Table of Contents
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
THE ELECTION TO THE OFFICE OF THE VICE-PRESIDENT OF INDIA, 2022
THE CONTEXT: The Election Commission of India announced that the election to the office of the vice-president of India would be held on August 6, 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Article 324 of the Constitution read with the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952 and the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Rules, 1974, vests the superintendence, direction and control of the conduct of election to the office of the Vice-President of India in the Election Commission of India.
- The Election Commission is mandated to ensure that the election to the office of the Vice-President of India must be a free and fair election and the Commission is taking all necessary steps for discharging its constitutional responsibility. The Election Commission of India is privileged and honoured to announce today the schedule of election for the 16th Vice-Presidential Election.
- As per Article 68 of the Constitution, the election to fill the vacancy caused by the expiration of the term of office of the outgoing vice-president is required to be completed before the expiration of the term.
- Section 4(3) of the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952 provides that the notification for election shall be issued on or after the sixtieth day before the expiration of term of office of the outgoing Vice-President.
- As per Article 66 of the Constitution of India, the Vice-President is elected by the members of the Electoral College consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote. For 2022, 16th Vice-Presidential Election, the Electoral College consists of:
- 233 elected members of Rajya Sabha,
- 12 nominated members of Rajya Sabha, and
- 543 elected members of Lok Sabha.
Electoral College comprises of a total of 788 members of both Houses of Parliament. Since all the electors are members of both Houses of Parliament, the value of the vote of each Member of Parliament would be the same i.e.1 (one).
- For marking the vote, the Commission will supply particular pens. The pen will be given to the electors in the polling station by the designated official when the ballot paper is handed over. Electors have to mark the ballot only with this particular pen and not with any other pen. Voting by using any other pen shall lead to invalidation of the vote at the time of counting.
- The Election Commission, in consultation with the Central Government, appoints the Secretary-General of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, by rotation, as the Returning Officer. Accordingly, the Secretary-General, Lok Sabha will be appointed as the Returning Officer for the present election to the Office of the Vice-President of India. The Commission has also decided to appoint Assistant Returning Officers in Parliament House (Lok Sabha) to assist Returning Officers.
THE SOCIAL ISSUES AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
NEW RESEARCH: BETTER ROAD SAFETY MEASURES COULD SAVE HALF A MILLION LIVES ANNUALLY WORLDWIDE
THE CONTEXT: According to a study published in the Lancet, the benefits of more motorcyclists wearing helmets would be the biggest in China, where 13,703 lives could be saved every year, followed by Brazil (5,802 lives), and India (5,683 lives).
THE HIGHLIGHTS OF THE REPORTS:
- New global and country-level estimates suggest that routinely wearing helmets and seat belts, obeying speed limits, and avoiding driving drunk could save between 347,000 and 540,000 lives worldwide every year.
- Analysis of data from 74 studies in 185 countries estimates that targeting four key risk factors for road injuries and deaths (speeding, drink driving, and non-use of crash helmets and seat belts) could prevent between 25% and 40% of all fatal road injuries worldwide every year.
- According to the study, the Interventions to reduce speeding such as infrastructure changes and electronic speed control could save an estimated 347,258 lives globally each year, while measures to tackle drunk driving such as enhanced drink driving enforcement could save a further 16,304 lives.
- An estimated 121,083 and 51,698 lives could be saved by passing and enforcing rules on wearing seat belts and motorcycle helmets respectively.
- Improving seat belt use would have a particularly large effect on reducing road deaths in the United States (saving an estimated 14,121 lives every year) and China (13,228). Tackling speeding would be the single most effective measure to reduce road fatalities in most countries, preventing an estimated 88,374 deaths in China, 1,027 in Spain, and 815 in the United Kingdom.
- The Lancet Series on road safety, published ahead of the first ever UN High-Level Meeting on Road Safety, calls for increased political and financial commitments, and for road safety to be included in mainstream development policies. It argues that this is essential to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including the target to halve road traffic crash fatalities and injuries by 2030.
- Deaths on roads are a major problem in India. Each year road accidents kill about 150,000 people and injure another 450,000 in the country. The World Bank noted in a report this month that with only 1 per cent of the world’s vehicles, India accounts for almost 10 per cent of all crash related deaths.
POINTS TO REMEMBER:
- Brasilia Declaration: Related to Road Safety.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
GREEN HYDROGEN IS CRITICAL TO INDIA’S ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AND NET-ZERO AMBITIONS: REPORT
THE CONTEXT: A new report released today by NITI Aayog highlights that green hydrogen can substantially spur industrial decarbonisation and economic growth for India in the coming decades.
THE EXPLANATION:
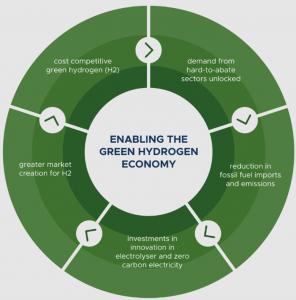
- THE REPORT: Harnessing Green Hydrogen: Opportunities for Deep Decarbonisation in India provides a pathway to accelerate the emergence of a green hydrogen economy, which is critical for India to achieve its net-zero ambitions by 2070.

- The report,co-authored by NITI Aayog and RMI, underscores that green hydrogen—produced by renewable energy through electrolysis of water—will be crucial for achieving decarbonisation of harder-to-abate sectors such as, fertilisers, refining, methanol, maritime shipping, iron & steel and transport.
- It further states that with emerging global momentum on hydrogen, India can situate this decarbonisation opportunity not just within the context of a low-carbon economy but also as an enabler of energy security and economic development for the nation.
- While hydrogen can be produced from multiple sources, India’s distinct advantage in low-cost renewable electricity means that green hydrogen will emerge as the most cost-effective form. The report concludes that hydrogen demand in India could grow more than fourfold by 2050, representing almost 10% of global demand. Given that the majority of this demand could be met with green hydrogen in the longterm, the cumulative value of the green hydrogen market in India could reach US $8 billion by 2030.
The report describes pathways that can capture the benefits of green hydrogen:
- Near-term policy measures can bring down the current costs of green hydrogen to make it competitive with the existing grey hydrogen (hydrogen produced by natural gas) prices. Medium-term price targets should be set to guide the industry towards making green hydrogen the most competitive form of hydrogen.
- Government can encourage near term market development by identifying industrial clusters and enacting associated viability gap funding, mandates and targets.
- Opportunities around research and development and manufacturing of components like electrolysers need to be identified and appropriately encouraged with adequate financial mechanisms such as production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes to enable 25 GW of manufacturing capacity of electrolysers by 2028.
- A globally competitive green hydrogen industry can lead to exports in green hydrogen and hydrogen-embedded low-carbon products like green ammonia and green steel that can unlock 95 GW of electrolysis capacity in the nation by 2030.
- NITI Aayog’s partner for this report, RMI, works for the transformation of global energy systems through market-driven solutions to align with a 1.5°C future and secure a clean, prosperous, zero-carbon future for all. It works in the world’s most critical geographies and engages businesses, policymakers, communities, and NGOs to identify and scale up energy system interventions that will cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50 percent by 2030.
VALUE ADDITION:
- ‘Green’ hydrogen is produced by using renewable energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. In contrast, the conventional process of making hydrogen uses fossil fuels.
- Hydrogen is a key input in fertilizers and refineries, so green hydrogen would help these industries cut aggregate emissions. It could also be used in steel manufacturing to reduce emissions by replacing the use of coal as an energy source and as a reducing agent.

THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
WHAT IS CAPSTONE, NASA’S NEW SATELLITE?
THE CONTEXT: Recently, NASA launched CAPSTONE, a microwave oven-sized CubeSat weighing just 55 pounds (25 kg). CAPSTONE, short for Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment, is designed to test a unique, elliptical lunar orbit.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The satellite, launched on Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1, is heading toward an orbit intended in the future for Gateway, a Moon-orbiting outpost that is part of NASA’s Artemis program.
- As a pathfinder for Gateway, CAPSTONE aims to help reduce risk for future spacecraft by validating innovative navigation technologies, and by verifying the dynamics of the halo-shaped orbit.
- The orbit is known as a near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO). It is significantly elongated, and is located at a precise balance point in the gravities of Earth and the Moon. This offers stability for long-term missions like Gateway, NASA said on its website.
- At the Moon, CAPSTONE will enter NRHO, where it will fly within 1,600 km of the Moon’s North Pole on its near pass and 70,000 km from the South Pole at its farthest. The spacecraft will repeat the cycle every six-and-a-half days and maintain this orbit for at least six months to study dynamics.
- According to NASA, CAPSTONE will gain experience with small dedicated launches of CubeSats beyond low-Earth orbit, to the Moon, and beyond.
- The spacecraft is currently in low-Earth orbit. It is attached to Rocket Lab’s Lunar Photon.
EXPLAINED: HOW INDIA’S FIRST MRNA VACCINE FOR COVID-19 WAS CREATED
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the country’s first home-grown mRNA Covid-19 vaccine — GEMCOVAC-19 — developed at Pune’s Gennova Biopharmaceuticals has got a ‘restricted emergency use’ nod for the 18-and-above age group.
THE EXPLANATION:
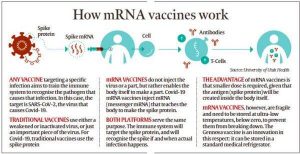
- As mRNA vaccines are required to be kept at sub-zero temperatures, it was a mammoth task for Gennova scientists to develop a thermostable mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. Scientists had to innovate to suit local needs to make it affordable and deployable. The new vaccine can now be stored at the temperature of a standard medical refrigerator.
The mRNA platform
- As the Covid-19 pandemic spread, an mRNA vaccine candidate was the first to enter human trials globally. The first two vaccines that were made available for use in the US were based on mRNA technology.
- Unlike vaccines that put a weakened or inactivated virus in your body to activate an immune response, these two Covid-19 vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) used messenger RNA or mRNA to deliver a message to your immune system.
- Basically, the technology uses genetically engineered mRNA to instruct cells to make the S-protein found on the surface of the Covid-19 virus. According to reports from US-based Mayo Clinic, after vaccination, the muscle cells begin making S-protein pieces and displaying them on cell surfaces. This causes the body to create antibodies.
But these vaccines have to be stored at sub-zero temperatures as mRNA is fragile and breaks down easily.
Thermostable vaccine
- “Unlike in the West, where the vaccine has to be stored at sub-zero temperatures, the challenge in India was to be able to store the vaccine between 2-8 degree Celsius. We had to innovate to suit our local needs as to what is affordable and deployable. GEMCOVAC-19 can now be stored at the temperature of a standard medical refrigerator,” says Dr Sanjay Singh, CEO of Gennova Biopharmaceuticals.
- The conversion from liquid to powder form of the vaccine takes place via Lyophilisation — this is freeze-drying, a process where the water is removed from the product after it is frozen and placed under a vacuum allowing the ice to change directly from solid to vapour without passing through a liquid phase.
- However, just removing water by Lyophilisation of the mRNA vaccine does not work. So, the surrounding pressure has to be tweaked and then kept stable to ensure the characteristics of the vaccine are the same as before Lyophilisation. For this to be achieved, the key was to add an external agent which at a certain critical concentration keeps it stable under lyophilized conditions. The Lyophilisation technology is not new, but a lyophilized mRNA vaccine is unique.
Trials and safety
- Freeze-drying the large and unstable mRNA molecule with the nanoparticle was a daunting challenge. However, Gennova invested countless man-hours in the hope of lyophilizing the mRNA vaccine in a single vial within a year. This thermostable vaccine was thoroughly tested in various animal models to ensure its safety and immunogenicity before entering human clinical trials.
- Phase 1 and 2 trial data across 480 participants had been submitted earlier, and data from Phase 3 trial across 4,000 participants was then presented to the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO). During the Phase 3 trials, 3,000 participants were administered the mRNA Covid-19 vaccine and 1,000 were given Covishield.
- According to officials at Gennova, the trial data showed that the vaccine was safe and well-tolerated. Immunogenicity measured at 2 weeks post-dose showed that GEMCOVAC-19 is non-inferior to Covishield.
- The two-dose vaccine will have to be administered intramuscularly, 28 days apart.
HIGH-SPEED EXPENDABLE AERIAL TARGET – ABHYAS – SUCCESSFULLY FLIGHT-TESTED
THE CONTEXT: Recently, ABHYAS – High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT) was successfully flight-tested from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The performance of the aircraft at low altitudes including sustained level and high manoeuvrability was demonstrated during the test flight. The target aircraft was flown from a ground-based controller in a pre-designated low-altitude flight path, which was monitored by various tracking sensors deployed by ITR,
 including radar and an electro-optical targeting system.
including radar and an electro-optical targeting system.
- ABHYAS is designed & developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The air vehicle was launched using twin under-slung boosters which provide the initial acceleration to the vehicle.
- It is powered by a small gas turbine engine to sustain a long endurance flight at high subsonic speed. The target aircraft is equipped with Micro-Electromechanical Systems-based Inertial Navigation System for navigation along with the Flight Control Computer for guidance and control along with Indigenous Radio Altimeter for very low altitude flight and Data Link for encrypted communication between the Ground Control Station and Target Aircraft. The vehicle is programmed for fully autonomous flight.
THE GOVERNMENT POLICIES AND INTERVENTION
EXPLAINED: WHY A PROPOSED MEGA TEXTILE PARK IN LUDHIANA UNDER THE PM MITRA SCHEME IS FACING OPPOSITION
THE CONTEXT: A proposal to set up a mega textile park in Punjab’s industrial hub, Ludhiana, has been red-flagged by locals, environmentalists and even some political leaders.
THE EXPLANATION:
The project
- A Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Park, under the PM-MITRA scheme, has been proposed to be set up in Ludhiana.
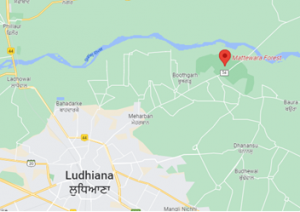
- The land required for the project, being undertaken jointly by the Centre and the state government, falls near the Mattewara forest and on the river Sutlej floodplains.
- The notification issued by the Union Ministry of Textiles says that under the PM-MITRA, a total of seven such parks will come up across the country with a total outlay of Rs 4,445 crore. The notification also specifies the ‘objective of the project’ as ‘sustainable industrialisation’ that does not harm the environment to ‘meet the United Nations sustainable development goal 9.’
The opposition
- The proposed project site is located near the Mattewara forest and on floodplains of river Sutlej.
- It touches Mattewara forest from two sides, and also borders river Sutlej on one side.
- There are fears that the project would not only disturb the biodiversity of the protected forest but might also lead to chemical discharge from factories into the river.
- Spread over 2,300 acres, the Mattewara forest is often called the lungs of Ludhiana district and is home to several animal and avian species including peacocks, sambhar, antelopes (nilgai), monkeys, deers etc.
VALUE ADDITION:
ABOUT PM MITRA SCHEME:
- Ministry of Textiles has issued a notification to set up 7 Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel (PM MITRA) Parks with a total outlay of Rs. 4,445 crore.
- These are aimed at helping India to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 9: “Build resilient infrastructure, promote sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”.
- It is hoped that the PM MITRA Parks will have world-class industrial infrastructure which would attract cutting age technology and boost FDI and local investment in the textiles sector.
KEY FEATURES
The PM MITRA scheme is Inspired by the 5F vision of Hon’ble Prime Minister – Farm to Fibre to Factory to Fashion to Foreign. It aspires to fulfil the vision of building an Aatmanirbhar Bharat and to position India strongly on the Global textiles map.
- PM MITRA Parks will offer an opportunity to create an integrated textiles value chain right from spinning, weaving, processing/dyeing and printing to garment manufacturing at 1 location
- Integrated Textile Value chain at 1 location will reduce logistics cost of Industry
- Intended to generate ~1 lakh direct and 2 lakh indirect employment per park
- Sites for PM MITRA Parks will be selected by a Challenge Method based on objective criteria
- Proposals of State Governments having ready availability of contiguous and encumbrance-free land parcel of 1,000+ acres along with other textiles related facilities & ecosystem are welcome
Several states such as Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Assam, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Telangana have expressed interest.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q. Haumea, Makemake, and Eris are –
a) Comets
b) Satellites of Jupiter
c) Plutoids
d) Stars
ANSWER FOR 29 JUNE 2022
Answer: D
Explanation:
- Gennova Biopharmaceuticals – mRNA vaccine
- Oxford-AstraZeneca – Vector based vaccine
- Zydus Cadila – DNA based vaccine
- Novavax – Protein Subunit Vaccine
Spread the Word


 including radar and an electro-optical targeting system.
including radar and an electro-optical targeting system.