Table of Contents
THE GOVERNMENT POLICIES AND INTERVENTION
1. CABINET APPROVES NUTRIENT BASED SUBSIDY (NBS) RATES FOR PHOSPHATIC AND POTASSIC (P&K) FERTILIZERS FOR KHARIF SEASON
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet chaired has approved the proposal of the Department of Fertilizers for Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) rates for Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers for Kharif Season – 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
Financial Implications:
Subsidy approved by Cabinet for the NBS Kharif-2022 will be Rs. 60,939.23 Crores including support for indigenous fertilizer (SSP) through freight subsidy and additional support for indigenous manufacturing and imports of DAP.
Benefits:
- The increase in the international prices of Di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) and its raw materials have been primarily absorbed by the Union Government. The Union Government has decided to provide subsidy of Rs. 2501 per bag on DAP instead of existing subsidy of Rs.1650 per bag which is a 50% increase over the last year’s subsidy rates (2021).
- The increase in the prices of DAP & its raw material is in the range of approx. 80%. It will help farmers to receive notified P&K fertilizers on subsidized, affordable and reasonable rates and support the agriculture sector.
Implementation Strategy and targets:
The subsidy on P&K fertilizers will be provided based on the NBS rates for Kharif season -2022 to ensure smooth availability of these fertilizers to the farmers at affordable prices.
Background:
- Government is making available fertilizers, namely Urea and 25 grades of P&K fertilizers to farmers at subsidized prices through fertilizer manufacturers/ importers. The subsidy on P&K fertilizers is being governed by NBS Scheme w.e.f 01.04.2010.
- In accordance with its farmer friendly approach, the Govt. is committed to ensure the availability of P&K fertilizers to the farmers at affordable prices. In view of steep increase in the international prices of fertilizers & inputs i.e. Urea, DAP, MOP and Sulphur, Government has decided to absorb the increased prices by increasing subsidy on P&K fertilizers including DAP.
- The subsidy would be released to fertilizer companies as per approved rates so that they can make available fertilizers to farmers at an affordable price than it would have been otherwise.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. INDIA’S DESIGNATION BY THE USCIRF
THE CONTEXT: The 2022 Annual report of the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) has recommended that India be designated a ‘Country of Particular Concern’ (CPC), i.e., the category of governments performing most poorly on religious freedom criteria.
THE EXPLANATION:
- It has also called for “targeted sanctions” on individuals and entities responsible for severe violations of religious freedom by freezing those individuals’ or entities’ assets and/or barring their entry” into the U.S.
What is the USCIRF?
- The USCIRF is an independent, bipartisan body created by the International Religious Freedom Act, 1998 (IRFA) with a mandate to monitor religious freedom violations globally and make policy recommendations to the President, the Secretary of State, and the Congress. It is a congressionally created entity and not an NGO or advocacy organisation.
- It is led by nine part-time commissioners appointed by the President and the leadership of both political parties in the House and the Senate.
What does a ‘Country of Particular Concern’ (CPC) designation mean?
- IRFA requires the USCIRF to annually identify countries that merit a CPC designation. As per IRFA, CPCs are countries whose governments either engage in or tolerate “particularly severe violations” of religious freedom, which are defined as “systematic, ongoing, egregious violations of the internationally recognized right to freedom of religion”.
- The other designation, for less serious violations, is Special Watch List (SWL).
Which other countries have been designated as CPCs?
- For 2022, based on religious freedom conditions in 2021, a total of 15 countries have been recommended for the CPC designation. They include India, Pakistan, Burma, China, Eritrea, Iran, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Nigeria, Syria and Vietnam.
- Countries recommended for an SWL designation include Algeria, Cuba, Nicaragua, Azerbaijan, Central African Republic, Egypt, Indonesia, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Turkey, and Uzbekistan.
Why does USCIRF want India to be designated as a CPC?
- The USCIRF, in its annual report, states that in 2021, “religious freedom conditions in India significantly worsened.”
- Noting that the “Indian government escalated its promotion and enforcement of policies —including those promoting a Hindu-nationalist agenda — that negatively affect Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Dalits, and other religious minorities,” the report observed that “the government continued to systemise its ideological vision of a Hindu state at both the national and State levels through the use of both existing and new laws and structural changes hostile to the country’s religious minorities.”
- It highlighted the use of the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) against those documenting religious persecution and violence, detailed the creation of “hurdles against the licensure and receipt of international funding” by religious and charitable NGOs, and observed that “numerous attacks were made on religious minorities, particularly Muslims and Christians, and their neighborhoods, businesses, homes, and houses of worship”. It also criticized the spate of fresh anti-conversion legislation’s, noting that “national, State and local governments demonized and attacked the conversion of Hindus to Christianity or Islam.”
- Taking into account all these aspects, it concluded that India met the criteria of “systematic, ongoing, egregious” violations of religious freedom and therefore deserved a CPC designation.
3. INDIA APPROVES NEW EMBASSY IN LITHUANIA
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet approved a proposal to open a new Indian embassy in Lithuania, the first full-fledged embassy in the Baltic region, currently at the forefront of forging a more aggressive European position against Russia over the Ukraine war. Lithuania is also at the centre of a diplomatic spat with China over the opening of a de-facto embassy by Taiwan.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Indian government said the opening of the mission in Lithuania would help India expand its political, strategic and economic engagements with that country.
- “Opening of the Indian mission in Lithuania will help expand India’s diplomatic footprint, deepen political relations and strategic cooperation, enable the growth of bilateral trade, investment and economic engagements and facilitate stronger people-to-people contacts”.
- The government said setting up the mission will provide more sustained political outreach and help garner support for India’s foreign policy objectives.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
4. INDONESIA’S PALM OIL EXPORT BAN
THE CONTEXT: Indonesia began imposing a complete ban on palm oil exports as the world’s largest producer of the commodity risked destabilising a global vegetable oil market already hitting peak prices.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The archipelago nation is facing a shortage of domestic supplies of cooking oil and soaring prices, with consumers in several cities having to wait for hours in front of distribution centres to buy the essential commodity at subsidised rates.
- Authorities in Southeast Asia’s most populous country fear the scarcity and rising costs could provoke social tensions and have moved to secure supplies of the product, which is used in a range of goods such as chocolate spreads and cosmetics.
How important is palm oil to global supply chains?
- Palm oil is the world’s most widely used vegetable oil with its global production in the year 2020 being over 73 million tonnes (MT), according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- It is estimated to be 77 million tonnes for the current year. Made from the African oil palm, it is used as cooking oil, and in everything from cosmetics, processed foods, cakes, chocolates, spreads, soaps, shampoo, and cleaning products to bio fuel.
- Indonesia and Malaysia together account for almost 90% of the global palm oil production, with Indonesia producing the largest quantity at over 45 million tonnes in 2021.
According to data, palm oil makes up 40% of the global supply of the four most widely used edible oils: palm, soybean, rapeseed (canola), and sunflower oil. Indonesia is responsible for 60% of the global supply of palm oil. India is the biggest importer of palm oil.
- The months-long shortage has been exacerbated by poor regulation and producers who are reluctant to sell at home because high international prices have made exports more profitable.
- Jakarta plans to resume exports when the price of bulk cooking oil in local markets has fallen to 14,000 rupiah (97 cents) per litre, having rocketed 70 percent in recent weeks to 26,000 rupiah ($1.80).
- Vegetable oils are among a number of staple food items that have seen prices hit record highs in recent weeks, following Russia’s invasion of agricultural powerhouse Ukraine, according to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation.
How will it impact India?
- India is the biggest importer of palm oil, which makes up 40% of its vegetable oil consumption, as per the USDA. India meets half of its annual need for 8.3 million tonnes of palm oil from Indonesia. In 2021, the Centre also unveiled its plan to boost India’s domestic palm oil production.
- Already grappling with record-high wholesale inflation, the late January (2021) export controls exercised by Indonesia had led to a 38% rise in the landed cost of CPO in India. The price of soybean oil, most consumed after palm, rose by 29% in the country this year; while sunflower oil, 90% of which India gets from Russia and Ukraine, stopped coming in almost completely.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN THE NEWS
5. J&K HYDROELECTRIC PROJECT APPROVED
THE CONTEXT: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved the investment of Rs 4,526.12 crore for the 540 MW Kwar Hydro-electric project located on Chenab River in Jammu & Kashmir’s Kishtwar district.
THE EXPLANATION:
- This is part of the Indus basin and would be one of the at least four projects coming up in the district, including the 1,000 MWs PakalDul hydroelectric project and 624 MWs run-of-the-river Kiru hydroelectric project.
- Under the 1960 vintage Indus Water Treaty (IWT) between India and Pakistan, the two countries share the waters of six rivers in the Indus basin that flow through India towards Pakistan. Of these, India has complete rights over three eastern rivers – Sutlej, Beas and Ravi, while Pakistan has rights over the western rivers – Chenab, Jhelum, and Indus.
- India can, however, build run-of-the-river projects on the western rivers. Over the last five years, the government has been on an approval and construction spree to fully tap the potential in the Indian side of the Indus basin.
- The Kwar hydropower project will be implemented by Chenab Valley Power Projects Private Ltd (CVPPL), a joint venture company between NHPC Ltd and Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development Corporation (JKSPDC) with equity contributions of 51 percent and 49 percent respectively. The project shall generate 1,975.54 million units in a 90 percent dependable year.
VALUE ADDITION: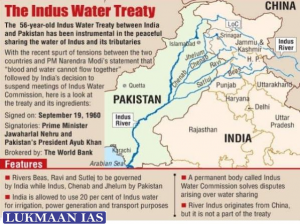
THE NEWS IN NUMBERS
6. REAL ESTATE GROWTH
Around 65,000 crore, the expected growth of Indian real estate (RE) by 2040, according to a report by consultancy firm CIRIL. By 2025, the sector is expected to contribute 13% of the country’s GDP (Gross domestic product). In 2019, the size of the RE market was ₹12,000 crore. Despite fears related to the Omicron crisis, the market in 2022 looked bullish while demand is accelerating across all categories, the report added.
7. DIGITAL ADVANCEMENT
20 million of women certified to be digitally literate in India under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) programme dedicated to digital literacy, according to Union Ministry of Women and Child Development of India and it aims to empower people in rural areas by training them to operate computers or digital access devices (like tablets, smartphones, etc.), send and receive e-mails, browse the internet, access government services, and undertake digital payment, among others
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. The government of India recently approved the construction of Kwar hydro-electric project across which of the following rivers?
- Jhelum river
- Chenab river
- Beas river
- Ravi river
ANSWER FOR 27TH APRIL 2022
Answer: D
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: After rising in 2020 for the first time since 2015, total coal power capacity under development slid last year to a record low of 457 gigawatts(GW), from 525 gigawatts.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: China-led global coal power expansion in 2021, with about 25,000 MW of new plants, followed by India with about 6,100 MW, re- ported the Global Energy Monitor which conducts an annual survey of coal power capacity under development or deployment.

