APPROACH AND STRUCTURE
- Brief intro about 4th industrial revolution.
- Discuss the associated digital transformation.
- Explain the role of government in digital age
- Conclude with what the government must do to be prepared.
INTRODUCTION:
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by the fusion of the digital, biological, and physical worlds, as well as the growing utilization of new technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, robotics, 3D printing, the Internet of Things, and advanced wireless technologies, among others—which has ushered in a new era. The sheer speed of innovation and rapid adoption of new technologies pushes traditional government to its limits: today’s governments must be more data-driven, people-focused, and agile than ever before.
Digital Transformation
Digital revolution has opened new vistas of transmission, storage and retrieval of information which are being increasingly used for decision-making in public administration. Together with increasing population and its massive burden on civic amenities and the socio-economic, e-Governance becomes not only a necessity but an integral part of government.
E-Governance initiatives in India have traditionally being confined to automating government departments and taking online services to the common man. It has moved beyond government departments. Governments have moved from the first generation (web 1.0) e-government to web 2.0, (immersive web-based services with online applications). Now, the age is of government 3.0 which is a shift in culture that views government as a platform for enabling the creation of public value.It is about transforming the way governments work and reinvent people’s participation in the democratic process. E-Governance provides a platform to integrate solutions and services between Government-to-Citizens (G2C), Government-to-Business (G2B) and Government-to-Government (G2G), empowering both the government and the citizen.
With a strong foundation of digital infrastructure and expanded digital access through Digital India, time is now for the next phase of growth creation of tremendous economic value and empowerment for citizens through new digital applications.Driven through technology, e- Governance is transforming citizen services by providing access to information, integrating various systems and services between government and citizens, thereby empowering and enhancing citizen’s social, environmental and economic values. India is getting ready for an era of increased digitalisation, heralding the advent of Industry 4.0.
Governing in the age of data
Innovations by many government entities delivered in terms of better public policies and improved government services. Fast-moving and evolving trends in digital technologies are leading to a radical change in citizen expectations. Citizens are changing their approach to interacting with governmental organizations and services. The nature of these evolving interactions is horizontal, empowering and spontaneous which is the opposite of the traditional hierarchical, bureaucratic systems. Central to this new form of interaction is data.
If used effectively, big data can be a powerful tool. It has the potential for performance enhancement for the public sector in terms of better policies, more tailored government services, and more effective and efficient distribution of resources. It can also lead to negative outcomes if used incorrectly, in addition to the much-discussed issue of privacy. With massive amounts of citizen and municipal data, governments can make data-driven impact. Andhra Pradesh created a dashboard to track water tankers and minimize water leakage and launched e-Pragati – a platform to open data to citizens, improve data privacy, deliver government services digitally, and bring citizen engagement online.
Governments need to design, refine and master a new set of capabilities, regulations, and shape a new culture. Governments must also improve their capabilities when it comes to citizen engagement to effectively and actively engage with both providers and users of data. This requires governments to create a culture of open data.
Agile governance
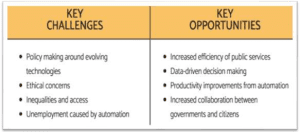
Agile governance means ensuring that governments and businesses are equipped to be quicker in anticipating and responding to new technologies.Governments must become agile to both keep up with and take advantage of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The changes that 4IR will bring demand new solutions to employment, faster policy-making, and ability to encourage and take advantage of innovation. Agile governance is necessary to ensure that people are not placed second to progress: systems. Regulating and keeping up with technological evolutions will enable the government to address the changes that emerging technologies bring.
CONCLUSION:
4IR helps governments foster an open, flexible, knowledge- and skills-based economy, and improves efficiency and effectiveness of health and social care systems Governments need to ensure adequate infrastructure and to be an enabler of change. Improving the trust between governments and citizens is fundamental to good governance and ICT is progressively becoming an essential tool for promoting accountability, convenience and transparent governance.
Spread the Word



