THE PARLIAMENTARY PROCEEDINGS: BUDGET SESSION 2022
1. THE DELHI MUNICIPAL CORPORATION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2022
THE CONTEXT: The Parliament passed Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Bill 2022 which seeks to merge three municipal corporations of Delhi into a single entity.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Delhi Municipal Corporation Act, 1957 passed by Parliament. The Act was amended in 2011 by Delhi Legislative Assembly to trifurcate the erstwhile Municipal Corporation of Delhi into: (i) North Delhi Municipal Corporation, (ii) South Delhi Municipal Corporation, and (iii) East Delhi Municipal Corporation. The Bill seeks to unify the three corporations.
- Unification of Municipal Corporations in Delhi: The Bill replaces the three municipal corporations under the Act with one Corporation named the Municipal Corporation of Delhi.
- Powers of the Delhi government: The Act as amended in 2011 empowers the Delhi government to decide various matters under the Act. These include: (i) total number of seats of councillors and number of seats reserved for members of the Scheduled Castes, (ii) division of the area of corporations into zones and wards, (iii) delimitation of wards, (iv) matters such as salary and allowances, and leave of absence of the Commissioner, (v) sanctioning of consolidation of loans by a corporation, and (vi) sanctioning suits for compensation against the Commissioner for loss or waste or misapplication of Municipal Fund or property. Similarly, the Act mandates that the Commissioner will exercise his powers regarding building regulations under the general superintendence and directions of the Delhi government. The Bill instead empowers the central government to decide these matters.
- Number of Councillors: The Act provides that the number of seats in the three corporations taken together should not be more than 272. The 14th Schedule to the Act specifies 272 wards across the three Corporations. The Bill states that the total number of seats in the new Corporation should not be more than 250.
- Removal of Director of Local Bodies: The Act provides for a Director of Local Bodies to assist the Delhi government and discharge certain functions which include: (i) coordinating between Corporations, (ii) framing recruitment Rules for various posts, and (iii) coordinating the collecting and sharing of toll tax collected by the respective Corporations. The Bill omits the provision for a Director of Local Bodies.
- Special officer to be appointed by the central government: The Bill provides that the central government may appoint a Special Officer to exercise powers of the Corporation until the first meeting of the Corporation is held after the commencement of the Bill.
- E-governance system for citizens: The Bill adds that obligatory functions of the new Corporation will include establishing an e-governance system for citizen services on anytime-anywhere basis for better, accountable, and transparent administration.
- Conditions of service for sweepers: The Act provides that a sweeper employed for doing house scavenging of a building would be required to give a reasonable cause or a 14 day notice before discontinuing his service. The Bill seeks to omit this provision.
2. THE CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS, THE COST AND WORKS ACCOUNTANTS AND THE COMPANY SECRETARIES (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2021
THE CONTEXT: The Chartered Accountants, the Cost and Works Accountants and the Company Secretaries (Amendment) Bill, 2021 was passed by both the houses of the Parliament.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Bill seeks to amend
- The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949,
- The Cost and Works Accountants Act, 1959, and
- The Company Secretaries Act, 1980.
- The three Acts provide for the regulation of the professions of chartered accountants, cost accountants and company secretaries, respectively. The Bill seeks to strengthen the disciplinary mechanism under these Acts, and provide for time bound disposal of cases against members of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, the Institute of Cost Accountants of India and the Institute of Company Secretaries of India.
Key features of the Bill include:
- Registration of firms: The Bill adds that firms must register with the Institutes by making an application to the respective Councils of the Institutes. The Councils must maintain a register of firms containing details such as pendency of any actionable complaint or imposition of penalty against the firms.
- Disciplinary Directorate: Under the Acts, the respective Councils of the three Institutes must each constitute a Disciplinary Directorate, headed by Director (Discipline) who is an officer of the Institute. The Bill adds that each Directorate must also include at least two Joint Directors.
- Under the Acts, on receiving a complaint, the Director arrives at a prima facie opinion on the alleged misconduct. Depending on the misconduct, the Director places the matter before the Board of Discipline or the Disciplinary Committee. The Bill amends this to empower the Directorate to independently initiate investigations against members or firms. The Director must decide whether a complaint is actionable within 30 days of receiving such complaint. If the complaint is actionable, the Director must submit a preliminary examination report to the Board or the Committee (as the case may be), within 30 days. Under the Acts, a complaint may be withdrawn if permitted by the Board or Committee. The Bill provides that a complaint filed with the Directorate will not be withdrawn under any circumstances.
- Board of Discipline: Under the three Acts, each Council constitutes a Board of Discipline. Members of the Board include: (i) presiding officer (having experience in law and knowledge of disciplinary matters), (ii) two members and (iii) Director (Discipline) as secretary. Under the Chartered Accountants Act, 1949, one of the two members is nominated by the central government while the other is a member of the Council. As per the other two Acts, both the members are from the Councils or the Institutes.
- The Bill empowers the three Councils to constitute multiple Boards. The presiding officer and one of the two members must not be a member of the institutes and will be nominated by the central government from a panel of persons provided by the Councils. An officer of the Institute, of the rank of Deputy Secretary, will function as the Secretary of the Board. After receiving the preliminary examination report, the Board must conclude its inquiry within 90 days.
- Disciplinary Committee: Under the three Acts, the Councils constitute Disciplinary Committees consisting of: (i) Presiding Officer (President or Vice-President of the Council), (ii) two members elected from the Council, and (ii) two members nominated by the central government. The Bill amends the Acts to provide that the Presiding Officer must not be a member of the institutes and shall be nominated by the central government. The Committee must conclude its inquiry in 180 days from the receipt of preliminary examination report.
- Penalties: Under the Acts, in cases of professional or other misconduct the Committees may: (i) reprimand or remove the member from the register of the Institute, or (ii) impose a fine of up to five lakh rupees. The Bill increases the maximum amount of fine to ten lakh rupees. The Bill also adds that if a partner or owner of a firm is repeatedly found guilty of misconduct during last five years, the Committee may take certain actions against the firm. The actions include: (i) prohibiting the firm from undertaking activities related to the profession of chartered account, cost accountant, or company secretary, as the case may be, for up to two years, or (ii) impose a fine of up to Rs 50 lakh.
Key Issues and Analysis
- The Bill proposes to change the composition of the two disciplinary entities to allow for more external representation. However, these external members will be selected from a panel of persons prepared by the three Councils. This may be against the objective of resolving conflict of interest between the disciplinary and administrative functions of the three professional Councils.
- The mandate of the proposed Coordination Committee may overlap with certain functions of the three Institutes. Further, being chaired by the Secretary of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, it may impinge on the independence of the three Institutes.
- The Bill provides for disclosure of pending complaints or actionable information against members and firms. Disclosing details of pending complaints before finding guilt may tarnish their professional reputation.
- Though the President will have a non-executive role, he will be held responsible for implementation of decisions of the Councils.
THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
3. MULLAPERIYAR SUPERVISORY PANEL CONTINUES FOR A YEAR WHILE AUTHORITY: CENTRE TO SUPREME COURT
THE CONTEXT: The Central Government suggested to the Supreme Court to let the Mullaperiyar dam supervisory committee continue for a year, by which time the National Dam Safety Authority under the new Dam Safety Act will become fully functional.
THE EXPLANATION:
- “According to the Government statement, during the period of one year, when the National Dam Safety Authority becomes fully functional, the Supervisory Committee on Mullaperiyar Dam may continue its functioning as per the existing mandate in regulating the operations of the Mullaperiyar dam”.
- The Centre suggested that the Chief Secretaries of Tamil Nadu and Kerala be made accountable in order to ensure that the decisions of the supervisory committee on the maintenance and safety of the dam are duly complied with by the two States.
- “To address the technical concerns of both the States, the Chief Secretaries of the States may be requested to nominate technical experts as members to participate in the meetings conducted by the supervisory committee. This would ensure accountability of the decisions/ action taken,” the Centre further recommended.
VALUE ADDITION:
ABOUT MULLAIPERIYAR DAM
- It is a masonry gravity dam on the Periyar River in the Indian state of Kerala.
- It was constructed between 1887 and 1895 and also reached an agreement to divert water eastwards to the Madras Presidency area.
- The dam created the Periyar Thekkady reservoir, from which water was diverted eastwards via a tunnel to augment the small flow of the Vaigai River.
- It originates from the Sivagiri hills of Western Ghats and flows through the Periyar National Park.
- The main tributaries of Periyar are Muthirapuzha, Mullayar, Cheruthoni, and Perinjankutti.
- According to a 999-year lease agreement made during British rule, the operational rights were handed over to Tamil Nadu.
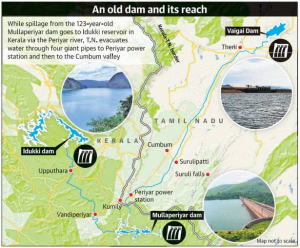
Mullaiperiyar dam: The current dispute
The Supreme Court order came after a court-appointed supervisory committee had suggested 139.50 ft as the permissible level. The court has directed both states to go by the committee’s recommendation. Tamil Nadu had wanted the level increased to 142 ft as fixed by the Supreme Court in 2014, while Kerala wanted it within 139 ft as per a rule curve fixed until the end of the month.
Kerala’s stance:
- The state governments of Kerala have pointed out the unfairness of the 1886 lease agreement and its validity itself. Its core issue is the safety of the Mullaperiyar Dam. Kerala wants to decommission the 100+-year-old dam and construct a new one in its place, as not doing so will endanger many lives in the process.
- The Kerala Government stated that it did not object to giving water to Tamil Nadu but pointed out that raising its level would add more pressure than the dam could take. The dams, as pointed out by Kerala, were leaking and had many structural faults.
- In addition, the Kerala government has accused Tamil Nadu of adopting an “obsolete” gate operation schedule dating back to 1939.
Tamil Nadu’s Stance:
- For Tamil Nadu, the Mullaperiyar dam and the diverted Periyar waters act as a lifeline for Theni, Madurai, Sivaganga, Dindigul and Ramnad districts, providing water for irrigation and drinking, and also for the generation of power in Lower Periyar Power Station.
- Tamil Nadu argues that building a new dam is for gaining unfair tax revenues from developing states.
- Tamil Nadu is not able to access data that is in Kerala’s terrain. There is no road built, the power supply has not been restored, although Tamil Nadu has paid for it.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES IN THE NEWS
4. BUDGET FOR PRADHAN MANTRI ANNADATA AAY SANRAKSHAN ABHIYAN(PM-AASHA)
THE CONTEXT: Under PSS, Government has provided Government Guarantee amounting to Rs. 40,500/- cr. for extending cash credit facilities to Central Nodal Agencies i.e. NAFED & FCI for procurement of pulses, oilseeds & copra at Minimum Support Price (MSP). Central Nodal Agencies withdraw the required funds against the Government Guarantee for making payment of MSP value to farmers and other incidental costs involved in the PSS operations.
THE EXPLANATION:
Components of PM-AASHA
The new Umbrella Scheme includes the mechanism of ensuring remunerative prices to the farmers and is comprised of,
Price Support Scheme (PSS):
- In Price Support Scheme (PSS), physical procurement of pulses, oilseeds and Copra will be done by Central Nodal Agencies with proactive role of State governments. It is also decided that in addition to NAFED, Food Cooperation of India (FCI) will take up PSS operations in states /districts.
- The procurement expenditure and losses due to procurement will be borne by Central Government as per norms.
Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS):
- Under Price Deficiency Payment Scheme this scheme (PDPS), it is proposed to cover all oilseeds for which MSP is notified. In this direct payment of the difference between the MSP and the selling/modal price will be made to pre-registered farmers selling his produce in the notified market yard through a transparent auction process. All payments will be done directly into the registered bank account of the farmer.
- This scheme does not involve any physical procurement of crops as farmers are paid the difference between the MSP price and Sale/modal price on disposal in the notified market. The support of central government for PDPS will be given as per norms.
The pilot of the Private Procurement & Stockist Scheme (PPPS):
- Under this scheme, participation of the private sector in procurement operations will be piloted.
- States have the option to roll out the scheme on a pilot basis in selected districts/APMCs involving private stockists.
Need for PM-AASHA:
- A major issue with the MSP is its poor coverage. Further, there are certain problems with the implementation of MSP such as the procurement centres being far away resulting into heavy transportation cost, non-opening of Procurement centres timely, lack of covered storage/godowns facility for the temporary storage of produces, delays in payments, etc. Thus to address the gaps in the MSP system and give better returns to farmers, PM-AASHA is an important step.
- Increasing MSP is not adequate and it is more important that farmers should get full benefit of the announced MSP. Further, it is essential that if price of the agriculture produce market is less than MSP, then in that case State Government and Central Government should purchase either at MSP or work in a manner to provide MSP for the farmers through some other mechanism.
- A holistic approach of solving any issue is important rather than in fragments. Thus, to address issue of farmer’s income and enhancing livelihood, a compressive policy has been the need of the hour
Significance of PM-AASHA:
- Income Security to farmers: The policy is an important step to achieve government’s commitment to double farmers’ income by 2022. If properly implemented, the scheme is expected to help revive the rural economy by assuring better income to farmers and thus address farmers’ distress
- Stabilizing commodity markets: It will help in stabilising commodity markets and will also benefit the farmers by providing options to the state governments to compensate farmers when the market prices fall below MSP.
- Better coverage of MSP: MSP procurement system has been very poor both in terms of geography and the crops covered. The new scheme would ensure better coverage of MSP and provision of crop-wise procurement is expected to benefit both farmers and states.
- Reduce the need for physical procurement: The PDPS scheme under PM-AASHA will reduce the need for the government to physically procure food crops as the difference between the support and market prices can instead simply be paid in cash to the farmer.
- Reduce storage and wastage: As the need for physical procurement will reduce, it will also reduce the consequent needs for transport and store them and then dispose of them under PDS. This would also reduce wastage of grains/crops.
- Reduce food subsidy bill: In recent years, the government has been seeing the accumulation of large food grain stocks in its godowns over and above the buffer requirement. This entails storage and wastage costs that add on to the food subsidy bill. Thus the new policy would help in bringing down India’s food subsidy bill.
THE DATASHEET
5. THE CORPORATE DONATIONS TO POLITICAL PARTIES
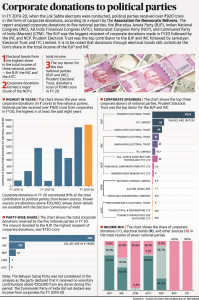
VALUE ADDITION:
WHAT IS AN ELECTORAL BOND?
An electoral bond is like a promissory note that can be bought by any Indian citizen or company incorporated in India from select branches of State Bank of India. The citizen or corporate can then donate the same to any eligible political party of his/her choice. The bonds are similar to bank notes that are payable to the bearer on demand and are free of interest. An individual or party will be allowed to purchase these bonds digitally or through cheque.
How to use electoral bonds?
Using electoral bonds is quite simple. The bonds will be issued in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 100,000 and Rs 1 crore (the range of a bond is between Rs 1,000 to Rs 1 crore). These will be available at some branches of SBI. A donor with a KYC-compliant account can purchase the bonds and can then donate them to the party or individual of their choice. Now, the receiver can encash the bonds through the party’s verified account. The electoral bond will be valid only for fifteen days.
The 29 specified SBI branches are in cities such as New Delhi, Gandhinagar, Chandigarh, Bengaluru, Bhopal, Mumbai, Jaipur, Lucknow, Chennai, Kolkata and Guwahati.
When are the bonds available for purchase?
The electoral bonds are available for purchase for 10 days in the beginning of every quarter. The first 10 days of January, April, July and October has been specified by the government for purchase of electoral bonds. An additional period of 30 days shall be specified by the government in the year of Lok Sabha elections.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. Consider the following statements about Antarctic Treaty:
- It was signed in 1959 and came into force in 1961.
- India is the foundation member of this treaty.
- The Treaty covers the area south of 60°S latitude.
- Its one of the objective is to create a nuclear tests free zone.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2, 3 and 4 only
c) 1, 3 and 4 only
d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 5TH APRIL 2022
Answer: b)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: It is built by the kings of the Ganga dynasty.
- Statement 2 is correct: It is an example of Kalinga Architecture.




