THE CONTEXT: Recently, Prime Minister launched the world’s largest grain storage plan in the cooperative sector. The pilot project is being carried out in 11 states by primary agricultural credit societies where the government is looking to “set up a storage infrastructure of 700 lakh metric tons’’.
MORE ON THE NEWS:
- The foundation stone for additional 500 PACS for construction of godowns and other agri infrastructure has also been laid.
- A project for computersation in 18,000 PACS across the country, aligning farming with cutting edge technology and shifting to fully digital payments has also been launched.
LARGEST GRAIN STORAGE PLAN:
- The pilot project is being undertaken in 11 Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in 11 states. Ministry of Cooperation will implement the project.
- The scheme aims to create storage capacity for storing 100 per cent of India’s grain production to strengthen food security, reduce wastage, and empower farmers.
- It aims to seamlessly integrate PACS godowns with the food grain supply chain, with a collaborative effort of NABARD and spearheaded by the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
- 700 lakh tonne storage capacity will be created in the next five years, with an investment of ₹1.25 lakh crore. In India, storage capacity with regards to food grain production is only 47%, whereas in the USA it is 161%, Brazil 149%, Canada 130% and China 107%.
- The Plan aims for creation of various agri infrastructure at Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level, including warehouses, custom hiring center, processing units, Fair Price Shops, etc. by leveraging the ‘whole-of-Government’ approach.
- The initiative is being implemented through the convergence of various existing schemes like the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agriculture Marketing Infrastructure (AMI), etc. to enable PACS participating in the project to avail subsidies and interest subvention benefits for undertaking infrastructure development.
- This ambitious project aims to converge eight ongoing schemes of three ministries to address the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in India.
- Ministry of Cooperation has constituted Inter-Ministerial Committee (IMC) with Hon’ble Home and Cooperation Minister as its chairman and Hon’ble Ministers and Secretaries of Ministries concerned as its members for smooth and effective implementation of the Plan.
- The Ministry of Cooperation has also constituted National Level Coordination Committee (NLCC) under the chairmanship of Secretary (Ministry of Cooperation) to steer the overall implementation of the Plan and reviewing the progress of implementation, etc.
BENEFITS OF THE PROJECT:
- Addressing Infrastructure Shortage:The plan aims to establish godowns at the level of PACS to alleviate the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in the country.
- Diversification of PACS Activities:PACS will be empowered to undertake various activities, including functioning as procurement centres for state agencies or the Food Corporation of India (FCI), serving as fair price shops, and setting up custom hiring centres and common processing units. This diversification will enhance the incomes of farmer members.
- Reduction of Food Grain Wastage:By creating decentralised storage capacity at the local level, the plan aims to reduce grain wastage, contributing to improved food security.
- Preventing Distress Sale:The plan provides farmers with various options, preventing distress sale of crops and enabling them to realise better prices for their produce.
- Cost Reduction:The establishment of storage facilities at the PACS level will significantly reduce transportation costs of food grains to procurement centres and fair price shops.
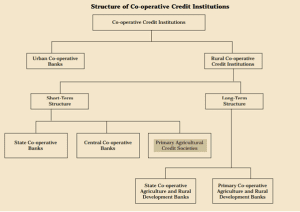
WHAT IS Primary Agricultural Credit Societies(PACS)?
- Primary Agricultural Credit Societies are the grass root level arms of the short-term co-operative credit structure.
- PACS deals directly with the rural (agricultural) borrowers, give those loans and collect repayments of loans given and also undertake distribution and marketing functions.
- They occupy a predominant position in the co-operative credit structure and form its base.
- It serves as the final link between the ultimate borrowers on the one hand and the higher financing agencies, namely the Scheduled Commercial Banks, and the RBI/NABARD on the other hand.
Organisational Structure of PACS
- General Body of PACS: Exercise the control over board as well as management.
- Management Committee: Elected by the general body to perform the work as prescribed by the society’s rules, acts, and by-laws.
- Chairman, Vice-Chairman, and Secretary: Work for the benefit of the members by performing their roles and duties as assigned to them.
- Office Staff: Responsible for performing day to day work.
GOVERNMENT EMPHASIS ON COOPERATIVES
- A separate Cooperation Ministry has been set up by the government as cooperatives have a great role in strengthening agriculture.
- The Ministry of Cooperation has developed the grain storage plan to leverage the strength of cooperatives and transform them into successful business enterprises,aligning with the vision of “Sahakar-se-Samriddhi” (Cooperation for Prosperity). The vision of Sahakar se Samriddhi is to rejuvenate the cooperative sector and empower small and marginal farmers.
- The government seems to be increasingly emphasising the role of cooperatives in agricultural marketing and storage, as opposed to government-owned entities such as Food Corporation of India and Central Warehousing Corporation.
- The government had even reduced minimum alternate tax on cooperative societies – bringing it at par with the corporate sector and raised the slab for tax to be deducted at source to income above Rs 3 crore.
- The government believe that the success achieved by Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (Amul) in augmenting income of farmers in their home state can be replicated across the country.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- Strengthen transportation networks: There is need to improve transportation infrastructure, including roads, rail networks, and logistics systems, will enable efficient movement of food from farms to storage facilities and distribution centers. This will reduce delays, minimize spoilage, and ensure timely delivery of food to the market.
- Encourage private sector participation: The involvement of the private sector in food storage infrastructure development and management can bring in expertise, technology, and investments. Public-private partnerships can help bridge the gap between demand and supply of storage facilities.
- Facilitate access to finance: Providing financial support, subsidies, and credit facilities to farmers, small-scale food businesses, and storage facility operators can help them invest in modern storage technologies and facilities. This will enable them to store food properly and efficiently.
- Promote research and innovation: Continued research and innovation in food storage technologies, packaging materials, and preservation methods is the need of hour. This can lead to the development of cost-effective and sustainable solutions tailored to Indian conditions.
THE CONCLUSION:
By strengthening Cooperatives, governments and stakeholders aim to improve the overall state of agriculture, uplift rural communities, and promote inclusive economic growth. These efforts can contribute to poverty reduction, food security, and sustainable development in agrarian economies.
UPSC PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1 In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Recently, Prime Minister launched the world’s largest grain storage plan in the cooperative sector. Highlight the key rationale behind the initiative and its significance in boosting agriculture economy.
Q.2 Critically assess whether cooperative can take over the role of government bodies to contribute towards promoting food security and for improvement of rural livelihoods.
Spread the Word



