THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Earth Science unveiled India’s Arctic Policy on 17 March 2022, titled “India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development”, with the aim of enhancing the country’s cooperation with the resource-rich and rapidly transforming region. The policy also seeks to combat climate change and protect the environment in the region, which is warming three times faster than the rest of the world. This article explains the need for an Arctic Policy for India, looks into the gaps in India’s present engagement in the Arctic, and analyses the features of India’s Arctic Policy released recently.
WHAT AND WHERE IS THE ARCTIC?
- It is commonly understood to refer to the region above the Arctic Circle, north of latitude 66° 34′ N, which includes the Arctic Ocean with the North Pole at its centre.
- The Arctic is a vast and varied region whose annual cycle is influenced by the strong variation in the amount of light. The further north you are, the more there are daylight hours in winter and nightless nights in summer. In the Arctic, winters are long, and the growing season is short. The Arctic land area comprises only about 5% of the land surface of Earth.
- The Arctic is home to almost four million inhabitants, of which approximately one-tenth are considered indigenous people.
- The Arctic Ocean and its surrounding landmass have been a topic of immense interest and a high-priority area of research among the global scientific fraternity, as well as of importance to policymakers.
- The Arctic influences the atmospheric, oceanographic and bio-geo-chemical cycles of the Earth’s ecosystem.
WHAT IS ARCTIC COUNCIL?
- The Arctic Council is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic Indigenous peoples and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic. It was formally established in 1996.
- It is not a treaty-based international legal entity like the UN organizations or trade or regional groupings such as NATO or ASEAN.
- It was set up by the 8 Arctic countries by means of the Ottawa Declaration of 1996. These countries are the US, Canada, Russia, Iceland, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, and Finland.
- In addition to these countries, 6 organizations representing the indigenous people of the Arctic region have also been given the status of permanent participants.
- India holds one of the 13 positions as the Observer in the Arctic Council.
What is the observer status of the Council?
- The observer status is provided to countries or entities that support the objectives of the Arctic Council through financial or other contributions.
- Observers cannot participate in the decision-making process.
- They are invited to participate only in the meetings of the Council, particularly at the level of the working groups.
- The renewal of the observer status is just a formality. The status, once given, continues until the entity carries out any activities that run against the objectives of the Council.
INDIA’S JOURNEY AT THE ARCTIC COUNCIL
1920: India’s engagement with the Arctic began when it signed the Svalbard Treaty in Paris between Norway, the US, Denmark, France, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Great Britain, and Ireland, and the British overseas Dominions and Sweden concerning Spitsbergen.
2007: India initiated its Arctic research program in 2007 with a focus on climate change in the region.
2008: India established Himadri- India’s first permanent Arctic research station located at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway.
2013: India was first granted the Observer status in 2013, along with five other nations.
2014: India deployed IndARC it is India’s first underwater moored observatory in the Arctic region 2014 at Kongsfjorden fjord, Svalbard, Norway. Its research goal is to study the Arctic climate and its influence on the monsoon.
2016: Another atmospheric laboratory was established in 2016 at Gruvebadet in Ny-Alesund with the aim of initiating studies on clouds, precipitation, long-range pollutants, and other background atmospheric parameters.
2019: India was re-elected as an Observer to the Arctic Council.
ABOUT: INDIA’S ARCTIC POLICY
India’s Arctic Policy aims to enhance the country’s cooperation with the resource-rich and rapidly transforming Arctic region. The policy also seeks to combat climate change and protect the environment in the region, which is warming three times faster than the rest of the world. It was released by the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
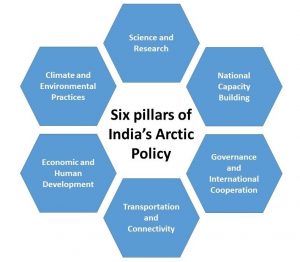
OBJECTIVES OF INDIA’S ARCTIC POLICY
- It aims to strengthen national capabilities and competencies in science and exploration, climate and environmental protection, and maritime and economic cooperation with the Arctic region.
- To strengthen institutional and human resource capacities within the government and academic, research and business institutions through inter-ministerial coordination in pursuit of India’s interests in the Arctic.
- To enhance understanding of the impact of climate change in the Arctic region on India’s climate, economic, and energy security.
- To promote better analysis, prediction, and coordinated policymaking on the implications of ice melting in the Arctic on India’s economic, military and strategic interests related to global shipping routes, energy security, and exploitation of mineral wealth.
- To study the linkages between polar regions and the Himalayas and deepen the cooperation between India and the countries of the Arctic region under various Arctic forums, drawing expertise from scientific and traditional knowledge.
- To increase India’s participation in the Arctic Council and improve understanding of the complex governance structures in the Arctic, relevant international laws, and geopolitics of the region.
RELEVANCE OF ARCTIC POLICY FOR INDIA?
The relevance of the Arctic for India can be broadly explained under three categories:
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH, CLIMATE CHANGE AND THE ENVIRONMENT:
- Under the banner of science and research, the Indian government hopes to build its research capabilities in the region by strengthening existing facilities, such as the Himadri Arctic station in Svalbard.
- It also hopes to align Indian research with international Arctic priorities. The policy further lays down plans to deploy space technology to better study the Arctic region.
ECONOMIC AND HUMAN RESOURCES:
- The Arctic region has rich deposits of coal, gypsum and diamonds and also substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz. Greenland alone possesses about a quarter of the world’s rare earth reserves.
- The Arctic contains a wealth of hydrocarbon resources.
- Arctic also has the potential to address India’s energy security needs and deficiency of strategic and rare earth minerals.
GEOPOLITICAL AND STRATEGIC:
- The Arctic region is significant due to the shipping routes that run through it.
- According to an analysis published by the Manohar Parrikar Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses, the adverse effects of the Arctic are not just impacting the availability of mineral and hydrocarbon resources but also transforming global shipping routes.
- According to the Ministry of External Affairs, India can play a constructive role in securing a stable Arctic.
- The region holds immense geopolitical importance as the Arctic is projected to be ice-free by 2050, and world powers are making a beeline to exploit the region rich in natural resources.
GAP IN INDIA’S APPROACH
LACK OF AN ARTICULATED POLICY:
- Even though the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) of the Government of India has listed India’s interests in the Arctic to be “scientific, environmental, commercial as well as strategic”, till recently, India was one among the four of the 13 Observer nations of the Arctic Council that did not have a nationally articulated Arctic Policy.
SCIENTIFIC ORIENTATION:
- India needs to go beyond the purely scientific approach in the Arctic. In keeping with its growing stature and consequent say in world affairs, India ought to be better equipped to understand the dynamics of the Arctic geo-politics and governance.
INADEQUATE FUNDING:
- Presently, India’s polar research for the Antarctic, Arctic, Southern Ocean and Himalayas is budgeted under the umbrella Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) programme of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES). Considering that India’s Antarctic Programme is about five times bigger than its Arctic programme.
POLAR RESEARCH VESSEL (PRV):
- The lack of a dedicated PRV is considered to be a serious impediment to the growth of India’s polar activities.
WHOLE-OF-GOVERNMENT FOCUS:
- Presently, the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), under the MoES, is the nodal agency for India’s polar research programme, which includes Arctic studies.
- The MEA provides the external interface to the Arctic Council through the United Nations Economic & Social (UNES) Division.
- However, the eight countries of the Arctic Council are divided between the Americas, Eurasia and Central Europe Divisions, possibly preventing a region-wide focus on the fast-changing geophysical and geopolitical Arctic landscape.
- Further, there is no nodal body to coordinate all the activities of the Government of India relating to the Arctic region.
AWARENESS AND CAPACITY:
- The Arctic has largely been ignored in India on the ground that it is far away and does not have a direct impact on India. This has resulted in a lack of national capacity on Arctic issues.
- As the Arctic opens up, India needs to expand domestic capability and capacity by building a wide-ranging institutional base on Arctic maritime, legal, environmental, social, policy and governance issues.
- This can only happen through the introduction of an Arctic-related curriculum in our education system at all levels. India’s engagement with the Arctic needs to be built on sound augmentation of its domestic capacity.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- Expand the capacity and awareness of Arctic-related scientific research by strengthening the NCPOR, involving other relevant academic and scientific institutions in India, identifying nodal institutes and promoting partnerships among institutions and agencies.
- Promote research capacities in Indian Universities in the fields of earth sciences, biological sciences, geosciences, climate change and space-related programmes relevant to the Arctic.
- Widen the pool of experts in sectors such as mineral, oil and gas exploration, blue-bio economy and tourism relevant to the Arctic.
- Strengthen training institutions for training seafarers in Polar/Ice-Navigation and build region-specific hydrographic capacity and skills necessary to undertake Arctic transits.
- Build indigenous capacity in building ships of Ice-class standards, including for research.
- Expand India’s trained manpower in maritime insurance, chartering, arbitration and brokerage for potential usage in the Arctic region.
- Build wide-ranging institutional capacity for the study of Arctic maritime, legal, environmental, social, policy and governance issues, including the application of UNCLOS and other Treaties governing the Arctic region.
THE CONCLUSION: India’s Arctic Policy is aimed to prepare the country for a future where the biggest challenges facing humankind, such as climate change, can be successfully addressed through, Collective will and effort. India can and is ready to play its part and contribute to the global good. Close partnership with countries of the Arctic region and other international partners to ensure sustainable development, peace and stability in the Arctic region will also be essential for the realization of India’s national development plans and priorities. This approach is in accordance with the challenges facing humankind, such as climate change, which can be successfully addressed only through the Indian philosophy of VasudhaivaKutumbakam-The world is one family.
Questions for Mains:
- India’s Arctic Policy is aimed to prepare the country for a future where the biggest challenge of climate change. Comment.
- In the changing geopolitics, initiatives such as New Arctic Policy can be vital to address the emerging energy challenges experienced by India in the recent past. Explain.
- How far do you agree with this view that India’s New Arctic is less about energy needs and more about being competitive in geopolitics? Justify your view.




