INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
1. AMRUT 2.0 AND SBM-U 2.0
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister launched Schemes for transforming Urban Areas- AMRUT 2.0 and Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0.
SBM-U 2.0
- The Mission will focus on ensuring complete access to sanitation facilities to serve additional populations migrating from rural to urban areas in search of employment and better opportunities over the next 5 years. This will be done through the construction of over 3.5 lakhs individual, community and public toilets.
- Complete liquid waste management in cities in less than 1 lakh population – a new component introduced under SBM-Urban 2.0 will ensure that all wastewater is safely contained, collected, transported and treated so that no wastewater pollutes our water bodies.
- Under Sustainable Solid Waste Management, greater emphasis will be on source segregation. Material Recovery Facilities, and waste processing facilities will be set up, with a focus on phasing out single-use plastic. Construction & demolition waste processing facilities will be set up and mechanical sweepers deployed in National Clean Air Programme cities and in cities with more than 5 lakh populations.
- Remediation of all legacy dumpsites will be another key component of the Mission.
- It is expected that under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, all statutory towns will become at least ODF+; and all cities with <1 lakh population ODF++.
- Systems and processes will be in place so that all wastewater is safely treated and optimally reused and no untreated wastewater pollutes water bodies.
- Regarding Solid Waste Management, it is expected that all cities will achieve at least 3-star Garbage Free certification under SBM-U 2.0.
- Special focus will be put on the well-being of sanitation and informal waste workers, through the provision of personal protective equipment and safety kits, linkages with government welfare schemes along with their capacity building.
- A financial outlay of ₹1,41,600 crores has been finalized for SBM-U 2.0, including the central share of Rs 36,465 for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26which is over 2.5 times the financial outlay of Rs 62,009 crores in the last phase of the Mission.
AMRUT2.0
- 0aims to make around 4,700 towns/cities‘ water secure’. It will build upon the progress of AMRUT to address water needs, rejuvenate water bodies, better manage aquifers, reuse treated wastewater, thereby promoting a circular economy of water.
- The total outlay of AMRUT 2.0 is RS 2,97,000 crores, including the central share of Rs 76,760 crores. This includes Rs 10,000 crores Central share and another Rs 10,000 crores states’ share for continuing financial support to AMRUT Mission up to March 2023.
- The Objective of AMRUT 2.0 is to provide100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 ULBs, by providing 2.68 crore urban household tap connections, thereby benefitting around 10.7 crores people.
- It will provide 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities, by providing 2.64 crore sewer connections/ septage connections, thereby benefitting around 10.6 crores people. Rejuvenation of water bodies and urban aquifer management will be undertaken to augment sustainable fresh water supply.
- Recycle and reuse of treated wastewater is expected to cater to 20% of the total water needs of the cities and 40% of industrial demand. Under the Mission, fresh water bodies will be protected from getting polluted to make natural resources sustainable.
- There will be upscaling from 500 cities covered under AMRUT with 1 lakh+ population to all 4,372 cities, covering 100% urban India. It will promote the circular economy of water through the formulation of the City Water Balance Plan for each city, focusing on recycle/reuse of treated sewage, rejuvenation of water bodies and water conservation. The digital economy will be promoted through being a Paperless Mission.
- Pey Jal Survekshanwill is conducted in cities to ascertain the equitable distribution of water, reuse of wastewater and mapping of water bodies w.r.t. quantity and quality of water through a challenging process. Technology Sub-Mission for water will leverage the latest global technologies in the field of water.
- The Mission seeks to promote AatmaNirbhar Bharatthrough encouraging Startups and Entrepreneurs. It will lead to the promotion of the GIG economy and on-boarding of youth & women.
- Urban Water Information System through NRSC will be developed, leading toAquifer Management system. Information, Education and Communication campaign will spread awareness among masses about conservation of water. A target-based capacity building program will be conducted for all stakeholders including contractors, plumbers, plant operators, students, women and other stakeholders.
- The AMRUT-2.0 Mission will promote Public-Private partnerships (PPP). It has been mandated for cities having million plus population to take up PPP projects worth a minimum of 10 per cent of their total project fund allocationwhich could be on the Annuity/ Hybrid Annuity / BOT Model.
- 4798 ULBs have already signed the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Central Government, outlining the role and commitments of all the stakeholders in both the Missions.
SOURCE: PIB
2. OVER 5 CRORE TAP WATER CONNECTIONS UNDER JAL JEEVAN MISSION
THE CONTEXT: Since the announcement of the Jal Jeevan Mission in August 2019, in just about 25 months, over 5 Crore families have been provided with tap water connections in their homes.
ANALYSIS:
- Jal Jeevan Mission was announced by Prime Minister on 15th August 2019 to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every home by 2024. In 2019, out of about 18.93 Crore households in rural areas, only 3.23 Crore (17%) had tap water connections. Thus, 15.70 Crore households are to be provided with tap water by 2024.
- In addition, the functionality of all existing water supply systems and tap connections is also to be ensured. The programme directly benefits more than 19 Crore rural families, bridging the rural-urban divide and improving public health. As of date, about 8.26 Crore (43%) rural households have a tap water supply in their homes.
- The motto of Jal Jeevan Mission is that ‘no one is left out.’ Every rural household in 78 districts and 1.16 lakh villages is getting a tap water supply.
- With a focus on the health and well-being of children, last year on Gandhi Jayanti, a campaign was launched to provide tap water connections to all schools, Anganwadi centres and ashram shalas (tribal residential schools) for drinking, cooking mid-day meals, hand washing and use in toilets. As of date, tap water supply has been provided in 7.72 lakh (76%) schools and 7.48 lakh (67.5%) Anganwadi centres.
- Following a bottom-up approach, JJM is being implemented as a decentralized, demand-driven and community-managed programme with Gram Panchayats and/ or its sub-committees, i.e. Village Water & Sanitation Committees (VWSC)/ Pani Samitis playing a key role in planning, implementation, management, operation and maintenance of in-village water supply systems, thereby providing clean tap water to every household on a regular and long-term basis.
- The Pani Samitis/ VWSCs function as a legal entity as envisaged in the 73rd Amendment to the Constitution. It consists of 10-15 members with at least 50% women members and proportionate representation from weaker sections.
- VWSC prepared a one-time Village Action Plan (VAP), co-terminus with the 15th Finance Commission period by dovetailing different resources at the village level, which is to be approved in a Gram Sabha. VAP comprises 4 key components of drinking water source augmentation, drinking water supply system, greywater treatment and its reuse, and regular operation and maintenance of in-village water supply system.
- Further, a cadre of 30-40 members in every village is being trained and skilled to build their capacities to manage their in-village water supply systems. 5 women from every village, viz. ASHA, Anganwadi teachers, SHG leaders, etc. are being trained to test water quality using Field Test Kits (FTKs).
SOURCE: PIB
3. VAYO NAMAN PROGRAMME
THE CONTEXT: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment organises VAYO NAMAN Programme on the occasion of International Day of Elder Persons.
ANALYSIS:
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment celebrates International Day of Older Persons every year on 1st October for the cause of elderly persons.
- Apart from dedicating an Elderly Line 14567 to the Nation, Shri M. Venkaiah also launched two portals – SAGE (Seniorcare Aging Growth Engine) and SACRED (Senior Able Citizens for Re-Employment in Dignity) on this occasion.
- While the SAGE portal, designed by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, aims to encourage entrepreneurs in the area of elderly care, the SACRED portal will connect senior citizens with job providers in the private sector.
SOURCE: PIB
4. KAMDHENU DEEPAWALI 2021 CAMPAIGN
THE CONTEXT: Kamdhenu Deepawali 2021 campaign was launched to manufacture and market more than 100 Crore Cow dung based Deepak lamps and Laxmi-Ganesh Idols.
ANALYSIS:
- Kamdhenu Deepawali is to make Cows be economically useful by proper economic use of Cow Dung and Cow Urine too along with its Milk, Curd, Ghee. More than 300 items are getting made now byPanchgavya from Cow.
- This includes Deepawali items too like – Deepak, Lamps, Candles, Sambrani cup, Havansamagri, Dhoopbatti, incense sticks, Hardboard, wall piece, Laxmi-Ganesh idols etc made up of Cow dung.
- The Gomaya lamps made by Cow Entrepreneurs and Cow owners will save the environment by providing eco-friendly alternatives to chemical-based Chinese lights.
SOURCE: PIB
5. NCRB REPORT: A STATUS CHECK ON CRIMES IN THE COUNTRY
THE CONTEXT: The Coronavirus pandemic and subsequent lockdown resulted in a drop in traditional crimes like theft, robbery, and assault on women and children in 2020, but there was a drastic jump in disobedience to government orders, primarily arising due to violations of COVID-19 norms.
ANALYSIS:
- According to the latest report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) on ‘Crime in India – 2020’, a total of 66,01,285 cognizable crimes comprising 42,54,356 Indian Penal Code (IPC) crimes and 23,46,929 Special and Local Laws (SLL) crimes were registered in 2020.
- India reported an average of 80 murders daily in 2020, totalling 29,193 fatalities over the year, with Uttar Pradesh topping the chart among states. This was an increase of one per cent over the total 28,915 murders in 2019, with a daily average of 79 killings during the year.
- Delhi accounted for nearly 40 per cent of all rape cases and almost 25 per cent murder cases among 19 metropolitan cities in India in 2020.
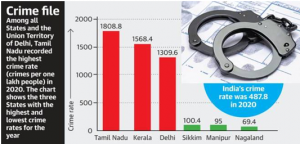
SOURCE: TH
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
6. NANO UREA
THE CONTEXT: Successful field trial of Drone spraying of Nano Urea undertaken.
ANALYSIS:
- A practical field trial of Drone Spraying of Nano Liquid Urea was conducted in Bhavnagar, Gujarat. The trial was attended by a large number of farmers.
- This demonstration of spraying liquid nano urea by drone was undertaken by IFFCO, a company involved in developing nano urea.
- India has become the first country in the world to start commercial production of Nano Urea.
- Not only has Nano Urea been produced on a large scale today, but farmers are adopting it on a large scale since the very beginning.
- It started production in June and till now we have produced more than 5 million bottles of Nano Urea. More than one lakh bottles of nano urea are being produced every day.
ABOUT NANO UREA
- Nano Urea (Liquid) contains nanoscale nitrogen particles which have more surface area (10,000 times over 1 mm Urea prill) and a number of particles (55,000 nitrogen particles over 1 mm Urea prill).which makes it more impactful. In comparison to Urea, the uptake efficiency of Nano Urea is more than 80 %.
- It is thus, required in lesser measure compared to the conventional urea fertiliser to fulfil the plant’s nitrogen requirement.
- Nano Urea (liquid) has been tested for biosafety and toxicity as per the guidelines of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India and OECD international guidelines.
- Nano Urea (liquid) is completely safe for humans, animals, birds, rhizosphere organisms and the environment at the recommended levels of application.
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, DAC & FW, Government of India, has notified IFFCO Nano Urea (Liquid) as a nano fertilizer under the Fertilizer Control Order (FCO).
SOURCE: PIB
7. A PROJECT TO SECURE INDIA’S ELEPHANT CORRIDORS
THE CONTEXT: As instances of human-elephant conflict rise, the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change has embarked on a massive project to identify and secure elephant corridors in the country.
ANALYSIS:
- The corridors could also be notified in order to give legal protection to the movement of elephants.
- According to Environment Minister, the Ministry has recently initiated the verification exercise of elephant corridors and is also working on mapping land use and land cover of elephant reserves in the country using GIS technology which will also aid conservation.
- Experts said elephant corridors have been changing over the years. Eighty-eight corridors were identified jointly by the Ministry and Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and published in 2005.
- In 2015, the second round of identification took place — and when published two years later, the number of corridors had gone up to 101.
- Ministry data on human-elephant conflict released last year showed 1,025 elephant deaths and 4,642 human deaths from 2009 until September 2019. The most human deaths were in West Bengal (821; 18%).
- The largest number of elephant deaths were caused by electrocution (640; 62% of the total in 10 years), followed by train accidents (170; 17%), poaching (153; 15%), and poisoning (62; 6%).
SOURCE: IE
8. CSIR-NGRI PROPOSES A LANDSLIP AND FLOOD WARNING SYSTEM
THE CONTEXT: The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research – National Geophysical Research Institute (CSIR-NGRI) has launched an ‘Environmental Seismology’ group to develop a ‘Landslide and Flood Early Warning System’ for the Himalayan region based on real-time monitoring with dense seismological networks, coupled with satellite data, numerical modelling and geomorphic analysis.
ANALYSIS:
- The need for such an early warning system was necessitated following February’s rockslide flood disaster in Chamoli (Uttarakhand), where a steep glacier on the Nandadevi peak in Garhwal Himalaya got detached, causing a major avalanche and inducing flash floods in the Rishi Ganga and Alaknanda rivers.
- It killed several persons downstream and caused damage to two power plants.
SOURCE: UNI
INDIAN ECONOMY
9. LABOUR MINISTRY’S QUARTERLY SURVEY OF EMPLOYMENT DATA
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Labour has recently released a survey of firm employment data for nine non-farm sectors. The survey will be conducted quarterly and will provide much-needed high-frequency employment data for the economy. The data will be collected from firms, and over time, will become a critical input for macroeconomic policymaking in the country.
ANALYSIS:
- The labour ministry report of the Quarterly Employment Survey for April-June 2021 presents the status of employment in nine non-farm sectors — Manufacturing, Construction, Trade, Transport, Education, Health, Accommodation and Restaurant, IT/ BPO, and Financial Services — employing 10 or more workers.
- The survey gives a picture of the state of employment in the organised sector. The government plans to conduct a similar survey for the unorganised sector as well. The two surveys taken together would give a holistic picture of the state of employment in the economy.
- Most mature economies have official monthly statistics on employment. India had to rely on low-frequency official surveys which, at best, give an outdated picture of employment.
- High-frequency data on the labour market bridges a critical gap in the Indian statistical framework. It would enable timely monitoring of the labour market, which is essential for devising policies for employment creation and skill development in the country.
- Such a survey would also give insights into the relative contribution of different sectors in employment generation over time.
- The employment surveys such as the PLFS by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation is household-based surveys and provides an assessment of employment from the supply side. The Quarterly Employment Survey released by the Ministry of Labour is an establishment-based survey and provides a picture of employment from the demand side.
SOURCE:TH PRINT
10. DIGITAL ECONOMY REPORT 2021
THE CONTEXT: The Digital Economy Report of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development examines the implications of growing cross-border data flows, especially for developing countries. It proposes to reframe and broaden the international policy debate with a view to building multilateral consensus.
ANALYSIS:
- The Philippines is one of six countries that allow unfettered cross-border data transmission.
- Canada, Australia, Mexico, Singapore, and the United States are the other five countries that allow unrestricted data movement across borders.
- Countries with strong regulatory environments and sufficient regulatory resources to check compliance with domestic laws choose a light-touch approach.
- According to the report, the Philippines’ employment of a light-touch strategy is due to the country’s “reliance” on the outsourcing industry, which is one of the country’s primary economic development drivers.
- The “restrictive” or “guarded” approach for cross-border data flows is followed by countries like India, China, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Rwanda, Russian Federation, Turkey, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam.
- According to UNCTAD proposals, facilitate global data sharing, develop global digital public goods, increase trust, and reduce uncertainty in the digital economy.
- According to UNCTAD, a lack of a worldwide framework would add to the difficulty of preserving private sector and government data privacy. As a result, a new regulatory framework is needed that considers both economic and non-economic considerations.
SOURCE:UNITED
11. PANDORA PAPERS
THE CONTEXT: According to an investigation published by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) media consortium, more than a dozen heads of state and government, including the King of Jordan and the Czech Prime Minister, have hidden millions in offshore tax-havens.
ANALYSIS:
- The “Pandora Papers” investigation — involving some 600 journalists from media, including The Washington Post, the BBC and The Guardian — is based on the leak of some 11.9 million documents from 14 financial services companies around the world.
- Some 35 current and former leaders are featured in the documents analyzed by the ICIJ — facing allegations ranging from corruption to money laundering and global tax avoidance.
- The “Pandora Papers” are the latest in a series of mass ICIJ leaks of financial documents that started with LuxLeaks in 2014 and were followed by the Panama Papers, the Paradise Papers and FinCen.
- The documents behind the latest investigation are drawn from financial services companies in countries including the British Virgin Islands, Panama, Belize, Cyprus, the United Arab Emirates, Singapore and Switzerland.
SOURCE:TH
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
12. GAMING DISORDER INCREASES DURING PANDEMIC
THE CONTEXT: Gaming addiction, a disorder, is quickly growing as the pandemic spurred increased use of Internet devices.
ANALYSIS:
- Behaviour changes in teenagers — insomnia, withdrawal from social contacts, academic failure, and extreme anger and irritability.
- A 2019 survey by the U.S. based Limelight Networks found that India had the second largest number of gamers after South Korea.
- The World Health Organization categorized gaming disorder as a mental health condition in 2018.
- In August 2021, China limited gamers under 18 years to just three hours of online games per week, during specified times, and made the industry responsible for enforcing the restriction.
- In India, the legal focus has been on recent laws in the southern states seeking to ban online games such as rummy, poker or even fantasy sports which offer prize money or financial stakes.
- In September 2021, the Kerala High Court quashed such a law in the State, accepting the industry’s stance that, as games of skill rather than chance, they should not trigger bans on gambling.
- However, worried parents, psychiatrists and mental health advocates warn that the dangers go well beyond monetary motivations.
SOURCE: TH
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Consider the following statements related to Pani Samitis:
- The Pani Samitis function as a legal entity as envisaged in the 73rd Amendment to the Constitution.
- It consists of at least 50% women members
- It prepares Village Action Plan (VAP).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Q2) Consider the following statements about Nano Urea
- In comparison to Urea, the uptake efficiency of Nano Urea is more than 80 %.
- India has become the first country in the world to start commercial production of Nano Urea.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER FOR OCTOBER 1, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER TO RELEVANT ARTICLE)
1. Answer: D)
Explanation:
- Senior Able Citizens for Re-Employment in Dignity (SACRED) Portal is an IT portal to be developed to bring the employment seeker senior citizens and employment providers on one platform.
- The aim is to devise ways to ensure Senior Citizens live healthy, happy, empowered, dignified and self-reliant life.
- Rs. 10 Cr would be provided for funding for the platform development along with a maintenance grant of Rs. 2 Cr per year for 5 years




