RELEVANCE TO UPSC SYLLABUS: GS 3: INDIAN ECONOMY AND ISSUES RELATING TO PLANNING, MOBILIZATION OF RESOURCES
THE CONTEXT
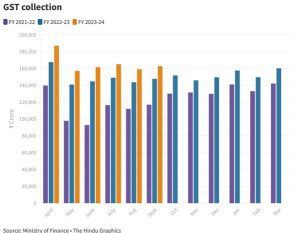
India’s gross revenues from the Goods and Services Tax (GST) stand at over ₹9.92 lakh crore in September 2023 which is halfway through the financial year, marking an 11.1% increase over collections between April and September 2022.
MORE ON THE NEWS
- Central and state governments collected ₹62 trillion in Goods and Services Tax (GST) in September, 2023 marking the fourth highest monthly collection since the inception of the indirect tax regime and a 10% annual growth from the year-ago period.
- It places government at a comfortable place regarding GST revenues in the fiscal context, as during the January-March 2024 quarter central bank expects real GDP growth to slow to 5.7% from 7.8% in the first quarter.
WHAT IS GST?
- GST has been introduced by 101st Amendment Act of 2016 and is one indirect tax for the whole nation, which will make India one unified common market. GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services, right from the manufacturer to the consumer. It essentially is a tax only on value addition at each stage.
- The final consumer will thus bear only the GST charged by the last dealer in the supply chain, with set-off benefits at all the previous stages.
At the Central level, the following taxes are being subsumed:
- Central Excise Duty
- Additional Excise Duty
- Service Tax
- Additional Customs Duty commonly known as Countervailing Duty
- Special Additional Duty of Customs.
At the State level, the following taxes are being subsumed:
- Subsuming of State Value Added Tax/Sales Tax,
- Entertainment Tax (other than the tax levied by the local bodies), Central Sales Tax (levied by the Centre and collected by the States),
- Octroi and Entry tax,
- Purchase Tax,
- Luxury tax, and
- Taxes on lottery, betting and gambling.
BENEFITS OF GST
- Easy compliance: All the tax payer services such as registrations, returns, payments, etc. are available to the taxpayers online, which would make compliance easy and transparent.
- Uniformity of tax rates and structures: GST ensure that indirect tax rates and structures are common across the country, thereby increasing certainty and ease of doing business.
- Removal of cascading: A system of seamless tax-credits throughout the value-chain, and across boundaries of States, ensure that there is minimal cascading of taxes. This reduce hidden costs of doing business.
- Higher revenue efficiency: GST mechanism decrease the cost of collection of tax revenues of the Government, and therefore, lead to higher revenue efficiency.
GST COUNCIL
- GST Council has been introduced for smooth and efficient administration of GST by cooperation and coordination under Article 279-A in the constitution of India.
- The GST Council consists of the following members:
- The Union Finance Minister (as Chairman).
- The Union Minister of State in-charge of Revenue or Finance.
- The Minister in charge of Finance or Taxation or any other Minister, nominated by each State Government.
- The members of the Council from the states have to choose one amongst themselves to be the Vice-Chairperson of the Council. They can also decide his term.
- The Union Cabinet also decided to include the Chairperson of the Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) as a permanent invitee (non-voting) to all proceedings of the Council.
- The council is devised in such a way that the centre will have 1/3rd voting power and the states have 2/3rd. The decisions are taken by 3/4th
Reasons for the Increase in GST Revenue
- Improvement in economic activity: One of the main reasons for the increase in GST revenue is the improvement in economic activity.
- Enhanced compliance: Another reason for the increase in GST revenue is the enhanced compliance and anti-evasion measures taken by the government.
- Reforms introduced by government: The government has introduced several reforms such as e-invoicing, e-way bills, Aadhaar authentication, data analytics, and artificial intelligence to plug leakages and prevent tax evasion.
THE ISSUES
- Impact of slowdown not evenly distributed: The impact of the slowdown has not been evenly distributed across income groups and categories.
- Beyond the macro resilience that these numbers indicate, a few areas of concern deserve closer scrutiny from policymakers and the GST Council:
- Slowdown in growth of GST: There is slowdown in the growth of GST inflows and in domestic transactions and services imports between July and September, the slowest since July 2021.
- Mandatory E-invoicing: E-invoicing became mandatory for all firms with a turnover of over ₹5 crore since August 1, 2023 ,so there comes need of another compliance mechanism.
- Shrink in revenue from goods: Revenues from goods imports that have shrunk four times in 2023 despite high import. Authorities must check for revenue leakages from imports.
THE TRENDS
- Increase in taxpayers: A substantial increase has been observed across different categories individuals, firms and companies. For example, number of taxpayers increased by 64% between 2014 and 2022.
- More number of returns filed: There is growth in number of taxpayers filing returns.
However, this growth in taxpayers is insufficient as the most of the tax returns are associated with nil taxes.
- Rise in direct tax: There is growth in direct tax collections and higher tax buoyancy with increase in taxpayers and increase in returns filed which suggests noticeable gains in compliance.
THE WAY FORWARD
- Strengthening of GST Council: There is need of strengthening of GST Council for its better functioning. There have been instances of disagreements in resolving issues such as dispute resolution mechanism and revenue-sharing formulas that needs to be resolved.
- Simplification of GST rates: The rationalization of GST rates and slabs would reduce compliance costs, improve tax buoyancy, and eliminate classification disputes.
- Mechanism for higher revenue generation: An increase in returns filed is however not an end in itself. It must lead to higher revenues for which newer mechanism needs to be developed.
- Need scrutiny: Amid broadly healthy GST inflows, some trends need greater scrutiny. There is need of capacity building of state tax authorities as success of GST depends on adapting to the new requirements.
THE CONCLUSION
With higher revenue and simplified tax regime, GST is termed as positive step towards shifting Indian economy from the informal to formal economy. There is need of certain reforms to overcome the impending challenges.
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
- Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
- Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the goods and services tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017.(2019)
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
- Although there has been improvement in GST revenue collection, the GST regime suffers from multiple challenges. Comment.


Related posts
LESSONS FROM THE CHOLA EMPIRE TO THE CONTEMPORARY INDIA
FROM SEAFLOOR RUPTURE TO SAFER SHORES: RE-IMAGINING TSUNAMI RISK GOVERNANCE FOR INDIA
MANGROVE RESTORATION AND COASTAL SECURITY IN INDIA