Table of Contents
THE INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS
1. MOU BETWEEN INDIA AND NEPAL FOR CONSTRUCTION OF BRIDGE
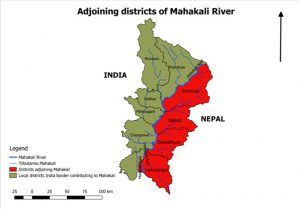
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister has approved the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Nepal for the construction of a bridge over Mahakali River at Dharchula (India)- Dharchula (Nepal).
THE EXPLANATION:
As close neighbours, India and Nepal share unique ties of friendship and cooperation characterized by an open border and deep-rooted people-to-people contacts of kinship and culture. Both India and Nepal have been working together on different regional forums i.e. SAARC, BIMSTEC as well as global fora.
IMPORTANCE:
- Nepal shares a border with 5 Indian states-Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Sikkim and Bihar. Hence an important point of cultural and economic exchange.
- Importance for India can be studied from two different angles: a) their strategic importance for India’s national security; and b) their place in India’s role perception in international politics.
- Nepal is right in the middle of India’s ‘Himalayan frontiers’, and along with Bhutan, it acts as northern ‘borderland’ flanks and acts as buffer states against any possible aggression from China.
- The two countries not only share an open border and unhindered movement of people, but they also have close bonds through marriages and familial ties, popularly known as Roti-Beti ka Rishta.
- India is Nepal’s largest trade partner and the largest source of foreign investments, besides providing transit for almost the entire third-country trade of Nepal.
- Indian firms engaged in manufacturing, services (banking, insurance, dry port), power sector and tourism industries etc.
THE INDIAN ECONOMY
2. THE SOVEREIGN GOLD BOND SCHEME 2021-22
THE CONTEXT: The Government of India in consultation with the Reserve Bank of India has decided to allow a discount of Rs 50 (Rupees Fifty only) per gram from the issue price to those investors who apply online, and the payment is made through digital mode. For such investors, the issue price of Gold Bond will be Rs 4,736 (Rupees Four thousand seven hundred thirty-six only) per gram of gold.
THE EXPLANATION:
About the Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme:
- The sovereign gold bond was introduced by the Government in 2015.
- The government introduced these bonds to help reduce India’s over-dependence on gold imports.
- The move was also aimed at changing the habits of Indians from saving in the physical form of gold to a paper form with Sovereign backing.
- Joint Holder: In the case of joint holding, the investment limit of 4 kg will be applied to the first applicant only.
- Collateral: Bonds can be used as collateral for loans. The loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is to be set equal to the ordinary gold loan mandated by the Reserve Bank from time to time.

Merits of investing in gold bonds:
- For investors, it is advisable to invest in gold for portfolio diversification.
- Sovereign gold bonds are considered one of the better ways of investing in gold as along with capital appreciation an investor gets a fixed rate of interest.
- Apart from this, it is tax-efficient as no capital gains is charged in case of redemption on maturity.
- Sovereign gold bonds are a good way to ensure an investment that does not need physical storage of the gold.
Demerits of sovereign gold bonds
- This is a long-term investment, unlike physical gold which can be sold immediately.
- Sovereign gold bonds are listed on an exchange, but the trading volumes are not high, therefore it will be difficult to exit before maturity
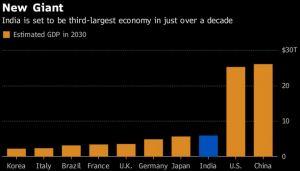
3. INDIA TO OVERTAKE JAPAN AS ASIA’S SECOND-LARGEST ECONOMY BY 2030: REPORT
THE CONTEXT: India is likely to overtake Japan as Asia’s second-largest economy by 2030 when its GDP is also projected to surpass that of Germany and the UK to rank as world’s No.3, according to the IHS Markit report.
THE EXPLANATION:
THE REPORT HIGHLIGHTS:
- Currently, India is the sixth-largest economy in the world, behind the US, China, Japan, Germany and the United Kingdom.
- According to the projection “India’s nominal GDP measured in USD terms is forecast to rise from USD 2.7 trillion in 2021 to USD 8.4 trillion by 2030.” “This rapid pace of economic expansion would result in the size of Indian GDP exceeding Japanese GDP by 2030, making India the second-largest economy in the Asia-Pacific region.” By 2030, the Indian economy would also be larger in size than the largest Western European economies of Germany, France and the UK.
- Overall, India is expected to continue to be one of the world’s fastest-growing economies over the next decade.
- “An important positive factor for India is its large and fast-growing middle class, which is helping to drive consumer spending,” forecasting that the country’s consumption expenditure will double from USD 1.5 trillion in 2020 to USD 3 trillion by 2030.
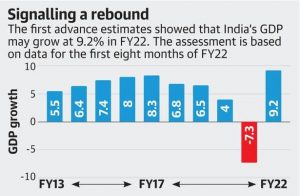
- For the full fiscal year 2021-22 (April 2021 to March 2022), India’s real GDP growth rate is projected to be 8.2 percent, rebounding from the severe contraction of 7.3 percent year-on-year in 2020-21.
- The rapidly growing domestic consumer market as well as its large industrial sector have made India an increasingly important investment destination for a wide range of multinationals in many sectors, including manufacturing, infrastructure and services.
- The digital transformation of India that is currently underway is expected to accelerate the growth of e-commerce, changing the retail consumer market landscape over the next decade.
- “The large increase in FDI inflows to India that has been evident over the past five years is also continuing with strong momentum in 2020 and 2021”.
- Being one of the world’s fastest-growing economies will make India one of the most important long-term growth markets for multinationals in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing industries such as autos, electronics and chemicals, and services industries such as banking, insurance, asset management, healthcare and information technology.
4. NSO ESTIMATES ON FY22 GDP GROWTH
THE CONTEXT: According to first advance estimates of the National Statistical Office (NSO), India’s gross domestic product (GDP) is estimated to grow 9.2% in the financial year 2021-22.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India’s gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to grow by 9.2% in the current financial year following last fiscal’s 7.3% contraction, the National Statistical Office (NSO) said in its first advance estimates of economic output released amid concerns over the likely impact of a third wave of the COVID pandemic.
- “GDP at constant prices (2011-12) in the year 2021-22 is estimated at ₹147.54 lakh crore, as against the provisional estimate of GDP for the year 2020-21 of ₹135.13 lakh crore”. It also added that growth in real GDP is pegged at 2%. “Real GVA at Basic Prices is estimated at ₹135.22 lakh crore in 2021-22, as against ₹124.53 lakh crore in 2020-21, showing a growth of 8.6%”.
Mining spurt
- The NSO’s GVA estimates show the mining sector outpacing others with the growth of 3% following in 2021 8.5% contraction, followed by manufacturing which is seen expanding by 12.5% after shrinking 7.2% in the previous 12-month period.
- The agriculture sector is estimated to grow at 3.9% in FY22 (3.6%). The electricity, water supply and other utility services category is estimated to grow at 8.5% (1.9%), while construction is expected to grow 10.7% (-8.6%) and trade, hotels, transport, communication and broadcasting services are projected to grow at 11.9% against a sharp contraction of 18.2% in 2022.
- “Compared to the pre-COVID performance of FY2020, the advance estimates project an anemic rise of 1.3% and 1.9%, respectively, for GDP and GVA in FY2022”.
GLOSSARY:
- Gross value added (GVA) is the measure of the total value of goods and services produced in an economy( area, region or country). The amount of value-added to a product is taken into account.
- GVA= Gross Domestic Product + Subsidies on products – Taxes on products.
About National Statistical Office (NSO) :
|
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5. THE SEASONAL FLUCTUATIONS IN DARTERS’ MOVEMENTS BEING MONITORED
THE CONTEXT: A new record has been set by the Chinese ‘artificial sun’ or the experimental advanced superconducting tokamak (EAST) fusion energy reactor in Hefei as it ran at 70 million°C for 1,056 seconds, which is over 17 minutes. The record was apparently achieved.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to a report have mentioned that the achieved temperature is almost five times hotter than the real Sun, which hits a temperature of 15 million°C at its core.
- The previous record set by EAST set was in May by running for 101 seconds at a higher temperature of 20 million°C.
- Also, researchers noted that “this time, steady-state plasma operation was sustained for 1,056 seconds at a temperature close to 70 million degrees Celsius, laying a solid scientific and experimental foundation toward the running of a fusion reactor”.
- It is important to note that nuclear fusion power works by colliding heavy hydrogen atoms to form helium. It releases vast amounts of energy.
ABOUT EXPERIMENTAL ADVANCED SUPERCONDUCTING TOKAMAK (EAST)
- The mission mimics the energy generation process of the sun.
- The reactor consists of an advanced nuclear fusion experimental research device located in Hefei, China.
- It is one of three major domestic tokamaks that are presently being operated across the country.
- The EAST project is part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) facility, which will become the world’s largest nuclear fusion reactor when it becomes operational in 2035.
- The ITER project includes the contributions of several countries, including India, South Korea, Japan, Russia and the United States.
HOW DOES THE ‘ARTIFICIAL SUN’ EAST WORK?
- It replicates the nuclear fusion process carried out by the sun and stars.
- For nuclear fusion to occur, tremendous heat and pressure are applied on hydrogen atoms so that they fuse together.
- The nuclei of deuterium and tritium — both found in hydrogen — are made to fuse together to create a helium nucleus, a neutron along with a whole lot of energy.
- Here, fuel is heated to temperatures of over 150 million degrees C so that it forms a hot plasma “soup” of subatomic particles.
- With the help of a strong magnetic field, the plasma is kept away from the walls of the reactor to ensure it does not cool down and lose its potential to generate large amounts of energy. The plasma is confined for long durations for fusion to take place.
WHY IS FUSION BETTER THAN FISSION?
- While fission is an easier process to carry out, it generates far more nuclear waste.
- Unlike fission, fusion also does not emit greenhouse gases and is considered a safer process with lower risk of accidents.
- Once mastered, nuclear fusion could potentially provide unlimited clean energy and very low costs.
- Like fission, fusion also does not emit greenhouse gases and is considered a safer process with lower risk of accidents.
Which other countries have achieved this feat?
- China is not the only country that has achieved high plasma temperatures. In 2020, South Korea’s KSTAR reactor set a new record by maintaining a plasma temperature of over 100 million degrees Celsius for 20 seconds.

Value Addition:
What is Nuclear Fusion?
Nuclear fusion is a reaction through which two or more light nuclei collide to form a heavier nucleus. The nuclear fusion process occurs in elements that have a low atomic number, such as hydrogen. Nuclear Fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission reaction in which heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements. Both nuclear fusion and fission produce a massive amount of energy.
Spread the Word
