Table of Contents
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. INDIA-AUSTRALIA INTERIM TRADE AGREEMENT AND FTA
THE CONTEXT: India and Australia have announced that they are set to conclude an interim trade agreement in March 2022 and a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) 12-18 months thereafter.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is the early harvest agreement likely to cover?
- An interim or early harvest trade agreement is used to liberalise tariffs on the trade of certain goods between two countries or trading blocs before a comprehensive FTA (Free Trade Agreement) is concluded.
- According to the Commerce Ministry, the interim agreement set to be announced in about 30 days will cover “most areas of interest for both countries” including goods, services, rules of origin, sanitary and phytosanitary measures and customs procedures.
- Bilateral trade between the two countries stood at about $12.5 billion in FY21 and has already surpassed $17.7 billion in the first 10 months of FY22.
- India has imported merchandise worth about $12.1 billion from Australia in the first 10 months of the fiscal and has exported merchandise worth $5.6 billion in the same period. Key imports from Australia include coal, gold and LNG while key exports to the country from India include diesel, petrol and gems and jewellery.
How has the Quad impacted trade relations between India and Australia?
India and Australia are both members of the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) along with the US and Japan. Both countries have noted that the coalition has given impetus to increasing trade relations between all members of the Quad. Australia noted that it already had FTAs with both the US and Japan and that all four countries could start building a framework for economic cooperation within the countries of the Quad after they announced a deal with India.
What other Free Trade Agreements is India currently negotiating?
India is currently in the process of negotiating FTAs with the UAE, the UK, Canada, the EU and Israel, besides Australia. India is also looking to complete an early harvest agreement with the UAE and the UK in the first half of 2022.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
2. THE INFLATION EDGES PAST 6% IN JANUARY 2022
THE CONTEXT: Retail inflation rose to a seven-month high of 6.01 per cent in January 2022, breaching the upper tolerance level of the medium-term inflation target of 4+/-2 per cent set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO). The rise was mainly on account of high food inflation, which jumped to a 14-month high of 5.43 per cent, along with an unfavourable base.
THE EXPLANATION: 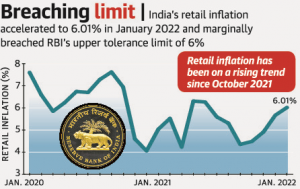
-
- Inflation at the wholesale level in January softened to 96 per cent from 13.56 per cent in December 2021 but marked the tenth consecutive month of being in double digits, another set of data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Wholesale food inflation was, however, at a 24-month high of 9.6 per cent. Wholesale Price Index (WPI)-based inflation rate is reflective of the price pressures on the inputs side and of manufacturers passing on the higher input costs to their output prices.
- According to Economists, the high inflation was now turning structural, with price rise being seen in non-food segments such as clothing, fuel and light, household goods, health, transport, and communication above 6 per cent.

- These prices are based on the MRP principle and will not come down once increased. Manufacturers are in the process of passing on the higher input cost to the consumer and this will carry on for the next two months too.
- The structural aspect of inflation is reflected in the core inflation remaining sticky (96 per cent in January). “Clothing & footwear inflation now stands at a 97-month high (8.84 per cent) on the back of higher cotton prices. Household goods and services inflation at 7.1 per cent is at a 94-month high in January 2022. Amid elevated input costs, various automobile, telecom and FMCG firms have announced price hikes. As a result, core inflation has remained sticky.
VALUE ADDITION:
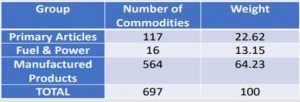
About Wholesale Price Index (WPI):
- Measures inflation at the first stage of the transaction, i.e. wholesale prices.
- Compiled by the Office of Economic Advisor, Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The Wholesale Price Index measures inflation on a year-on-year basis.
- It consists of 3 major groups as below:
QUICK FACTS
GLOSSARY
- Disinflation: Reduction in the rate of inflation.
- Deflation: Persistent decrease in the price level (negative inflation).
- Reflation: Price level increases when the economy recovers from recession based on the value of inflation.
- Creeping inflation – If the rate of inflation is low (up to 3%).
- Walking/Trotting inflation – Rate of inflation is moderate (3-7%).
- Running/Galloping inflation – Rate of inflation is high (>10%).
- Runaway/Hyper Inflation – The rate of inflation is extreme.
- Stagflation: Inflation + Recession (Unemployment).
- Misery index: Rate of inflation + Rate of unemployment.
- Inflationary gap: Aggregate demand > Aggregate supply (at full employment level).
- Deflationary gap: Aggregate supply > Aggregate demand (at full employment level).
- Suppressed / Repressed inflation: Aggregate demand > Aggregate supply. Here govt will not allow rising of prices.
- Open inflation: A situation where the price level rises without any price control measures by the government.
- Core inflation: Based on those items whose prices are non-volatile. (All items in CPI -Food & Energy).
- Headline inflation: All commodities are covered in this. (Goods + Services).
- Structural inflation: Due to structural problems like infrastructural bottlenecks.
3. CENTRE CUTS AGRI-CESS ON CRUDE PALM OIL
THE CONTEXT: According to the the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution the Centre Government has reduced the Agri-cess on crude palm oil (CPO) from 7.5 per cent to 5 per cent. This will benefit the domestic edible oil refiners and also check prices of cooking oils.
BEHIND THE MOVE?
“With a view to provide further relief to consumers and to keep in check any further rise in the prices of domestic edible oils due to rise in the prices of edible oils globally, the Government of India has reduced the agri-cess for Crude Palm Oil (CPO) from 7.5% to 5% with effect from 12th February, 2022.”
“After reduction of the agri-cess, the import tax gap between CPO and Refined Palm Oil has increased to 8.25%. The increase in the gap between the CPO and Refined Palm Oil will benefit the domestic refining industry to import crude oil for refining”.
The rate of import duty on Refined Palm Oils at 12.5%, Refined Soyabean oil and Refined Sunflower Oil at 17.5% will remain in force up to 30th September 2022. This measure will help in cooling down the prices of edible oils which are witnessing an upward trend in the international market due to lower availability and other international factors”.
Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC)
- It was proposed in the 2021 Budget and it is applied on a small number of items.
- Under the norms, no additional burden will be placed on consumers on most items.
- AIDC was announced because there was an immediate need to improve the agricultural infrastructure in order to produce more along with conserving and processing agricultural output efficiently.
- This cess would also ensure enhanced remuneration for the farmers.
About National Edible Oil Mission-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)
- The government will invest more than ₹11,000 crore via the National Mission on Oilseeds and Oil Palm to provide farmers with everything possible.
- Under the scheme, the government will ensure that farmers get all facilities, from quality seeds to technology to promote farming to produce palm oil and other oil seeds.
- The Centre plans to raise the domestic production of palm oil by three times to 11 lakh MT by 2025-26.
- It will involve raising the area under oil palm cultivation to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26 and 16.7 lakh hectares by 2029-30.
- Under the scheme, oil palm farmers will be provided financial assistance and will get remuneration under a price and viability formula.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
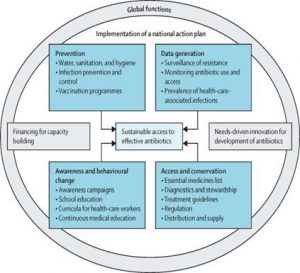
4. THE FIGHT AGAINST ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
THE CONTEXT: According to the paper titled Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, “Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis”, published by the Lancet, found that AMR is a leading cause of death around the world, with the highest number of deaths occurring in low-resource settings.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Antimicrobial resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of microorganisms to persist or grow in the presence of drugs designed to inhibit or kill them. These drugs, called antimicrobials, are used to treat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan parasites.
Bacterial antimicrobial resistance occurs when changes in bacteria causes the drugs used to treat the infection to become less effective. A paper authored by Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators states that around 4.95 million deaths were associated with bacterial anti microbial resistance in 2019 alone.
Impact
When infections can no longer be treated by first-line antibiotics, more expensive medicines must be used. A longer duration of illness and treatment, often in hospitals, increases health care costs as well as the economic burden on families and societies.
Antibiotic resistance is putting the achievements of modern medicine at risk. Organ transplantation’s, chemotherapy and surgeries such as caesarean sections become much more dangerous without effective antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of infections.
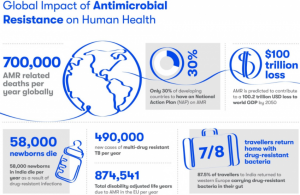
Research on a massive scale
The paper is an analysis of the burden of AMR, producing estimates for 204 countries and territories, 23 bacterial pathogens, and 88 drug-pathogen combinations in 2019. The six leading pathogens for deaths associated with resistance included E. coli, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, S. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. They have been registered as priority pathogens by WHO.
The indiscriminate use of antibiotics, no proper sanitation and the lack of awareness among the public about the dangers of AMR are some of the reasons which need to be tackled in order to fight against antimicrobial resistance.

The way forward
- Reducing exposure to antibiotics that are used in the farming sector and poultry industry is also key. In this context, doctors point out that India’s move to ban colistin usage in the poultry industry will go a long way in reducing the AMR burden in the country.
- Antibiotic stewardship, or minimising the use of antibiotics unless absolutely necessary, remains at the core of the fight against AMR.
- It is the hope of all collaborators, who continue to fight the big war with bacterial antimicrobial resistance, before, and through pandemics, that this new data provides the urgency and fresh momentum for global action to counter the single biggest burden that poses a major threat to human health.
5. ISRO’S FIRST LAUNCH OF 2022
THE CONTEXT: ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-C52 successfully injected Earth Observation Satellite EOS-04, into an intended sun-synchronous polar orbit of 529 km altitude.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The INSPIREsat-1 is a student satellite from the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology in association with the University of Colorado, USA and is aimed at improving the understanding of ionosphere dynamics and the Sun’s coronal heating processes. The Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and the National Central University, Taiwan, were part of the development team of the INSPIREsat. Taiwanese is the first time collaborated with an international team to launch a satellite from India.
- The INS-2TD is a precursor to the India-Bhutan joint satellite [INS 2-B] and will assess land and water surface temperatures, delineation of crops and forest and thermal inertia.
- According to ISRO, with a mission life of 10 years, the EOS-4, a radar imaging satellite is designed to provide high quality images in all weather conditions for applications such as agriculture, forestry, plantation, flood mapping, soil moisture and hydrology. The satellite will collect earth observation data in C-band and will complement and supplement the data from Resourcesat, Cartosat series and RISAT-2B series.

THE SECURITY AFFAIRS
6. WHY DID THE GOVT BAN MORE CHINA-LINKED APPS?
THE CONTEXT:The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) issued orders to ban 54 more apps, which either have originated in China or have some Chinese connection. These apps were banned for being a threat to national security.
THE EXPLANATION:
What are these new apps and why have they been banned?
As per the new list, video editing apps such as Viva Video Editor- Snack Video Maker with Music and Nice Video Baidu, which are used extensively for making short videos, games such as Onmyoji Chess and Conquer Online II have been banned in India. Garena Free Fire– Illuminate, a game, which had gained popularity among children, teenagers and youth in India after the ban on PUBG, has also been banned.
According to the Meity, the new apps have been banned using emergency powers under Section 69 of the Information Technology Act. Most of these apps, , were operating as clones or shadow apps of the apps that had earlier been banned by the government.
Which other apps have been banned by the government in the past?
- In June 2020, the IT ministry had, in a similar order issued under Section 69 of the IT Act, banned 59 apps, including TikTok, ShareIt, UC Browser, Likee, WeChat, and Bigo Live. In its reasoning then, the ministry had said that these apps were “prejudicial to sovereignty and integrity of India, defence of India, security of state and public order”.
- The first ban was followed by another set of 47 apps being barred from operations in India from July 2020. These apps were mostly proxies of the apps banned in June 2020.
- Later, on September 2, 2020, the IT ministry banned another 118 Chinese mobile apps, which included the popular gaming platform PUBG as well as Baidu, which is China’s largest search engine provider. In total so far, close to 300 apps and their proxies have been banned by the IT ministry.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES/INITIATIVES IN NEWS
7. THE NHA TO INTEGRATE DATABASES WITH PM-JAY
THE CONTEXT: According to the Union Health Ministry the National Health Authority (NHA) is working to integrate the database of Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011 beneficiaries with the National Food Security Act (NFSA) portal so that beneficiaries can seek information regarding their entitlements under the AB PM-JAY using their ration card number.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The NHA is mandated with the implementation of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri–Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The scheme provides health assurance of up to ₹5 Lakhs per family per year, for secondary and tertiary care-related hospitalizations.
- The Ministry added that the NHA is also working on a proposal to use Fair Price Shops or ration shops for providing information related to the scheme and entitlement under the scheme to eligible beneficiaries.
- “According to the Ministry, that this will provide an additional avenue to beneficiaries along with the existing Common Service Center, UTI-ITSL etc., for card creation. This will make the beneficiary identification process very convenient”.
Aadhar based
- It added that the existing beneficiary data available with various government welfare schemes can be meaningfully utilized only if a common identifier is available. “Aadhaar being a common identity across the majority of government databases will enable this integration.
- The beneficiary database enrichment under ABPM-JAY would mean adding additional parameters to the database for making searching easier. The majority of ABPM-JAY beneficiaries from SECC 2011 are also eligible for benefits under National Food Security Portal.
About National Health Authority (NHA)
- It is the apex body responsible for implementing India’s flagship public health insurance/assurance scheme called “Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana” & has been entrusted with the role of designing strategy, building technological infrastructure and implementation of “Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission” to create a National Digital Health Eco-system.
- NHA is leading the implementation for Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission ABDM in coordination with different ministries/departments of the Government of India, State Governments, and private sector/civil society organizations.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY 15TH FEBRUARY 2022
Q Consider the following statements about Earth Observation Satellite (EOS-04):
- It is a geo-stationary satellite.
- It has applications in the fields of disaster management, resource survey and agriculture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a 1 only
b 2 only
c Both 1 and 2
d Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR 14TH FEB 2022
Answer: C
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: It is the world’s largest nature conservation partnership. It consist of 120 BirdLife Partners worldwide.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The term ‘biodiversity hotspot’ was coined by Norman Myers (1988). The Conservation International in association with Myers made the first systematic update of the hotspots.
- Statement 3 is correct: It identifies the sites known/referred to as ‘Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas’. It is the official Red List authority for birds, for the IUCN.
Note: According to Birdlife International, designation of IBAs is based on standardized criteria, namely (i) hold significant numbers of one or more globally threatened bird species, (ii) be one of a set of sites that together hold a suite of restricted-range species or biome-restricted species and (iii) have exceptionally large numbers of migratory or congregatory birds. The Bombay Natural History Society and Birdlife International have identified 467 IBAs in India. Forty percent of these IBAs fall outside the PA network.
Spread the Word

