TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists have shared new insights into a colossal black hole located 53 million light-years away.
EXPLANATION:
- This celestial giant was first captured by the Earth-wide Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) in 2017, marking a historic moment in astrophysics.
- It provided the first visual evidence of the existence of black holes, a phenomenon predicted by Einstein’s general relativity.
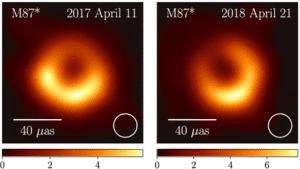
- The initial image from the EHT in 2017 showcased the black hole’s ‘shadow,’ a consequence of the gravitational effects near its event horizon.
- This shadow not only confirmed the presence of the black hole but also aligned with the predictions of general relativity regarding its mass, size, and shape.
Enhancements in Telescope Capabilities
- In a recent paper published on January 18, 2024, EHT scientists revealed that subsequent observations, conducted after improving the telescope’s coverage and resolution, reaffirmed the earlier findings.
- The upgrades included increasing data-recording rates, enhancing spatial tracking capabilities, and incorporating the Greenland Telescope into the EHT array, which improved resolution in the north-south direction.
The Global Telescope Network
- The EHT is not a single telescope but a global collaboration of radio telescopes, utilizing very-long baseline interferometry.
- This technique involves correlating data from multiple telescopes worldwide to study a common celestial object.
- The maximum distance between these telescopes defines the network’s resolution.
Insights from Data Correlation
- During the 2018 observation campaign, nine EHT stations collected data over six days, utilizing four frequencies.
- Correlating these datasets revealed significant changes in the closure phase, providing insights into the dynamic configuration or structure of the black hole.
Simulation Models and Gravitational Lensing
- To understand the intricate dynamics near the event horizon, scientists employed general relativistic magnetohydrodynamic (GRMHD) simulations.
- These simulations helped create models of the black hole, incorporating gravitational lensing effects predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Confirmation of Lensing Effects
- The findings confirmed the presence of an asymmetric ring structure approximately 42 microarcseconds wide, akin to observing a grain of sand from 25 km away.
- This observation matched predictions for a shadow formed by lensed emission around a rotating black hole with a mass of approximately 6.5 billion times that of the Sun.
Shifts in Accretion Disk and Jet
- Observations of the M87 galaxy, housing the black hole, revealed a prominent jet of high-energy particles extending from the black hole into space.
- Shifts in the accretion disk and jet between 2017 and 2018 suggested changes in position or orientation, potentially linked to the black hole’s spin and its magnetic field structure.
Ongoing and Future Endeavors
- The EHT collaboration plans to continue its exploration, with a future ‘movie project’ in 2026 aiming to track the black hole over a month or two.
- This ongoing effort highlights the dedication to understanding the hidden physics governing the relationship between the accretion disk, the jet, and the magnetic environment around the black hole.
Black Hole:
- Black holes are points in space that are so dense they create deep gravity sinks. Beyond a certain region, not even light can escape the powerful tug of a black hole’s gravity.
- In other words, Black holes are regions in space where an enormous amount of mass is packed into a tiny volume.
Conclusion
- The recent findings not only reaffirm the features of the black hole reported in 2019 but also showcase the continuous improvement in observational techniques.
- The EHT’s ability to measure the ring’s diameter more accurately suggests advancements in image-based techniques, bridging the gap with direct modeling methods.
- As humanity delves deeper into the cosmos, these revelations open new avenues for understanding the enigmatic nature of black holes and the universe at large.

