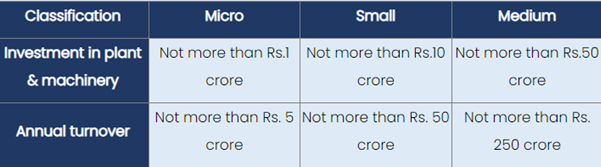
Revised Definition of MSMEs
In 2020, the Government of India revised the definition of MSMEs to include both manufacturing and service units, making the classification based on investment in plant and machinery or equipment and annual turnover. The updated criteria are as follows:
Role and Importance of MSMEs
1. Contribution to GDP and Employment:
-
- MSMEs contribute approximately 30% to India’s GDP.
- They account for more than 40% of India’s total exports.
- As per the Economic Survey 2023-24, the MSME sector employed around 12 crore people, representing about 50% of India’s total industrial employment.
2. Industrialisation and Rural Development:
-
- MSMEs play a crucial role in the industrialisation of rural and backward areas.
- They promote balanced regional development and help in reducing urban-rural disparities.
3. Women Entrepreneurship:
-
- Around 20.37% of MSMEs are operated by women, reflecting the sector’s role in promoting gender equality and women empowerment.
4. Diversity and Reach:
-
- The MSME sector comprises approximately 633.88 lakh units, with 99% being micro enterprises.
- These enterprises are diverse in nature, covering a wide range of sectors from traditional industries to high-tech manufacturing.
Challenges Faced by the MSME Sector
1. Access to Finance
-
- MSMEs face significant challenges in accessing adequate and timely credit.
- High cost of credit and stringent collateral requirements hinder their growth and expansion.
2. Infrastructure Issues
-
- Inadequate infrastructure facilities affect the efficiency and competitiveness of MSMEs.
- Delay in getting power connection, water connection, permission of concerned authorities to discharge effluents, etc.
3. Regulatory Hurdles
-
- The sector grapples with multiplicity of labour laws and complicated compliance procedures, which can be cumbersome for small enterprises.
4. Market Access
-
- Limited access to global markets restricts the growth potential of MSMEs.
5. Technology Adoption
-
- Many MSMEs operate with outdated technologies due to lack of access to modern equipment and capital for technology upgrades.
6. Supply Chain Disruptions:
-
- Problems in supply to government departments and agencies affect the liquidity and operational stability of MSMEs.
Government Initiatives for Promotion of MSMEs1. Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)Objective: To generate self-employment opportunities through the establishment of micro-enterprises. Key Features
2. Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)Objective: To provide credit without collateral/third-party guarantee to MSEs. Key Features
3. Micro and Small Enterprises – Cluster Development Programme (MSE-CDP)Objective: To enhance the productivity and competitiveness of MSEs by setting up Common Facility Centers (CFCs). Key Features
4. Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)Objective: To provide financial support to micro-enterprises through various financial institutions. Key Features
5. Udyam Registration PortalObjective: To simplify the registration process for MSMEs and provide a unique identification number. Key Features
6. Self-Reliant India (SRI) FundObjective: To support MSMEs in scaling up and enhancing their competitiveness. Key Features
7. RAMP (Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance)Objective: To improve the capacity and productivity of MSMEs by addressing issues such as delayed payments and market access. Key Features
8. ZED Certification SchemeObjective: To encourage MSMEs to adopt Zero Defect Zero Effect (ZED) practices in manufacturing. Key Features
|