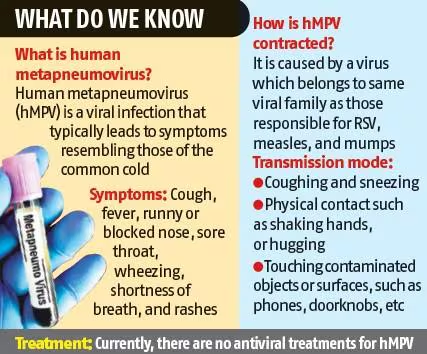
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: In the pursuit of health improvement, diagnostic tests play a crucial role, but interpreting the results requires a nuanced understanding of correlation and causation.
EXPLANATION:
- We will delve into the intricate link between High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) and cardiovascular health, emphasizing the need to discern between correlation and causation in making intervention decisions.
Correlation vs. Causation:
- Crucial Distinction:
- The importance of distinguishing between correlation and causation when interpreting diagnostic test results has been emphasized.
- It uses a vivid example of the correlation between ice cream sales and shark attacks to highlight the need for identifying underlying causative factors before implementing interventions.
- Media Influence:
- The impact of media headlines linking certain foods like coffee or chocolate to health benefits is discussed, emphasizing that terms like “linked” and “associated” imply correlation rather than causation.
- The necessity of clear causative factors for effective interventions has been stressed.
The Case of HDL-C:
- Historical Context:
- HDL-C, labeled the “good” cholesterol due to its negative correlation with cardiovascular disease (CV) risk, has been a focus of research.
- However, attempts to establish a causal link through pharmaceutical interventions raising HDL-C have not shown a reduction in CV disease risk.
- Understanding Lipids:
- A clarification is made regarding the discussion of lipids and cholesterol, differentiating between LDL and HDL particles and their cholesterol content (LDL-C and HDL-C).
- The dynamic nature of these particles, constantly exchanging cholesterol with their surroundings has been emphasized.
Role of HDL-C in Cardiovascular Health:
- Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT):
- The role of HDL-C in the RCT pathway, a crucial process in preventing cholesterol deposits in coronary arteries.
- HDL-C facilitates cholesterol efflux from cells and tissues, transporting it back to the liver for elimination.
- Efflux Rate:
- The critical factor in understanding HDL-C’s role is the rate of cholesterol removal (efflux rate) via HDL.
- However, the routinely available measurement is HDL-C concentration, which does not provide insights into the efflux rate.
Complexity Revealed in Clinical Trials:
- Failed Trials:
- The failure of clinical trials attempting to establish a direct link between increased HDL-C and reduced CV risk.
- Additional studies on the efflux rate highlight the complexity of HDL’s role, raising questions about its contribution to cardiovascular health.
- Viewing HDL-C as an Indicator:
- Presently, HDL-C is viewed as an indicator of overall good health, correlating with low CV risk.
- The complexity of HDL-C pathway suggests that its role as a transporter of cholesterol remains a mystery.
Practical Implications:
- Interpreting HDL-C Numbers:
- While a high HDL-C number correlates with low CV risk, the article emphasizes the importance of considering other parameters.
- A low HDL-C, however, may not be cause for concern, as modifiable factors like LDL-C, Apolipoprotein-B, exercise, and diet also influence CV risk.
- Caution in Interpretation:
- The article concludes by advising caution in interpreting correlational markers, drawing parallels with media headlines about coffee benefits.
- Enjoying a morning cup of coffee may be pleasant, but the need to differentiate enjoyment from disease risk reduction has been stressed.