THE CONTEXT: Recently, the ruling party suspended its national spokesperson and expelled its Delhi spokesperson, following comments they had made about Islam and the Prophet. The move came after three countries in the Gulf region had summoned the Indian ambassadors to their nations to register their protest and demanded a public apology from India.It underlines the significance of the Gulf region for India. This article explains in detail the relations between India and the Gulf countries.
WHAT IS THE PERSIAN GULF REGION?
- The lands around the Persian Gulf are shared by eight countries- Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
- These countries are major producers of crude oil and natural gas and thereby contribute critically to the global economy and to their own prosperity.
- The area has approximately two-thirds of the world’s estimated proven oil reserves and one-third of the world’s estimated proven natural gas reserves.
- This factor has added to their geopolitical significance.
- A considerable amount of sea trade passes through the Gulf, leading to heavy traffic in the region.
WHY IS THE GULF REGION IMPORTANT FOR INDIA?
India has enjoyed centuries of good relations with countries like Iran, while smaller gas-rich nation Qatar is one of India’s closest allies in the region. India shares good relations with most of the countries in the Gulf. The two most important reasons for the relationship are oil and gas and trade. Two additional reasons are the huge number of Indians who work in the Gulf countries and the remittance they send back home.
FOUR PILLARS OF INDIA-GULF RELATIONS
TRADE RELATIONS
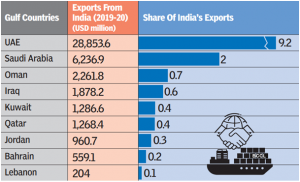
UAE: The UAE was India’s third-largest trading partner in 2021-2022 and second largest for both exports ($28 billion) and imports ($45 billion) when these are counted individually.
- In terms of total trade volume, the UAE ($72.9 billion) was behind the United States ($1.19 trillion) and China ($1.15 trillion).
- The UAE accounted for 6.6% of India’s total exports and 7.3% of imports in the last financial year, up 68.4% since the previous year when international trade was impacted by the pandemic.
Saudi Arabia: At a total volume of $42.9 billion in 2021-22, Saudi Arabia was India’s fourth-largest trading partner.
- While exports were low at $8.76 billion (2.07% of India’s total exports), imports from Saudi Arabia were the fourth largest at $34.1 billion (7%), up 50% from the previous year. Most of it was crude oil.
Iraq: It was India’s fifth-largest trading partner in 2021-22 at $34.3 billion.
Qatar: The total trade was $15 billion, accounting for just 1.4% of India’s total trade, but the country is India’s most important supplier of natural gas.
- Qatar accounts for 41% of India’s total natural gas imports. The UAE accounts for another 11%.
Oman: For Oman, India was the 3rd largest (after UAE and China) source for its imports and 3rd largest market (after UAE and Saudi Arabia) for its non-oil exports in 2019.
- Major Indian financial institutions have a presence in Oman. Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, textile etc.
OIL IMPORTS
- The 239 million tonnes of oil petroleum imports were worth USD 77 billion and accounted for nearly one-fifth of the country’s total imports in 2021.
- The share of Persian Gulf countries in India’s crude imports has remained at around 60% over the last 15 years.
- In 2021-2022, the largest exporter of oil to India was Iraq, whose share has gone up from 9% in 2009-2010 to 22%.
- Saudi Arabia has accounted for 17-18% of India’s oil imports for over a decade.
- Kuwait and UAE remain major oil exporters to India. Iran used to be the second-largest oil exporter to India in 2009-2010; its share went down to less than 1% in 2020-21 due to US sanctions.
INDIAN DIASPORA
- Counting only the 13.4 million non-resident Indians (NRIs), the Gulf has the largest numbers. The UAE (3.42 million), Saudi Arabia (2.6 million) and Kuwait (1.03 million) together account for over half of all NRIs.
REMITTANCES
- According to Ministry of External Affairs data, more than 13.46 million Indian citizens work abroad.
- Counting only the 13.4 million non-resident Indians (NRIs), the Gulf has the largest numbers. The UAE (3.42 million), Saudi Arabia (2.6 million) and Kuwait (1.03 million) together account for over half of all NRIs.
- In terms of remittances from abroad, India was the largest recipient in 2020 at $83.15 billion, according to World Bank data. This was near twice the remittances to the next highest recipient, Mexico, at $42.9 billion.
- The largest contributor is the huge Indian diaspora in the Gulf. In a bulletin in November 2018, it’s last on this subject, the Reserve Bank of India said the GCC countries accounted for more than 50% of the total $69 billion in remittances received by India in 2016-17.
- The UAE accounted for 26.9%, Saudi Arabia for 11.6%, Qatar for 6.4%, Kuwait for 5.5% and Oman for 3%. Beyond the GCC, remittances from the US accounted for 22.9%, second only to the UAE.
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF INDIA-GULF TRADE RELATIONS
EFFORTS BY THE INDIAN GOVERNMENT
SPECIAL FOCUS
- Since coming to power in 2014, the present Government has kept a special focus on maintaining or enhancing India’s relations with most of the countries in the region.
VISITS TO THE REGION
- The Indian Prime Minister (PM) has visited the region several times since 2014.
- He visited the UAE in 2015, 2018 and 2019, and Abu Dhabi’s crown prince came to India in 2017 and 2018.
- Visits were made to Qatar and Iran in 2016 and Saudi Arabia in 2016 and 2019.
- In 2018, he went to Jordan, Palestine and Oman, besides UAE, and became the first Indian Prime Minister to visit the Palestinian territory of Ramallah.
- He visited Bahrain in 2019.
- There have been similar reciprocal visits by leaders from these countries during these eight years.
- Even during the pandemic, Indian and Gulf region leaders maintained regular contact.
HIGHEST CIVILIAN HONOUR
- Palestine, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE and Jordan have excellent relations with India and Maldives, and Bahrain have bestowed their highest civilian honour on India’s Prime Minister.
GIVING IMPORTANCE TO THEIR RELIGION
- On his visits, PM visited some of the most popular mosques in those countries, including the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi in 2015 and the Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque in Muscat in 2018.
INDIA’S PRIORITIES IN THE GULF
- Securing long-term energy supply is of primary importance for India in the region.
- India is currently the fourth largest energy-consuming country in the world, and it may go up to the third position in the next couple of decades.
- India’s annual GDP growth at the rate of eight per cent would require further industrial growth, which would demand more energy supply for the country.
- The growing energy necessity has undoubtedly dictated India’s initiative of building up a ‘strategic energy partnership’ with the region to secure long-term energy supply for the country.
- The Gulf countries look at India as a fast-growing economy which holds the potential to compete with the major world economies.
- Realising the trade potential of the Gulf countries, India has entered into a negotiation with the GCC to finalise a Free Trade Agreement.
- The Gulf countries have huge potential for investing in different sectors in India as FDI for mutual benefit.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- There is a need to focus on the new and long-term possibilities for economic cooperation with the Gulf countries, which are looking at a future beyond oil.
- The Gulf states have embarked on massive economic diversification and are investing in a variety of new projects, including renewable energy, higher education, technological innovation, smart cities, and space commerce.
- With the rise of Khaleeji capitalism, the Gulf countries today deliver economic and security assistance to friendly states, build ports and infrastructure, acquire military bases and broker peace between warring parties and states.
- The UAE currently chairs the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and has been eager to work with India in developing joint infrastructure projects.
- India needs to bring scale and depth to its regional initiatives on connectivity and security in the Indian Ocean.
- Avoiding any such conflicts, there must be a clear synergy between India and the GCC countries, consolidating their traditional areas of cooperation — energy, trade and investment.
- They need to adopt an integrated and cohesive approach to develop ties in diverse areas — renewables, water conservation, food security, digital technology and skills development.
THE CONCLUSION: The Government and the diplomatic establishment can never underestimate the power of hurt sentiment, religious sensitivities in foreign policy, or the speed of social media. Many have questioned whether the reaction would have been as tough if the Government had taken the controversy and protests more seriously domestically and engaged with the problem much earlier. It was a lesson the US learned in 2012 after protests over a movie on Prophet Muhammad turned violent and led to the terrorist attack on the US embassy in Benghazi in which the US Ambassador was killed. The attacks on Charlie Hebdo and cartoonists in Europe in 2007 were another case in point- clearly, the sensitivities over a religious matter are important- as is protecting freedom of speech and ensuring no violence or harm comes to anyone.
Value Addition
What is GCC?
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a political and economic alliance of six countries in the Arabian Peninsula: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
Established in 1981, the GCC promotes economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the six states and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), two absolute monarchies(Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates).
Structure:
The GCC comprises six main branches that carry out various tasks, from the preparation of meetings to the implementation of policies. They are- the Supreme Council, Ministerial Council, Secretariat-General, Consultative Commission, Commission for the Settlement of Disputes and the Secretary-General.
Role of GCC today:
Whether the GCC still has a relevant function and role in the region is questionable. Though it was created for the purpose of solidifying union ranks, the blockade imposed on Qatar by its neighbours has largely annulled these principles.
The Gulf states have in the past differed in their views on several issues that have unfolded in the region over the past two decades. The role of the GCC has also been diminishing ever since the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq, with the six states illustrating various approaches to the war and its consequences. This has been enhanced during the wave of protests that swept the Middle East in 2011, known as the Arab Spring. Saudi Arabia has gained a dominant role within the GCC today.
Question for mains examination:
- Critically analyse India’s relations with the Gulf countries.
- In the 21st century, India needs to weigh the relationship with the Gulf countries not merely through an economic but strategic prism. Discuss.

