THE CONTEXT: A few months ago, India’s drug regulator Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), approved the market authorisation for NexCAR19, India’s first indigenously-developed CAR-T cell therapy. This paves the way for the commercial launch of this therapy in India, where it is expected to be available to cancer patients at a tenth of the cost abroad. Recently, a 64-year-old former army doctor has become the first patient in the country to be free of cancer cells after being administered this therapy.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS:
- For decades, oncologists have relied on chemotherapy, radiation and surgery to treat cancer patients which the primary methods to treat the dreaded disease. In the past two decades, however, research has extended the frontiers of anti-cancer interventions.
- Drugs have been developed to home in on the molecules cancer cells require to survive and spread. Immune system-boosting drugs have shown the ability to shrink tumours in some patients with advanced malignancy.
- CAR T-cell therapy is among the most promising recent developments, especially because it has shown the ability to eradicate advanced leukemias and lymphomas. Most of the early research in this field was conducted in laboratories in the US, Europe and China.
- In October, 2023, India joined this elite list after the country’s drug regulator approved a CAR T-cell therapy incubated at Tata Memorial Centre and IIT Bombay laboratories.
WHAT IS CAR-T CELL THERAPY, AND HOW DO CAR-T CELLS FIND AND DESTROY CANCER CELLS?
- CAR-T is a revolutionary therapy that modifies immune cells, specifically T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
- T-cells are special cells (white blood cells) whose primary function is cytotoxic, meaning it can kill other cells.
- T-cells are then put back into the body, and they go after cancer cells especially in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
- CAR T-cell therapies are customised for each patient. The treatment is far less difficult for the patient compared to several sessions of chemotherapy.
- Laboratory and animal studies have shown that India’s homegrown therapy has significantly fewer side effects compared to those developed in the West.
How effective and different is this from other cancer treatments like, say, chemotherapy?
- While chemotherapy and immunotherapy may add a few months or years to a cancer patient’s life, cell-and-gene therapy is designed to cure and provide lifelong benefit.
- It makes treatment easier with a one-time therapy unlike several sessions of chemotherapy. It is a lifeline for non-responsive cancer patients.
NEXCAR19:
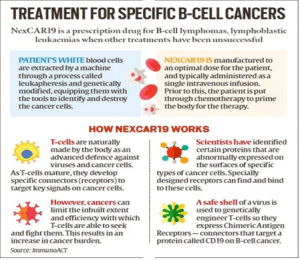
- NexCar19 is a type of CAR-T and gene therapy developed indigenously in India by ImmunoACT, which is a company incubated at IIT Bombay.
- The therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein. This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
- India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
- The therapy is for people with B-cell lymphomas who didn’t respond to standard treatments like chemotherapy, leading to relapse or recurrence of the cancer.
- Recovery typically occurs within two weeks after one cycle of the treatment. Approximately 70% of patients respond to the treatment, with variations between leukaemia and lymphoma cases. About 50% of these responsive patients achieve a complete response.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THERAPY:
- Lower drug-related toxicities: Laboratory and animal studies have shown that it leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities.
- Minimal damage to neurons: It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity. However, neurotoxicity can sometimes occur when CAR-T cells recognise the CD19 protein and enter the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- Minimal Cytokine Release syndromes: The therapy also results in minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which is characterised by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body. Inflammation are caused due to the death of a significant number of tumour cells, as CAR-T cells are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells.
ISSUES RELATED TO THERAPY:
- Affordability: Cancer incidence and mortality continue to rise driven by spikes in the Global South. In India, where the disease claims about 8 lakh people every year, treatment is expensive for an overwhelming section of the population. Critics argue that developing CAR T-cell therapy in India may not be as cost-effective as it will still be unaffordable for most people.
- Accessibility: High costs and the need for specialized infrastructure for production and administration remain significant barriers to widespread adoption and accessibility.
- Preparation: One of the issue faced by CAR T-cell therapies is its preparation that has been major hindrance to their widespread use. CAR T-cell therapy requires technical and human resources, making it challenging to administer.
- Side Effects: The potential side-effects of CAR T-cell therapy is also significant which are associated with cytokine release syndrome and neurological symptoms.
THE CONCLUSION:
The development of indigenous CAR-T cell therapy in India marks a significant advancement in the country’s healthcare landscape. Researchers and planners must work to cut costs of the therapy to lower the cancer mortality rates in the coming decades.
UPSC PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1 What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)
Q.2 COVID-19 pandemic has caused unprecedented devastation worldwide. However, technological advancements are being availed readily to win over the crisis. Give an account of how technology was sought to aid the management of the pandemic. (2020)
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTION
Q.1 Highlight the significance of the development of indigenous CAR-T cell therapy in India. Discuss the challenges in terms of its accessibility and affordability for cancer treatments in the country.
Spread the Word

Related posts
KHELO BHARAT NITI 2025
FROM RANK 110 TO RANK 99: ACCELERATING INDIA’S SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS JOURNEY—ACHIEVEMENTS, FAULT-LINES AND THE ROAD TO 2030
GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATIONS AS SHIELDS OF HERITAGE: LESSONS FROM THE PRADA–KOLHAPURI EPISODE