TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: The Darien Gap is a hazardous stretch of dense jungle spanning across northern Colombia and southern Panama, approximately 60 miles wide. It lacks paved roads and is characterized by muddy, wet, and unstable terrain, making it a formidable obstacle for migrants.
EXPLANATION:
Darien Gap
- The Darien Gap is a stretch of densely forested jungle across northern Colombia and southern Panama. Roughly 60 miles (97 kilometres) across, the terrain is muddy, wet and unstable.
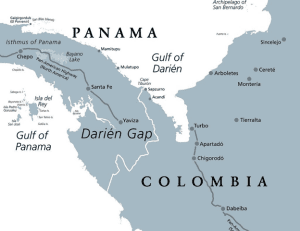
- Topography:
- The journey involves traversing mountains, fast-flowing rivers, and muddy paths, often lasting from four to 10 days.
- Migrants, including young children, must carry all their belongings through the rugged terrain.
- Criminal Activity:
- Criminal organizations control the area, demanding payment for passage and sometimes extorting migrants for more money.
- There are reports of armed groups ambushing migrants, leading to theft, extortion, and even mass sexual assault.
- Environmental Hazards:
- The jungle’s extreme conditions contribute to the danger, with risks of slipping, falling, drowning in rivers, and suffering from dehydration, vector-borne diseases, and fungal-related illnesses.
- Mortality:
- The challenging environment leads to fatalities, with bodies often left along the path, marking the perilous nature of the journey.
- Reported deaths are likely underestimated due to the difficulty in recovery and reporting.
Recent Surge in Crossings:
- Drivers:
- Violence, insecurity, and instability in migrants’ home countries prompt them to seek safer havens, driving the increase in migration.
- Limited legal immigration options, such as travel visa restrictions, force migrants to seek alternative routes.
- Impact of Policy Changes:
- Policy shifts, like Mexico’s requirement for Venezuelans to carry travel visas, redirect migration flows, pushing more individuals towards the perilous Darien Gap route.
Demographics of Migrants:
- Nationalities:
- In 2023, Venezuelans constituted the majority of migrants, followed by Haitians, Chinese, Afghans, Nepali, Cameroonians, and Angolans, reflecting the global nature of human migration.
- Gender and Age Diversity:
- Migration demographics include a diverse range of ages and genders, with adult men comprising over half of migrants, adult women accounting for 26%, and children under 18 constituting 20% of the population, with half being under the age of 5.
Government Responses and Challenges:
- Limited Options:
- Government policies restricting legal immigration channels exacerbate the reliance on dangerous routes like the Darien Gap.
- Humanitarian Concerns:
- Governments have been hesitant to support humanitarian groups aiding migrants, potentially increasing the risks faced by migrants.
- Regional Coordination:
- Initiatives like the Los Angeles Declaration on Migration and Protection aim to enhance regional cooperation in managing migration, but challenges persist in ensuring access to legal pathways for all migrants.




