THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
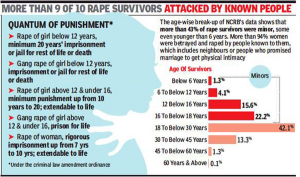
1. DEATH PENALTY FOR RAPE
THE CONTEXT: Maharashtra is the second state in India after Andhra Pradesh to approve the death penalty for heinous offences of rapes and gang-rapes, with the Maharashtra Assembly unanimously passing the Shakti Criminal Laws (Maharashtra Amendment) Bill.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Bill, which aims to curb crime against women and children, provides stricter punishment including the death penalty in rape cases.
- The Bill provides for the death penalty or life imprisonment for cases of heinous offences of rape, gang-rape and rape and gang-rape on women under 16 years of age, punishment to men, women, and transgenders in cases of insulting the modesty of a woman and intimidating a woman by any mode of communication and completing the investigation in 30 days.
- Other provisions include punishment such as imprisonment up to three months and a fine of Rs 25 lakh or both against the social media platform, internet, or mobile telephony data providers for failure to share data for police investigation.
- In case of filing false cases or providing false information to any person, it provides for punishment such as the imprisonment of not less than three years and up to three years and a fine of Rs 1 lakh.
- In acid attack cases, the punishment is imprisonment of at least 15 years that may extend to the remainder of a convict’s natural life, and a fine to be paid to the victim. Also, the expenditure of plastic surgery and face reconstruction operations for the victim will be taken care of from the monetary fine to be charged on the accused.
Add to your Knowledge:
- According to the Project 39 A, (criminal laws advocacy group with the National Law University in Delhi), corresponding to the legislative expansion of the death penalty for sexual crimes against women, more than 65 percent of all death sentences imposed by trial courts were linked to such cases in 2020, the annual study in the death penalty in India.
- Since 2016, the share of sexual crimes in the list of crimes for which trial courts are imposing the death penalty has been steadily increasing. From 6 percent in 2016, it jumped to 37.27 percent in 2017,41.1 percent in 2018 and 53.39 percent in 2019.
- Incidentally, in over 80 percent of cases — 41 of the 50 death sentences — involving sexual crimes in 2020, the victim is below the age of 18 years. While only nine cases involve rape and murder of adults, 21 are connected to the rape and murder of children below the age of 12, and 16 in which the age of the victim was between 12-18 years.
- The study also found that the restricted functioning of courts in the country due to the pandemic contributed to a drop in the number of death sentences imposed in 2020. Nearly 62 percent — 48 of the 77 — death sentences imposed in 2020 were awarded before the nationwide lockdown was enforced to deal with the pandemic. In comparison, 2019 saw less than half the sentences in the same period with 20 death sentences. In 2018, 27 death sentences were imposed in the same time period.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. 10TH NON-EUROPEAN COUNTRY TO JOIN EUROPOL
THE CONTEXT: South Korea has become the 10th country outside of Europe to join the European Union (EU) law enforcement cooperation agency that fights terrorism and other international crimes.
WHAT IS EUROPOL?
Europol is the European Union’s law enforcement agency. Their main goal is to achieve a safer Europe for the benefit of all the EU citizens. It is established in 1992 and its headquarter is in The Hague, the Netherlands, we support the 27 EU Member States in their fight against terrorism, cybercrime and other serious and organized forms of crime.
Large-scale criminal and terrorist networks pose a significant threat to the internal security of the EU and to the safety and livelihood of its people. The biggest security threats come from:
- international drug trafficking and money laundering.
- organized fraud.
- the counterfeiting of euros.
- trafficking in human beings.
The networks behind the crimes in each of these areas are quick to seize new opportunities, and they are resilient in the face of traditional law enforcement measures.
However, EUROPOL has no executive powers. The officials of EUROPOL cannot arrest the suspects without prior approval from competent authorities.
Under the agreement, police can now exchange information on crime and cooperate with member states of EUROPOL 17 European and nine non-European countries as well as international organizations and research institutes collaborating with the agency.
Who are the other 9 Non- EU members?
- Andorra
- San Marino
- UK
- Chile
- Mexico
- New Zealand
- Israel
- Kosovo
- Japan
India and EUROPOL:
In the year 2020, India-EU Strategic Partnership: A Roadmap to 2025 was held, during the summit between India and the EU talked about implementing a working arrangement between Europol and the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
3. THE WORLD’S LEGGIEST ANIMAL HAS BEEN DISCOVERED IN AUSTRALIA
THE CONTEXT: The eyeless, subterranean creature with 1,306 legs discovered 60 meters underground is the first ‘true millipede’.
THE EXPLANATION:

- The eyeless, subterranean Eumillipespersephone, discovered 60 meters underground near the south coast of Western Australia, has up to 1,306 legs, making it the first “true millipede” and the leggiest animal on Earth.
- The name “millipede” comes from the Latin for “thousand feet”, but until now no known species had more than 750 legs.
- Millipedes were the first land animals, as of today scientists know of more than 13,000 species. There are likely thousands more species of the many-legged invertebrates awaiting discovery and formal scientific description.
- These incredibly elongated millipedes, less than a millimeter wide and almost 10 centimeters long. They pointed out how their triangular faces placed them in the family Siphonotidae, comprised of sucking millipedes from the order Polyzoniida.
- Researchers classify any millipede with more than 180 body segments as “super-elongated”. E Persephone has 330.
Finding unknown

- Finding this incredible species, which represents a unique branch of the millipede tree of life, is a small first step towards the conservation of subterranean biodiversity in arid landscapes.
- A large proportion of the species of arid Australia are undescribed. For subterranean fauna, this may be more than 90%. Not knowing these animals exist makes it impossible to assess their conservation status.
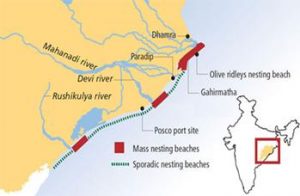
4. MASS TAGGING MISSION OF OLIVE RIDLEY TURTLES
THE CONTEXT: Scientists have resumed tagging of Olive Ridley turtles at Rushikulya rookery along the Odisha coast, which would help them identify the migration path and places visited by the marine reptiles after congregation and nesting.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Researchers of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) are carrying out tagging of the Olive Ridleys at three mass nesting sites — Gahirmatha, Devi River mouth and Rushikulya. The exercise was undertaken in Odisha in January 2021 after a span of about 25 years and 1,556 turtles had been tagged.
- They are studying the path taken by turtles in the sea if they keep coming to one nesting site for laying eggs, and the number of sites they visit over the years. Besides, the growth of turtles could be measured during the current study.
- Also, the study would reveal the inter-rookery movement of turtles in Odisha. The migration pattern to other countries would be recorded in detail.”
Mass Tagging:
- The metal tags affixed to turtles are non-corrosive and they do not harm their body. It can be removed later. The tags are uniquely numbered containing details such as the name of the organization, country code and email address.
- “If researchers in other countries come across the tagged turtles, they will email their location in longitude and latitude to the forest official. There is an established network working on turtles”. “The researchers intend to tag 30,000 turtles over a period of 10 years.
Olive Ridley Sea Turtles
- Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea) are migratory species visiting Indian coasts for nesting.
- These turtles travel all the way from the South Pacific Ocean to breed on the coast of Gahirmatha. Their mass nesting phenomenon is called arribadas.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable; CITES: APPENDIX 1
- They have the highest degree of protection as they are included in Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.

- The turtle eggs normally take 45 days to hatch. After this, tiny hatchlings come out and make their way to the sea.
- Threats: Heavy predation of eggs by dogs and wild animals, indiscriminate fishing with trawlers and gill nets, and beach soil erosion.
- Every year, the Indian Coast Guard’s “Operation Olivia”, initiated in the early 1980s, helps protect Olive Ridley turtles as they congregate along the Odisha coast for breeding and nesting from November to December.
- KURMA App: It is aimed at turtle conservation by providing users a database to identify a species but also provides the location of the nearest rescue center for turtles across the country.
Developed by: The application has been developed by the Indian Turtle Conservation Action Network(ITCAN) in collaboration with the Turtle Survival Alliance-India and Wildlife Conservation Society-India.
DEFENCE AND SECURITY
5. INDIGENOUS AERIAL TARGET – ‘ABHYAS’ SUCCESSFULLY TESTED
THE CONTEXT: DRDO successfully conducted the flight test of Indigenously developed High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT) Abhyas from Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast, Odisha.
THE EXPLANATION:

- ABHYAS is designed and developed by DRDO’s Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE); Bengaluru-based DRDO laboratory along with other DRDO laboratories has developed this indigenous unmanned aerial target system to meet the requirement of aerial targets of Indian Armed Forces.
- The aircraft is controlled from a ground-based controller and an indigenously developed MEMS-based Inertial Navigation System along with the Flight Control Computer which helps it to follow the pre-designated path in a fully autonomous mode.
- The air vehicle is launched using twin under-slung boosters which provide the initial acceleration to the vehicle.
- It is powered by a gas turbine engine to sustain a long-endurance flight at subsonic speed. The vehicle is programmed for fully autonomous flight. The check-out of air vehicles is done using a laptop-based Ground Control Station (GCS).
THE PRELIM PRACTICE QUESTION
1. Who among the following are eligible beneficiaries under Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana(PMUY)?
- An adult woman who is also a beneficiary of Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana.
- An adult woman who is also a beneficiary of Antyodaya Anna Yojana.
- An adult woman who is also a beneficiary of Pradhan Mantri Matritva Vandana Yojana.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All of them
ANSWER FOR 23rd DECEMBER 2021
Answer: a)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Summoning of parliamentary session is done by the President
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Prorogation of parliamentary session is done by the President.




