Table of Contents
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
WHY IS DCP’S NOD REQUIRED FOR FILING POCSO FIRS?
THE CONTEXT: After facing criticism over a circular which mandated that no FIR for molestation or offences under the POCSO Act should be registered without the zonal DCP’s permission, the Mumbai police commissioner said the directive can be reconsidered.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO), 2012:
It was enacted to protect children from offences of sexual assault, sexual harassment, and pornography with due regard for safeguarding the interest and well-being of children.
- It was amended in August 2019 to provide more stringent punishment, including the death penalty, for sexual crimes against children.
- It defines a child as any person below eighteen years of age and regards the best interests and welfare of the child as a matter of paramount importance at every stage, to ensure the healthy physical, emotional, intellectual and social development of the child.
- It deems a sexual assault to be “aggravated” under certain circumstances, such as when the abused child is mentally ill or when the abuse is committed by a person in a position of trust or authority like a family member, police officer, teacher, or doctor.
- It also casts the police in the role of child protectors during the investigative process.
- The Act stipulates that a case of child sexual abuse must be disposed of within one year from the date the offence is reported.
- Implementation of Act by statutory bodies- the National Commission for the Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) and State Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights (SCPCRs).
POCSO (Amendment) Act 2019:
Provision of the death penalty in cases of sexual offences against children.
- Levy of fines and imprisonment to curb child pornography.
- Protection of children from sexual offences in times of natural calamities.
Why was the POCSO Act enacted?
- The act was required as the Indian Penal Code was inadequate to address Sexual Assault, Sexual Harassment, Pornography and Sexual Violence against boys and a child.
- The act is gender-neutral and recognizes both girls and a boy as a victim of sexual violence.
- The POCSO was also required as the procedure for the crime reported under IPC is more rigid and also not child friendly.
- Also, India is a signatory of the United Nations Convention on Rights of Children (UNCRC).
- The POCSO Act, 2012 was enacted to ensure a child-friendly procedure for the filing of the report and fulfils the requirement of Article 15(3) of the Constitution of India.
- Clause 3 of Article 15 of the Constitution gives powers to the legislature to create special provisions for women and children.
Features of the POCSO Act:
- The Act defines the various types of offences, touch-based, non-touch, penetrative, pornographic crimes etc., in detail and doesn’t leave any kind of offence.
- The act also defines a person under the age of 18 as a child.
- The act also has a feature to give compensation to the victim.
- Only the POCSO Court has the jurisdiction to deal with the matter related to the act.
- The INNOCENT TILL PROVEN GUILTY principle does not apply in the matter related to the POCSO Act, 2012.
- Once a complaint gets filed in this case, it gets presumed that the intention was to commit a sexual act.
- If a child goes through abuse at home, he will get relocated by the Child Welfare Commission for care and protection.
EXPLAINED: WHAT IS THE E-VIDHAN SYSTEM FOR PAPERLESS LEGISLATION?
THE CONTEXT: A delegation of MLAs from Gujarat visited the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly on June 9, to learn about the novel e-Vidhan system for paperless proceedings that has been recently adopted by the UP-state assembly.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Uttar Pradesh is one of the few state legislatures in India that has implemented the digital Vidhan Sabha system, and its last session was completely digitised. Earlier in May, a training programme was organised to familiarise the representatives with the technology.
- The National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) is a system for digitising the legislative bodies of all Indian states and the Parliament through a single platform on which house proceedings, starred/unstarred questions and answers, committee reports etc. will be available. Nagaland became the first state to implement NeVA, in March 2022.
What is the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) system?
The NeVA system has been developed to make all the work and data related to legislative bodies available online for the use of both citizens and the members of Assemblies. It includes a website and a mobile app.
Why is NeVA being introduced?
- This has been done for streamlining information related to various state assemblies, and to eliminate the use of paper in day-to-day functioning. Its website states: “Several thousand tons of papers would be saved, which in turn would help in saving lakhs of trees annually”.
In December 2021, the Government of Dubai became the world’s first government to go 100 per cent paperless. It announced all procedures were completely digitised. This, as per a government statement, would cut expenditure by USD 350 million and also save 14-million-manhours.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
INDIA-RUSSIA DEAL ON RADIO EQUIPMENT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Radio technical Systems (RTS) of Russia has signed a large-scale contract with the Airports Authority of India (AAI) for the supply of radio equipment.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Russian company will manufacture 34 sets of instrument landing systems (ILS) 734 for the modernisation of 24 airports in India. The contract comes amid the war in Ukraine and pressure from the West on India to diversify its dependence on defence needs.
- “The domestic manufacturer received the right to conclude a contract based on the results of a global tender, in which, in addition to RTS, the world’s largest suppliers of radio equipment took part.
- According to the contract, the first part of landing systems ILS-734 must be shipped before November 2022. “The contract between RTS and AAI has become a breakthrough for Russian business in the highly competitive market of ground-based radio equipment in India. There is no doubt that the successful execution of the contract will open up new opportunities for the implementation of joint projects to modernise Indian airport infrastructure.
THE HEALTH ISSUES
EXPLAINED: WHY BABIES MUST ONLY BE BREASTFED FOR 6 MONTHS
THE CONTEXT: According to the recently published guidelines on nutrition, the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences recommended that newborns be given a mixture of ghee and honey, a paste of gold, and several herbs some of which contain psychoactive ingredients.
THE EXPLANATION:
The guidelines recommend just honey and butter with some herbs on the first day of birth, ghee with herbs on the second day, and colostrum (mother’s first milk) with ghee and honey only on the third day of birth.
Several doctors have called out these guidelines for contradicting the proven benefits of breastfeeding. Some have noted that feeding newborns honey could lead to a rare but serious infection called botulism.
When should breastfeeding start?
According to the Doctors, the breastfeeding should start as soon as possible, preferably within one hour of birth, and babies should be exclusively breastfed for six months. “It is important that babies start breastfeeding soon after birth; the colostrum is rich in antibodies and protects them from infections. In fact, honey, sugar, salt, nuts, and cow’s milk should not be given to a child until age 1.
Why six months?
“Breast milk contains adequate calories needed for up to six months. Babies can consume only a certain amount of liquids. Say they can consume 800 ml fluids — if you give them 100 ml of water, they miss out on calories contained in 100 ml of milk”.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: DEFENCE TECHNOLOGY
A LOOK AT THE 21-YEAR JOURNEY OF THE VERSATILE ASSET
THE CONTEXT: On June 12, 2001, the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was first tested from a land-based launcher in Chandipur. In the 21 years since, BrahMos has been upgraded several times, with versions tested on land, air and sea platforms., which recently bagged an export order from the Philippines.
BACKGROUND AND DEVELOPMENT
- An Inter-Governmental Agreement was signed with Russia in Moscow in 1998 by Dr Kalam, who headed the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), and N V Mikhailov, Russia’s then Deputy Defence Minister. This led to the formation of BrahMos Aerospace, a joint venture between DRDO and NPO Mashinostroyenia (NPOM), the Indian side holding 50.5% and the Russians 49.5%.
- In 1999, work on the development of missiles began in the labs of DRDO and NPOM after BrahMos Aerospace received funds from the two governments. The first successful test in 2001 was conducted from a specially designed land-based launcher. The missile system has since reached some key milestones, with the first major export order of $375 million received from the Philippines Navy in 2022.

PRESENT AND FUTURE
- According to scientists, what makes the missile system unparalleled is its extreme accuracy and versatility. Land-based BrahMos formations along the borders, BrahMos-equipped Sukhoi-30s at bases in Northern theatre and Southern peninsula, and BrahMos-capable ships and submarines deployed in sea together form a triad.
- With requirements evolving in multi-dimensional warfare, the BrahMos is undergoing a number of upgrades and work is on developing versions with higher ranges, manoeuvrability and accuracy.
- Versions currently being tested include ranges up to 350 km, as compared to the original’s 290 km. Versions with even higher ranges, up to 800 km, and with hypersonic speed are said to be on cards. Efforts are also on to reduce the size and signature of existing versions and augment its capabilities further.
Versions deployed in all three Armed forces are still being tested regularly, and so are versions currently under development.
LAND-BASED: The land-based BrahMos complex has four to six mobile autonomous launchers, each with three missiles on board that can be fired almost simultaneously. Batteries of the land-based systems have been deployed along India’s land borders in various theatres.
The upgraded land-attack version, with the capability of cruising at 2.8 Mach, can hit targets at a range up to 400 km with precision. Advanced versions of higher range and speed up to 5 Mach are said to be under development. The ground systems of BrahMos are described as ‘tidy’ as they have very few components.
SHIP-BASED: The Navy began inducting BrahMos on its frontline warships in 2005. These have the capability to hit sea-based targets beyond the radar horizon. The Naval version has been successful in sea-to-sea and sea-to-land modes. The BrahMos can be launched as a single unit or in a salvo of up to eight missiles, separated by 2.5-second intervals. These can target a group of frigates with modern missile defence systems.
AIR-LAUNCHED: On November 22, 2017, BrahMos was successfully flight-tested for the first time from a Sukhoi-30MKI against a sea-based target in the Bay of Bengal. It has since been successfully tested multiple times.
BrahMos-equipped Sukhoi-30s, which have a range of 1,500 km at a stretch without mid-air refuelling, are considered key strategic deterrence for adversaries both along land borders and in the strategically important Indian Ocean Region. The IAF is said to be integrating BrahMos with 40 Sukhoi-30 fighter jets across the various bases.
SUBMARINE-LAUNCHED: This version can be launched from around 50 m below the water surface. The canister-stored missile is launched vertically from the pressure hull of the submarine and uses different settings for underwater and out-of-the-water flights. This version was successfully tested first in March 2013 from a submerged platform off the coast of Visakhapatnam.
EXTRA CHROMOSOME IN 1 IN 500 MEN, DISEASE RISK HIGHER: STUDY
THE CONTEXT: According to researchers at the University of Cambridge around one in 500 men could be carrying an extra X or Y chromosome, most of them unaware. This puts them at increased risk of diseases such as type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis and thrombosis, the researchers report in a study published in Genetics in Medicine.
THE EXPLANATION:
- They analysed genetic data collected on over 200,000 men aged 40-70 from UK Biobank, a biomedical and anonymised database on half a million UK participants. They found 356 men who carried either an extra X chromosome or an extra Y chromosome.
-
Sex chromosomes determine our biological sex. Men typically have one X and one Y chromosome, while women have two Xs. However, some men also have XXY or XYY.
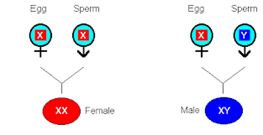
- In the study, the researchers identified 213 men with an extra X chromosome and 143 men with an extra Y chromosome. As the participants in UK Biobank tend to be ‘healthier’ than the general population, this suggests that around one in 500 men may carry an extra X or Y chromosome.
- Only a small minority of these men had a diagnosis of sex chromosome abnormality on their medical records or by self-report: 23% men with XXY and only one of the 143 XYY men (0.7%) had a known diagnosis.
- By linking genetic data to routine health records, the team found that men with XXY have much higher chances of reproductive problems, including a three-fold higher risk of delayed puberty and a four-fold higher risk of being childless. These men also had significantly lower blood concentrations of testosterone. Men with XYY appeared to have a normal reproductive function.
-
Men with either XXY or XYY had higher risks of several other health conditions. They were three times more likely to have type 2 diabetes, six times more likely to develop venous thrombosis, three times as likely to experience pulmonary embolism, and four times more likely to suffer from Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION FOR 13TH JUNE 2022
Q1. Consider the following statements about Environment Performance Index:
- It is published by researchers from Yale and Columbia Universities.
- It is published annually.
- India ranked last among 180 countries ranked in 2022.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 2 and 3 only
ANSWER FOR 11TH JUNE 2022
Answer: D
Explanation:
Impact of rupee depreciation
- It benefits exporters.
- Non-resident Indians (NRIs) who send money back home will end up sending more in Rupee value.
- Costly imports: imported items get costlier e.g. oil imports, will get costlier, which can directly impact consumers.
- Costlier loans: Interest rates are hiked to stabilise inflation. High rates will make borrowing costlier, discouraging consumers and businesses to spend on big-ticket items.
- Foreign investors pull out of Indian equities. This means that there could be a sharp fall in equity markets, resulting in a decline in stock and equity mutual funds investments.
- Foreign education would get more expensive. This will be because one will have to give more Rupees for every Dollar due to its depreciation.
- Expensive foreign tours and travel.
- It poses a risk of imported inflation (cost-push inflation).
- The current account deficit will widen.
- Depletion of foreign exchange reserves.

