the Bill
b). may withhold assent to the Bill, that is, reject the Bill in which case the Bill fails to become law
c). may return the Bill for reconsideration of the State Legislature; or
d). may reserve the Bill for the consideration of the President.
(TH)
Art and culture
Tripura Sundari Temple (Tripura):
“The Northeast is the most diverse region of our diverse nation. The North East is a complete package for tourism.” PM Narendra Modi -Rising North East Investors Summit 2025.
-
- The Tripura Sundari Temple in Udaipur town, Tripura, one of the 51 Shakti Peethas, was inaugurated after major redevelopment on September 22, 2025, under the PRASHAD scheme by PM Modi.
- The PRASHAD (Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive) scheme aims to rejuvenate pilgrimage sites by upgrading facilities, improving connectivity, and fostering local economic growth through heritage-led development.
- The temple, built in 1501 AD by Maharaja Dhanya Manikya, is architecturally unique, a square plan resembling Bengal huts and a tortoise-shaped base (Kurma Pith), symbolizing auspiciousness in Hindu tradition.
- The temple serves as a symbol of syncretism, involving diverse communities and uniting various faiths, and remains a cultural and social cornerstone for Tripura.
- The broader impact includes rising tourism, improved local livelihoods, growing employment (young guides, homestays), and strengthening Tripura’s place on India’s spiritual tourism map, following similar PRASHAD-driven projects across Northeast India.

(PIB)
International Developments
$100,000 entry fee on H-1B visas:
-
- The new $100,000 fee applies only to new H-1B visa applicants entering the US after September 21, 2025, and does not apply to current visa holders extending or changing status within the US.
- Existing H-1B visa holders traveling abroad and re-entering are currently not impacted by this fee, but some legal ambiguities remain and may be clarified with time.
- The fee may be charged annually each time the visa holder travels out and re-enters the US, but exact payment details remain unclear.
- F-1 students in the US applying for H-1B status change are exempt from the fee; however, those outside the US getting selected in the H-1B lottery will face this fee.
- The move aims to curb perceived abuses of the H-1B program and promote hiring US workers but has caused significant concern among Indian tech workers and companies.
- Major visa categories relevant to Indian applicants for tourism, study, work, business, and specialized purposes as of 2025 are as follows:
| Visa Type | Purpose/Description |
|---|---|
| B-1 | Business visitors for conferences, meetings, negotiations |
| B-2 | Tourist visitors |
| F-1 | Students pursuing academic studies in the US |
| H-1B | Temporary skilled workers (professional employment) |
| L-1 | Intracompany transferees (executives, managers, specialized workers) |
| O-1 | Individuals with extraordinary ability or achievement (artists, scientists, athletes, entrepreneurs) |
| J-1 | Exchange visitors including students, trainees, au pairs |
| E-1/E-2 | Treaty traders and investors from treaty countries |
| M-1 | Vocational or non-academic students |
| K-1 | Fiancé(e)s of US citizens |
| R-1 | Religious workers |
| TN | NAFTA professionals (not applicable for Indians, mainly Canada/Mexico) |
(PIB)
Science & Technology
Smog-eating technology:
-
- Smog-eating technology uses materials infused with titanium dioxide (TiO2) that act as photocatalysts activated by sunlight or UV light to chemically break down harmful air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), which cause smog.
- This technology is applied in urban infrastructure, such as roads, pavements, building facades, tiles, and coatings, turning these surfaces into active agents that neutralize smog.
- When exposed to sunlight, TiO2 generates hydroxyl radicals and superoxides that oxidize smog components into less harmful substances like nitrates, which are then washed away by rain, improving air quality.
- Smog-eating concrete and tiles not only reduce pollution but also offer structural benefits like improved compressive strength compared to conventional materials.
- The technology is seen as a promising and cost-effective solution to reduce urban air pollution, especially in heavily congested cities prone to smog, helping mitigate health risks associated with poor air quality.
- Field trials and large-scale implementation are underway in various cities globally, including pilot projects in Delhi and other metropolitan areas.

(TH)
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM):
-
- The NSM is a flagship initiative launched by the Government of India in 2015 to boost the country’s high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities and promote self-reliance in supercomputing technology.
- It is jointly steered by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) and implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune, and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
- The mission aims to install a grid of over 70 high-performance computing facilities across academic and research institutions nationwide, connected through the high-speed National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- NSM supports diverse research domains including climate modelling, weather prediction, aerospace engineering, computational biology, disaster management, drug discovery, and material science.
- The mission emphasizes indigenization, moving from assembling supercomputers domestically to fully designing and manufacturing key components in India, aiming for complete self-reliance.
- Human resource development is a key focus with five dedicated HPC training centers to cultivate skilled professionals in supercomputing and artificial intelligence.
- As of March 2025, 34 supercomputers with a combined capacity of 35 petaflops have been deployed under NSM, benefiting over 10,000 researchers and facilitating more than 1 crore compute jobs with high utilization rates.
- NSM strengthens India’s position in global supercomputing and supports strategic sectors including national security and advanced scientific research.
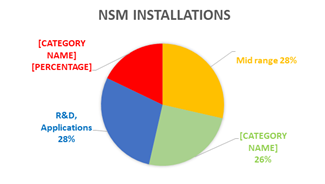
(TH)
Defence News
Maiden bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and Hellenic (Greek) Navy:
-
- The first bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and Hellenic Navy was conducted in the Mediterranean Sea from 13 to 18 September 2025, featuring INS Trikand from India.
- The exercise included a harbour phase at Salamis Naval Base with cross-deck visits, professional interactions, and cultural exchanges, and a sea phase with complex joint manoeuvres such as night VBSS, anti-submarine warfare, and coordinated gun firing.
- This exercise marked a milestone in India-Greece defence cooperation by enhancing interoperability, sharing best practices, and reinforcing shared interests in maritime security and free navigation.
(PIB)
MiG-21 fighter jets:
-
- The MiG-21 is a supersonic, single-seat, delta-wing fighter aircraft originally developed by the Soviet Union and first introduced in 1960.
- It is capable of speeds over Mach 2 (about 2,200 km/h) with a service ceiling around 57,000 feet and a rapid climb rate, making it highly agile and fast.
- Armed with a 23mm internal cannon and capable of carrying various air-to-air missiles and bombs, it was used extensively as an interceptor and multirole fighter.
- The MiG-21 became the most produced supersonic jet fighter in history with over 10,000 built, serving in more than 50 countries.
- It was a backbone of the Indian Air Force’s fighter fleet for several decades, notable for its speed and agility but also notorious for training and maintenance challenges.
- It played crucial roles in the 1965 and 1971 wars, the 1999 Kargil conflict, the 2019 Balakot air strikes, and most recently Operation Sindoor.
- The Indian Air Force will officially retire its legendary MiG-21 fighter jets on September 26, marking the end of nearly six decades of service for the aircraft widely hailed as the “workhorse” of India’s air defence.
- Tejas Light Combat Aircraft Mk 1A will step in to replace the ageing fighter in the years to come.

(TH)
Schemes in the News
PRASHAD Scheme:
-
- The Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD)was launched in 2014–2015 by the Ministry of Tourism to enable tourist convenience, accessibility, security and cleanliness.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme, financed by the Central Government.
- It has created new opportunities for tourism-linked livelihoods while reflecting Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of “Vikas Bhi, Virasat Bhi”— development alongside heritage as a vital step towards the goal of Viksit Bharat 2047.
- The scheme funds a wide range of works including the following,

(PIB)
Terms in the News
Spiritual tourism:
-
- Spiritual tourism involves travel for religious, sacred, or spiritual purposes, encompassing both pilgrimage to sacred sites and educational travel focused on diverse spiritual traditions and practices.
- Types of spiritual tourism are healing, experimental, quest, retreat, and collective.
- Inbound spiritual tourism saw a significant 4% rise in January 2025, linked to major events such as the Maha Kumbh and the Ram Mandir opening.
(PIB)
Exascale computing:
-
- It refers to supercomputers capable of performing at least a quintillion (10^18) floating-point operations per second, enabling them to tackle the world’s most complex challenges by simulating and analyzing massive datasets for advances in areas like weather forecasting, drug development, and AI.
(TH)
Neuromorphic computing:
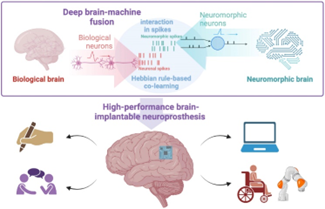
-
- It is a brain-inspired approach to computer design that replicates the human nervous system’s structure and function in hardware and software.
- It uses artificial neurons and synapses, integrating memory and processing, to create more energy-efficient, faster, and robust systems capable of complex, real-time learning and cognitive tasks, moving beyond traditional binary computing.
(TH)
MPI (Message Passing Interface):
-
- Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a portable, standardized message-passing protocol that enables communication between separate processes in a parallel, distributed-memory computing environment.
- It provides a set of routines for developers to write parallel programs in languages like C, C++, and Fortran, and it is widely used in high-performance computing (HPC) to scale applications beyond a single computer.
- MPI ensures that programs can run on different parallel systems, as each implementation is optimized for specific hardware.
(TH)
Places in the News
Bagram air base:
-
- Bagram Airfield-BAF, also known as Bagram Air Base, is located southeast of Charikar in the Parwan Province of Afghanistan.
- It is under the Afghan Ministry of Defence.
(TH)
Personality in the News
Krishnakumarsinh Ji:
-
- Krishnakumarsinhji Bhavsinhji Gadhvi founded state of Bhavnagar near Vadava village in 1743.
- He was a Gohil Rajput ruler of the Suryavanshi clan.
- The former princely state of Bhavnagar was also known as Gohilwad, “Land of the Gohils”.
- He was the reigning Maharaja from July 17, 1919, until India’s independence on August 15, 1947.
- Maharaja Shree Krishnakumar Sinhji was the first king to merge his state with the union of India, at the behest of Shree Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.

(PIB)
Miscellaneous
Mohanlal being awarded the Dadasaheb Phalke Award 2023:
-
- Legendary actor, director, and producer Mohanlal will receive the prestigious Dadasaheb Phalke Award at the 71st National Film Awards ceremony on September 23, 2025, for his outstanding contribution to Indian cinema.
- He was honoured with Padma Shri (2001) and Padma Bhushan (2019) and recognized internationally, including for his film screened at Cannes.
- The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is India’s highest film honour, awarded for lifetime contribution to the growth and development of Indian cinema.
- The award was instituted in 1969, commemorating Dadasaheb Phalke, the director of India’s first feature film “Raja Harishchandra” (1913), known as the “Father of Indian Cinema”.
- The award includes a Swarna Kamal (Golden Lotus) medallion, a ceremonial shawl, and a cash prize of ₹10 lakh.
- The first recipient was Devika Rani, known as the “First Lady of Indian Cinema”, in 1969.
(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
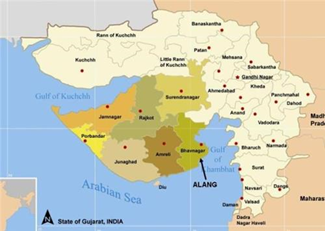
Q1. Consider the following statements about Bhavnagar, Gujarat:
1. It is a historic city founded by Maharaja Bhavsinhji I in 1723.
2. It is located on the eastern coast of the Gulf of Khambhat.
3. The world’s largest ship-breaking yard, Alang, is in the Bhavnagar district.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: It was founded in 1723 by Bhavsinhji Gohil. It was the capital of Bhavnagar State, which was a princely state before it was merged into the Indian Union in February 1948.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It is located on the western coast of the Gulf of Khambhat.
Statement 3 is correct: The world’s largest ship-breaking yard, Alang, is in the Bhavnagar district.
Q2. Consider the following statements about PRASHAD Scheme:
1. The Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD) was launched by the Ministry of Culture.
2. It is a Central Sector Scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD) was launched in 2014–2015 by the Ministry of Tourism.
Statement 2 is correct: Yes, it is a Central Sector Scheme.
Q3. With reference to the Tripura Sundari Temple, consider the following statements:
1. It is also known as Matabari Temple and is a significant Hindu site of Tripura.
2. It is located next to the sacred Kalyansagar lake, which is home to revered tortoises.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Tripura Sundari Temple, also known as Matabari Temple, is a significant Hindu site in Udaipur, Tripura, built by King Dhanya Manikya in 1501 AD to house the deity Tripura Sundari, or Shoroshi.
Statement 2 is correct: The temple is situated next to the Kalyansagar lake, known for its tortoises, which are considered sacred by devotees.
Q4. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is the highest honour in Indian cinema, presented annually as part of the National Film Awards ceremony.
Statement II: National Film Awards are a comprehensive set of awards presented annually by the Government of India to honour excellence in various aspects of Indian cinema.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is not correct
d) Statement-I is not correct but Statement-II is correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is the highest honor in Indian cinema, presented annually as part of the National Film Awards ceremony. It specifically recognizes an individual’s outstanding lifetime contribution to the growth and development of Indian cinema.
- Statement 2 is correct: National Film Awards are a comprehensive set of awards presented annually by the Government of India to honor excellence in various aspects of Indian cinema, including acting, directing, music, and technical categories across regional and language films.
Q5. Consider the following statements about major ports of India:
1. Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT) is India’s largest container port.
2. New Mangalore Port is an important port on India’s west coast, particularly for handling iron ore.
3. Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port is the oldest major port in India.
How many of the statements given are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) All three
d) None
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT), Maharashtra, located near Mumbai, is India’s largest container port.
Statement 2 is correct: New Mangalore Port, Karnataka is an important port on India’s west coast, particularly for handling iron ore.
Statement 3 is correct: Kolkata Port also known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port in West Bengal is the oldest major port in India.
Spread the Word
