Table of Contents
THE INDIAN HISTORY
1.PINGALI VENKAYYA: THE DESIGNER OF INDIAN NATIONAL TRICOLOUR
THE CONTEXT: To mark the birth anniversary of Venkayya on August 2, the Central government has decided to release a special commemorative postage stamp on that day.
THE EXPLANATION:
- As India marks 75 years of Independence, the Tricolour represents the sovereignty and freedom, and each colour (saffron, white and green) points at courage, truth and peace, and faith and chivalry.
- And this Tricolour was planted by freedom fighter Pingali Venkayya. On his 126th birth anniversary, the culture ministry has organised ‘Tiranga Utsav’, and a special commemorative postage stamp honouring Venkayya will be released.
WHO IS PINGALI VENKAYYA?
Venkayya was born on August 2, 1876 at Bhatlapenumarru, near present-day Machilipatnam town in Andhra Pradesh. He completed his high school in Madras and went to Cambridge University and acquired knowledge in geology, agriculture, education and languages.
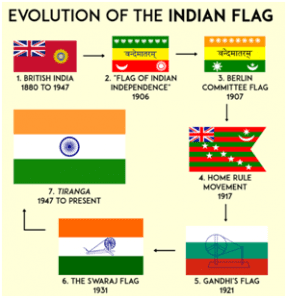
JOURNEY OF FLAG
Venkayya designed several models of national flag, starting from the one designed in 1921, which was approved by Mahatma Gandhi at a Congress meeting in Vijayawada. This version had two stripes (green and red) and Gandhian ‘charkha’ at the Centre. A white stripe was added on top at Gandhi’s suggestion, which became the original Tricolour.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2.LIST OF OUTCOMES: OFFICIAL VISIT OF PRESIDENT OF MALDIVES TO INDIA
THE CONTEXT: Indian Prime Minister stated that India will extend an additional $100 million line of credit to the Maldives. Following bilateral talks between PM and President of Maldives Ibrahim Mohamed Solih, India and Maldives signed six pacts to facilitate cooperation in capacity building, cyber security, housing, disaster management, and infrastructure.
THE EXPLANATION:
- In his remarks, Mr. Solih referred to India as the “highest priority” of the Maldives and said, “Maldives-India relation, goes beyond diplomacy. Our values, our cultures and our histories are intertwined, making it a traditional relationship. Our centuries-old relationship is grown with political trust, economic cooperation and coherent strategic policies between our two countries.”
KEY TAKEAWAYS OF THE MEETING:
A.Groundbreaking/Review of Projects
- Pouring of first concrete of the Greater Male Connectivity Project- an USD 500 Mn India funded project- marking the commencement of permanent works.
- Review of the progress on the construction of 4,000 social housing units in Hulhumale being funded under Exim Bank of India Buyer’s credit finance of USD 227 Mn.
- Overview of India Maldives development cooperation including Addu roads and reclamation, water and sanitation in 34 islands and Friday Mosque restoration projects.
Β.Agreements/MoUs Exchanged
- MoU on Capacity Building & Training of Members of Local Councils & Women Development Committee of Maldives between NIRDPR, India and Local Government Authority, Maldives.
- MoU on Collaboration in potential fishing zone forecast capacity building and data sharing and marine scientific research between INCOIS, India and Ministry of Fisheries, Maldives.
- MoU for Cooperation in the area of Cyber Security between CERT-India and NCIT, Maldives.
- MoU for cooperation in the field of disaster management between NDMA, India and NDMA, Maldives.
- Agreement between EXIM Bank, India and Ministry of Finance, Maldives for USD 41 Mn Buyer’s Credit Financing of Police Infrastructure in Maldives.
- Letter of Intent between Exim Bank of India and Ministry of Finance, Maldives on Buyer’s Credit funding approval of USD 119 Mn for additional 2,000 social housing units to be constructed in Hulhumale. C
C.Announcements
- Extension of USD 100 Mn new Line of Credit to finance infrastructure projects in Maldives.
- Approval for award of EPC contract for the USD 128 Mn Hanimadhoo Airport Development project under Line of Credit.
- Approval of DPR and commencement of tendering process of the USD 324 Mn Gulhifahlu Port development project under Line of Credit.
- Approval of Feasibility Report and financial closure for the USD 30 Mn Cancer Hospital project under Line of Credit.
- USD 119 Mn Buyer’s Credit financing by Exim Bank of India for additional 2,000 social housing units in Hulhumale.
- Facilitation of duty free tuna exports to India from Maldives.
- Supply of a replacement ship for the earlier provided ship-CGS Huravee -to Maldives National Defence Force.
- Supply of the second Landing Craft Assault (LCA) to Maldives National Defence Force.
- Gifting of 24 utility vehicles to Maldives National Defence Force.
India-Maldives Relations:
- India was first among countries, that recognised the Independent Maldives in 1965. India was also the first among countries to establish diplomatic relations with Maldives. Both the countries share linguistic, ethnic, cultural, religious and commercial ties. Maldives started its full-fledged High Commission in New Delhi in November 2004.
- Maldives has extended its support to India, consistently, at multilateral for a like United nations, the Commonwealth, the NAM and the SAARC. India has actively aided Maldives. After the 2004 tsunami in Maldives, India was the first country send relief and aid to the Maldives.
Significance of Maldives for India:
Maldives acts as a Toll Gate for India in Indian Ocean. Maldives is situated at the southern and northern parts of island chain. It includes two important Sea Lanes of Communication, which are significant for the flow of maritime trade between Gulf of Aden and Gulf of Hormuz. Around 50% of external trade of India and 80% of India’s energy imports transit through SLOCs in Arabian Sea.
3.UN PEACEKEEPING MISSION
THE CONTEXT: Recently the two BSF personnel who were part of the UN Peacekeeping Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), were among five people killed during a protest in an eastern town near the border with Uganda.
THE EXPLANATION:
- A total 175 Indian peacekeepers have so far died while serving with the United Nations. India has lost more peacekeepers than any other UN Member State.
- Since 1948, UN Peacekeepers have undertaken 71 Field Missions. There are approximately 81,820 personnel serving on 13 peace operations led by UNDPO, in four continents currently. This represents a nine-fold increase since 1999.
- A total of 119 countries have contributed military and police personnel to UN peacekeeping. Currently, 72,930 of those serving are troops and military observers, and about 8,890 are police personnel.
- India has a long history of service in UN Peacekeeping, having contributed more personnel than any other country. To date, more than 2,53,000 Indians have served in 49 of the 71 UN Peacekeeping missions established around the world since 1948.
- Currently, there are around 5,500 troops and police from India who have been deployed to UN Peacekeeping missions, the fifth highest amongst troop-contributing countries.
- India has also provided, and continues to provide, eminent Force Commanders for UN Missions. India is the fifth largest troop contributor (TCC) with 5,323 personnel deployed in 8 out of 13 active UN Peacekeeping Missions, of which 166 are police personnel.
- India’s contribution to UN Peacekeeping began with its participation in the UN operation in Korea in the 1950s, where India’s mediatory role in resolving the stalemate over prisoners of war in Korea led to the signing of the armistice that ended the Korean War. India chaired the five-member Neutral Nations Repatriation Commission, while the Indian Custodian Force supervised the process of interviews and repatriation that followed.
- The UN entrusted the Indian armed forces with subsequent peace missions in the Middle East, Cyprus, and the Congo (since 1971, Zaire).
- India also served as Chair of the three international commissions for supervision and control for Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos established by the 1954 Geneva Accords on Indochina.
VALUE ADDITION:
United Nation Peacekeeping Mission:
- United Nations Peacekeeping was created in 1948.
- They are often referred to as Blue Berets or Blue Helmets because of their light blue berets or helmets
- Purpose: It provides security, political, and peacebuilding support to countries under conflicts. It helps countries make the difficult, early transition from conflict to peace.
- Principles: They are guided by three basic principles:
- Consent of the parties
- Impartiality
- Non-use of force except in self-defense and defense of the mandate.
- Authorised by: Every peacekeeping mission is authorized by the UN Security Council.
- Peacekeeping forces: Member states contribute their manpower for Peacekeeping forces on a voluntary basis.
- Funding: The financial resources of UN Peacekeeping operations are the collective responsibility of UN Member States. Every Member State is legally obligated to pay their respective share for peacekeeping.
- The UN Peacekeeping Force won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1988.
India and the UN Peacekeeping forces:
- India is consistently among the top troop-contributing nations to the UN. At present, 5,528 personnel of India are serving in eight countries. It is currently the fifth-largest
- India’s contribution to the regular budget is 0.83% and 0.16% of the peacekeeping budget.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
4.HELLFIRE R9X MISSILE
THE CONTEXT: The US military used its ‘secret weapon’ — the Hellfire R9X missile – to kill Al Qaeda chief Ayman al-Zawahiri on the balcony of a safehouse in Kabul on July 31.
THE EXPLANATION:
Al-Zawahiri, an Egyptian surgeon who had a $25 million bounty on his head, had helped coordinate the September 11, 2001, attacks that had killed nearly 3,000 people.
What is the Hellfire R9X missile?
- Better known in military circles as the AGM-114 R9X, the Hellfire R9X is a US-origin missile known to cause minimum collateral damage while engaging individual targets.
- Also known as the ‘Ninja Missile’, this weapon does not carry a warhead and instead deploys razor-sharp blades at the terminal stage of its attack trajectory. This helps it to break through even thick steel sheets and cut down the target using the kinetic energy of its propulsion without causing any damage to the persons in the general vicinity or to the structure of the building.
The blades pop out of the missile and cut down the intended target without causing the massive damage to the surroundings which would be the case with a missile carrying an explosive warhead.

Where has the Hellfire missile been used on previous occasions?
- In 2017, the ‘Ninja Missile’ was reportedly used to kill the then No. 2 leader of Al Qaeda, Abu Khayr Al Masri, in Syria. It was also used against other targets in Syria at around the same time. The damage caused to the vehicles which carried the targets, particularly the shredded roofs of cars, gave the first clues that a normal warhead was not used on the missile and that it had sharp blades. It has also been used against Taliban targets in Afghanistan in 2020 and again in 2022.
What is known about the other Hellfire missile variants?
- Hellfire is actually an acronym for Heliborne, Laser, Fire and Forget Missile and it was developed in the US initially to target tanks from the Apache AH-64 attack helicopters. Later, the usage of these missiles spread to several other variants of helicopters and also ground and sea-based systems and drones.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
5.REVISION SERIES: MISSION AMRIT SAROVAR
On 24th April 2022, Prime minister launched a mission to conserve water for the future which is known as Amrit Sarovar Mission. For celebrating the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, Amrit Sarovar aims to develop and rejuvenate 75 water bodies in each district of India. Under this mission, 50,000 water bodies of size of about an Acre will be created.
Amrit Sarovar Mission: Governing Bodies
The government has approached six ministries and departments which are mentioned below.
- Department of Rural Development
- Department of land resources
- Department of Drinking water resources
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Forest
- Environment and Climate change department.
The other institutions that were engaged with the mission are the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Application and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) as a technical partner.
The mission refocuses on various other missions like Mahatma Gandhi NREGA, XV Finance Commission Grants, PMKSY sub-schemes such as Watershed Development Component, and Har Khet Ko Pani. Also, the mission aims to increase the mobilisation of citizen and non-government resources for supplementing these efforts.
Amrit Sarovar Mission: Objectives
The government and secretary of all states have requested to complete the construction of the Amrit Sarovar as planned by the government of India. The government has ensured that there will be the use of technology in the construction of Amrit Sarovar. The states are requested to form the water structure for user’s association and impart required training for better development of the Amrit Sarovar. Till now, 12,241 sites are finalised for the construction of Amrit Sarovar out of which work has been started for 4,856 Amrit Sarovar.
Amrit Sarovar: Mission
- The mission is aimed it be completed by 15th August 2023.
- 50,000 Amrit Sarovar to be constructed all over the country.
- Every Amrit Sarovar will be approximate 1 acre with 10,000 cubic meters of water holding capacity.
- The focal point of the mission is people’s participation.
- The local freedom fighters, their family members, Martyr’s family members, Padma Shri Awardees and citizens of the local areas are the sites where Amrit Sarovar is to be constructed and they will be engaged in all stages of construction.
- On every Amrit Sarovar, Flag hosting will be done every Independence Day, 15 August.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6.ONE WORD A DAY – ASTROBEE
THE CONTEXT: Recently for the first time ever, two Astrobee robots have begun working independently on the International Space Station, side by side with humans.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Astrobee?
Astrobee is NASA’s new free-flying robotic system.
- According to NASA, “it will help astronauts reduce the time they spend on routine duties, leaving them more time to focus on the things that only humans can do.
- Working autonomously or via remote control by astronauts, flight controllers or researchers on the ground, the robots are designed to complete tasks such as taking inventory, documenting experiments conducted by astronauts with their built-in cameras or working together to move cargo throughout the station.”
- Astrobee also consists of a system that serves as a research platform that can be outfitted and programmed to conduct microgravity experiments. Thus, it will help to learn more about how robotics can benefit astronauts in space.
What are Honey, Queen and Bumble?
- The three free-flying robots are named Honey, Queen, and Bumble. The robots are shaped like cubes 12.5 inches wide.
- The Astrobee system consists of three cube-shaped robots, some software and a docking charging station used for recharging. They are about 32 centimetres wide.
- The three robots propel themselves using electric fans that allow them to fly through the microgravity environment of the International Space Station.
- They “look around” and navigate their surroundings using cameras and sensors.
- All of the robots are equipped with a perching arm that allows them to grasp handrails to either conserve energy or grab and hold items.
- When they are running low on charge, they can automatically return to their docking station to begin recharging.
What else you should know about Astrobee?
The Astrobee robots are built on the knowledge acquired from operating SPHERES (Synchronised Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellite) robots which have been operating on the International Space Station for over a decade. Once fully commissioned, the Astrobee system will take over for SPHERES as the space station’s robotic test facility.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY
Q.Consider the following statements with respect to UN peace keeping mission:
- UN peace keeping comprises of civilian, police and military personnel.
- In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN Peacekeeping Mission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) only 1
b) only 2
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR THE PRACTICE QUESTION
ANSWER: C
EXPLANATION:
- UN peacekeepers come from all walks of life, with diverse cultural backgrounds and from an ever-growing number of Member States.
- Peacekeepers are civilian, military and police personnel all working together. The roles and responsibilities of peacekeepers are evolving as peacekeeping mandates become more complex and multidimensional.
- In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN peacekeeping mission. The Formed Police Unit in Liberia provided 24-hour guard duty and conducted night patrols.
- Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed. In this mechanism, the electric traction motor uses the vehicle’s momentum to recover energy that would otherwise be lost to the brake discs as heat.
- Regenerative braking turns kinetic energy into electricity by reversing the process that drives the car forward.
- In electric cars, the drivetrain is powered by a battery pack that powers a motor (or motors), creating torque–rotational force–on the wheels.
- With regenerative braking, the energy from your spinning wheels is used to reverse the direction of electricity – from the electric motor(s) to the battery. All you have to do is remove your foot from the accelerator or, in some cases, press the brake pedal to activate regenerative braking. The electric motor not only acts as an electric generator, but it also helps slow your car down because energy is consumed by the wheels as they rotate the shaft in the electric motor.

