INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
1. COVAXIN FOR CHILDREN
THE CONTEXT: Health ministry sources said that the subject expert committee on Covid-19 vaccines has recommended the national drug regulator to grant an emergency use authorisation to Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin for the age group of 2 to 18 years.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The development is significant as India is just one step away from a Covid-19 vaccine being formally approved for children above the age of 2 years.
- The recommendation of the SEC regarding Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin is based on the pediatric study that is evaluating the safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of Covaxin. It is being conducted at six sites across the country in healthy volunteers above the age of 2 years.
- India’s drug regulator has already approved Zydus Cadila’s DNA Covid-19 vaccine for children aged above 12.
- The third vaccine that is being tested in children in India is the Covavax that will be manufactured by the Pune-based Serum Institute of India.
- The trials of Novavax’s recombinant nanoparticle protein-based COVID-19 vaccine – NVX-CoV2373 – in India is being branded as Covavax by SII. The trials will be conducted across 23 sites across the country.
- The fourth vaccine that is being tested in children in India is the Hyderabad-based Biological E’s Corbevax. The trials are expected to take place across ten sites across the country.
SOURCE: IE
2. THE CONTINUATION OF SBM U
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet approved the continuation of Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) till 2025-26, with a focus on sustainability of Open Defecation Free (ODF) outcomes, achieving scientific processing of Solid Waste in all cities, and managing Wastewater in cities with less than 1 lakh population in Census 2011 [cities not covered under Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)].
THE EXPLANATION:
- The financial outlay of ₹1,41,600 crores for SBM-U 2.0, 2.5 times more than the first phase of the mission.
- SBM-U 2.0 targets complete elimination of Open Defecation, including faecal sludge management in all cities with less than 1 lakh population.
- Eradication of hazardous entry into sewers and septic tanks
- No untreated wastewater to pollute water bodies
- All cities to achieve at least 3-star Garbage Free certification
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION-URBAN 2.0: KEY FEATURES
- Over the next 5 years, the focus of SBM-U 2.0, launched on 1st October 2021 by Hon’ble Prime Minister, will be on sustaining the sanitation and solid waste management outcomes achieved and accelerating the momentum generated, thus achieving the Mission’s vision of a “Garbage Free” Urban India.
- The implementation of the Mission components will be done in a structured and time-bound manner, with a thorough gap analysis of required infrastructure, detailed 5-year action plans, and annual action plans with timelines.
- The Mission will be completely paperless, digital, leveraging digital technology for complete transparency and accountability through GIS-mapped waste management infrastructure, robust user interface, online grievance redressal system, end-to-end online monitoring of projects starting from project creation to fund release, and project progress monitoring on integrated GIS-based platform.
- Enablers such as outcome-based fund release, greater funding support for smaller ULBs and convergence with 15thFC grants for added funding support, a structured implementation plan for each component, robust capacity building, communication and advocacy for sustainable behaviour change, intensified thrust on private sector participation, and extensive industry collaboration will help in achieving the Mission’s objectives within the scheduled timelines
SOURCE: PIB
3. CABINET APPROVED– AMRUT 2.0 TILL 2025-26
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet approved the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation 2.0 (AMRUT 2.0) till 2025-26, as a step towards AatmaNirbhar Bharat and with aim of making the cities ‘water secure’ and ‘self-sustainable through circular economy of water.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT), the first focused national water Mission was launched in June 2015 to facilitate ease of living to citizens in 500 cities by providing tap connections and sewer connections.
- So far, 1.1 crore household tap connections and 85 lakh sewer/ septage connections have been provided. 6,000 MLD sewage treatment capacity is being developed, of which 1,210 MLD capacity is already created, with provision for reuse of 907 MLD treated sewage. 1,820 parks with an area of 3,600 acres have been developed, while another 1,800 acres of area is under greening. So far, 1,700 flooding points have been eliminated.
- Taking forward the remarkable strides made under AMRUT, AMRUT 2.0, targets universal coverage of water supply by providing household tap connections in all 4,378 statutory towns.
- 100% coverage of household sewerage/ septage management in 500 AMRUT cities is another objective. Mission targets to provide 2.68 crore tap connections and 2.64 crore sewer/ septage connections to achieve the intended outcomes.
- The total indicative outlay for AMRUT 2.0 is ₹ 2,77,000 crore including the central share of ₹76,760 crores for five years from FY 2021-22 to FY 2025-26.
- The mission will be monitored on a robust technology-based portal. The projects will be geo-tagged. There will be an endeavour to make it a paperless Mission. Cities will assess their water sources, consumption, future requirement and water losses through a city water balance plan.
- Based on this, city water action plans will be prepared which will be summed up as State Water Action Plan and will be approved by the Ministry of Housing and Urban affairs. The funds for the projects will be shared by the Centre, State and ULBs. Central funds will be released to the States in three tranches based on allocation to the State as per State Water Action Plan.
- Other key features of AMRUT 2.0 (U) include Pey Jal Survekshan which will encourage competition among cities for benchmarking urban water services. Mission will also encourage the mobilization of market finance by mandating the implementation of 10% of the worth of projects in cities with populations above ten lakh through Public-Private Participation.
- Mission will also bring in the leading technologies in the water sector in the world through technology sub-Mission. Entrepreneurs/ start-ups will be encouraged in the water ecosystem. Information Education and Communication (IEC) campaign will be undertaken to spread awareness among the masses about water conservation.
- Mission has a reform agenda focussed on the financial health and water security of ULBs. Meeting 20% of water demand through recycled water, reducing non-revenue water to less than 20% and rejuvenation of water bodies are major water-related reforms. Reforms on property tax, user charges and enhancing creditworthiness of ULBs are other important reforms. ULBs will be rewarded with incentives for accomplishing the reforms.
SOURCE: PIB
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
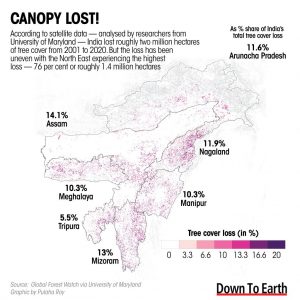
4. NORTHEAST SAW THE LARGEST SHARE OF THE COUNTRY’S TREE COVER LOSS
THE CONTEXT: According to an analysis by Down To Earth, the northeastern region of India lost 79 per cent of its tree cover in 2020, recording the biggest dip in the country.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Over 110,000 hectares of tree cover vanished from the region last year, according to the University of Maryland’s forest change data.
- Researchers from the University of Maryland processed and analysed over a million satellite images to demonstrate the loss. Tree cover loss is ‘complete removal of tree cover canopy’, the scientists wrote.
- They used algorithms to identify individual pixel values for every tree canopy lost, to calculate even the smallest changes in the forest area.
- India lost close to 143,000 hectares of forest cover in 2020 when the overall forest area was 4.6 per cent lower than in 2001. But the loss has been uneven.
- The ‘seven sisters’ Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Tripura, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram and Nagaland individually were responsible for 5-14 per cent of the country’s loss in forest area from 2001 through 2020.
- Assam, the largest of the seven states, contributed the most (14.1 per cent) to the national tree cover loss during the period.
- Nagaland saw its forest cover shrink the fastest since 2001, suffering a 17 per cent drop in the two decades. It was followed by Tripura, where the area under forest cover decreased by 15 per cent in the years studied.
- Outside the North East, Odisha lost the largest area of land under tree cover (125,004 hectares) from 2001-2020 — 6.5 per cent of India’s total. It was followed by Kerala that contributed 4 per cent of the forest area lost.
- Tree cover loss can be triggered by various reasons, ranging from anthropogenic factors such as deforestation or timber harvesting to natural causes like forest fires or storms.
SOURCE: TH
5. CHINA LAUNCHES BIODIVERSITY FUND
THE CONTEXT: China pledged to inject $233 million into a new fund to protect biodiversity in developing countries during a key UN conservation summit, despite disagreements among major donors on the initiative.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Its pledge came as delegates from about 195 countries gathered in the southern Chinese city of Kunming for the first of a two-part summit on safeguarding plants, animals and ecosystems.
- The summit aims to establish a new accord setting out targets for 2030 and 2050.
- A key proposal being debated at the conference is the “30 by 30” agenda that would afford 30% of the Earth’s land and oceans protected status by 2030.
- But some rich country donors say a new fund for conservation is unnecessary because the United Nations’ Global Environment Facility already helps developing nations finance green projects.
SOURCE: TH
INDIAN ECONOMY
6. INDIA’S GROWTH PROJECTIONS BY IMF
THE CONTEXT: according to the latest projections released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) India’s economy is expected to grow by 9.5 per cent in 2021 and 8.5 per cent in 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India’s growth projection released by the latest World Economic Outlook (WEO) remains unchanged from its previous WEO update of July this summer but is a three-percentage point in 2021 and a 1.6 percentage point drop from its April projections.
- According to the latest WEO update, released ahead of the annual meeting of the IMF and the World Bank, the world is expected to grow at 5.9 per cent in 2021 and 4.9 per cent in 2022.
- The United States is projected to grow at six per cent this year and 5.2 per cent the next year.
- China is projected to grow at 8 per cent in 2021 and 5.6 per cent in 2022.
SOURCE: IE
7. MAHARATNA STATUS TO PFC
THE CONTEXT: The government of India accorded ‘Maharatna’ status to the state-owned Power Finance Corporation Ltd (PFC), thus giving PFC greater operational and financial autonomy.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Incorporated in 1986, PFC is the largest Infrastructure Finance Company today, exclusively dedicated to Power Sector under the administrative control of the Ministry of Power.
- This new recognition will enable PFC to offer competitive financing for the power sector, which will go a long way in making available affordable & reliable ‘Power for All 24×7’.
- The enhanced powers that come with Maharatna Status will also help PFC in pushing the Government’s agenda of funding under the National Infrastructure Pipeline, the national commitment of 40% green energy by 2030 and effective monitoring and implementation of the New Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme with an outlay of more than Rs.3 Lakh crore.
SOURCE: PIB
8. RETAIL INFLATION FALLS TO 4.35%
THE CONTEXT: India’s retail inflation cooled off to a five-month low of 4.35% in September, thanks to a sharp dip in food price inflation, while industrial output growth accelerated to 11.9% in August.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Economists cautioned against reading too much into these encouraging official data prints yet, with adverse headwinds lurking on both fronts.
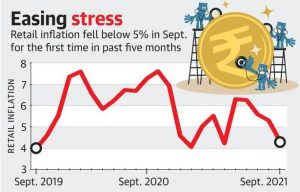
- Food inflation based on the Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI) fell to just 0.68% in September after having declined to a seven-month low of 3.1% in August.
- While vegetables recorded negative inflation of 22.5%, price rise in oils and fats remained sticky at 34.2% and in the range of 7% to 8.75% for key protein sources such as pulses, eggs and meat.
- However, core inflation which doesn’t include food and fuel price trends remained elevated at 5.8% for the third month in a row, and economists said the moderation in the inflation rate could be transient, with rising energy, metals and logistics costs being key risk factors.
SOURCE: TH
9. CENTRE ANNOUNCES PLASTIC WASTE RECYCLING TARGETS
THE CONTEXT: The Environment Ministry has issued draft rules that mandate producers of plastic packaging material to collect all of their produce by 2024 and ensure that a minimum percentage of it be recycled as well as used in subsequent supply.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Companies would have to collect at least 35% of the target in 2021-22, 70% by 2022- 23 and 100% by 2024.
- Non- compliance would not invite a traditional fine.
- It has also specified a system whereby makers and users of plastic packaging could collect certificates — called Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates — and trade in them.
- Only a fraction of plastic that cannot be recycled — such as multi-layered multi-material plastics — would be eligible to be sent for end-of-life disposal such as road construction, waste to energy, and waste to oil and cement kilns.
- Only methods prescribed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) would be permitted for their disposal.
SOURCE: TH
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
10. PM MODI AT G20 SUMMIT
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated virtually in the G20 Extraordinary Summit on Afghanistan.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Meeting was convened by Italy, which currently holds the G20 Presidency, and chaired by Italian Prime Minister Mr Mario Draghi.
- Issues under consideration at the meeting related to the humanitarian situation; concerns relating to terrorism; and human rights in Afghanistan.
- In his remarks, the Prime Minister welcomed the initiative of the Italian G20 Presidency in convening the meeting to take stock of the current situation in Afghanistan.
- He emphasized the centuries-old people-to-people ties between India and Afghanistan. The Prime Minister mentioned that over the last two decades, India has contributed to promoting socio-economic development and capacity building of youth and women in Afghanistan. He recalled that over 500 development projects have been implemented by India in Afghanistan.
- The Prime Minister noted that the Afghan people have a great feeling of friendship with India. He conveyed that every Indian feels the pain of Afghan people facing hunger and malnutrition. He emphasized the need for the international community to ensure that Afghanistan has immediate and unhindered access to humanitarian assistance.
- The Prime Minister also underlined the need to ensure that Afghan territory does not become a source of radicalization and terrorism, regionally or globally. He emphasized the need to enhance our joint fight against the nexus of radicalization, terrorism and the smuggling of drugs and arms in the region.
- In order to preserve the socio-economic gains of the last 20 years and to restrict the spread of radical ideology, the Prime Minister called for an inclusive administration in Afghanistan, which includes women and minorities.
- He conveyed support for the important role of the United Nations in Afghanistan and called for renewed support of the G20 for the message contained in UN Security Council Resolution 2593 on Afghanistan.
- The Prime Minister called on the international community to forge a unified international response without which it would be difficult to bring about the desired change in Afghanistan’s situation.
SOURCE: PIB
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR THE DAY
Q1. Consider the following statement about the Kunming biodiversity fund:
- It was announced by China during the UN conservation summit.
- It is part of the United Nations’ Global Environment Facility.
- It will be used to protect biodiversity in developing countries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only d) 1, 2 and 3
ANSWER FOR OCTOBER 12, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Answer: a)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: NHRC consists of a Chairman and five members.
- Statement 2 is correct: The chairman and members hold office for a term of three years or until they attain the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier.
- Statement 3 is correct: The salaries, allowances and other conditions of service of the chairman or a member are determined by the Central government.




