INDIAN HISTORY
1. UP GOVERNMENT RENAMES KAKORI KAND TO KAKORI TRAIN ACTION
THE CONTEXT: Uttar Pradesh government has renamed the ‘Kakori Kand’ to ‘Kakori Train action’ as the word ‘Kand’ denotes a sense of insult to this incident under India’s Independence struggle.
ANALYSIS :
- As India is celebrating ‘Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav’ to commemorate 75 years of its Independence, the Uttar Pradesh government celebrated the anniversary of the ‘Kakori Train action’ under the program ‘Chauri Chaura Mahotsav’ which is going to complete 100 years in 2022.
- The Kakori Train Action or Kakori Conspiracy was a train robbery that took place at Kakori, a village near Lucknow, on 9 August 1925 during the Indian Independence Movement against the British colonial rule.
- The robbery was organized by Hindustan Republican Association and more than 40 persons were arrested in this incident and they were finally sentenced to death by the British government and also severe punishments were given to those people who helped this incident.
Source: NewsOnAIR
INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
2. UJJWALA 2.0 LAUNCHED
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister launched the second phase of the Ujjwala gas connection scheme for the poor.
ABOUT UJJWALA 2.0
- The government will distribute about 1 crore gas connections in this financial year to the poor.
- Along with a deposit-free LPG connection, it will provide the first refill and hotplate (stove) free of cost to the beneficiaries.
- The enrollment procedure will require minimal paperwork.
- In Ujjwala 2.0, migrants will not be required to submit ration cards or address proof. A self-declaration for both ‘family declaration’ and as a ‘proof of address will suffice.
BACKGROUND
- During Ujjwala 1.0 launched in 2016, a target was set to provide LPG connections to 5 crore women members of BPL households.
- Subsequently, the scheme was expanded in April 2018 to include women beneficiaries from seven more categories (SC/ST, PMAY, AAY, Most backward classes, tea garden, forest dwellers, Islands).
- Also, the target was revised to 8 Crore LPG connections. This target was achieved in August 2019, seven months ahead of the target date.
SOURCE: TH
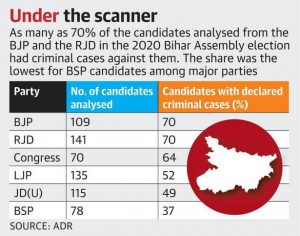
3. PARTIES GET 48 HOURS TO PUBLISH CANDIDATES’ CRIMINAL RECORDS
THE CONTEXT: The Supreme Court had directed political parties to publish the criminal history if any, of their election candidates on the homepage of their party websites under the caption ‘candidates with criminal antecedents’ within 48 hours of their selection.
ANALYSIS:
- The court said it did not take political parties much time to flout its February 2020 judgment, which had directed them to prominently publish the criminal antecedents of their candidates in newspapers and on social media accounts, including Twitter and Facebook.
- The court imposed ₹1 lakh each on the BJP, Congress, JD(U), RJD, Lok Janshakti Party, and the Communist Party of India for subverting the February 2020 judgment.
- It slapped 5 lakh Rupees each on the Communist Party of India (Marxist) and the Nationalist Congress Party for completely ignoring the February judgment.
- In a series of directions to make the right of information of a voter “more effective and meaningful”, the court further ordered the Election Commission of India to launch a dedicated mobile app for voters to get details of the criminal history of the candidates at the touch of a button.
- The Commission should also form a separate cell to monitor political parties on their compliance with the court’s judgment.
SOURCE: TH
4. CONSTITUTION 127TH AMENDMENT BILL, 2021
THE CONTEXT: The Lok Sabha passed the 127th Constitution Amendment Bill, 2021, with unanimous support from the House.

ABOUT THE 127TH CAB 2011
- The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Seventh Amendment) Bill, 2021 was introduced in Lok Sabha by the Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- The Bill amends the Constitution to allow states and union territories to prepare their own list of socially and educationally backward classes.
- The Constitution (One Hundred and Second Amendment) Act, 2018 gave constitutional status to the NCBC and empowered the President to notify the list of socially and educationally backward classes for any state or union territory for all purposes.
- The 2021 Bill amends this to provide that the President may notify the list of socially and educationally backward classes only for purposes of the central government. This central list will be prepared and maintained by the central government. Further, the Bill enables states and union territories to prepare their own list of socially and educationally backward classes. This list must be made by law, and may differ from the central list.
- Article 338B of the Constitution mandates the central and state governments to consult the NCBC on all major policy matters affecting the socially and educationally backward classes. The Bill exempts states and union territories from this requirement for matters related to the preparation of their list of socially and educationally backward classes.
BACKGROUND:
- In May 2021, Supreme Court in its order on Maratha reservation upheld the 102nd Constitutional Amendment Act that inserted Articles 338B and 342 A (with two clauses) after Article 342, which said the President of India, in consultation with the Governors, would specify socially and educationally backward classes, taking away the powers of State governments to do so.
5. GLOBAL YOUTH DEVELOPMENT INDEX
THE CONTEXT: India is ranked 122nd on a new Global Youth Development Index measuring the condition of young people across 181 countries, released by the Commonwealth Secretariat in London.
ANALYSIS:
- The index ranks countries between 0.00 (lowest) and 1.00 (highest) according to the developments in youth education, employment, health, equality and inclusion, peace and security, and political and civic participation. It looks at 27 indicators including literacy and voting to showcase the state of the world’s 1.8 billion people between the age of 15 and 29.
- The triennial rankings of youth development found India among the top five risers on the index between 2010 and 2018, alongside Afghanistan and Russia, advancing their score on average by 15.74 percent across areas such as education and employment.
- Singapore ranked topmost followed by Slovenia, Norway, Malta, and Denmark. Chad, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Afghanistan, and Niger came last respectively.
- The 2020 Global Youth Development Index reveals that the conditions of young people have improved around the world by 3.1 percent between 2010 and 2018.
- Overall, the index shows advances in youth’s participation in peace processes and their education, employment, inclusion, and health care since 2010.
SOURCE: THE PRINT
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
6. A THIRD OF INDIA’S COASTLINE UNDER EROSION
THE CONTEXT: As per information provided in parliament, about 32 percent of the Indian coastline is under varying degrees of erosion (low, moderate or high), 27 percent is of accreting nature and the remaining 41 percent is in a stable state.
ANALYSIS:
- The National Centre for Coastal Research has carried out a national shoreline change assessment mapping for the Indian coast, using 28 years of satellite data from 1990-2018.
- The study was done along with nine coastal states and two Union territories (UT) to provide information for coastal management strategy.
- Around 41 percent of the coastline of Kerala is experiencing erosion, 31 per cent is stable and 21 per cent is accreting, as per the National Centre of Coastal Research studies.
FEW OTHER FACTS FOR PRELIMS
- A total of 720 persons have lost their lives due to cyclones from 2016-17 to 2021-22.
- As per the report on ‘Women and Men in India, 2020’, the share of workforce of men and women in agriculture has declined in both the rural and urban areas during the period from 1987-88 to 2019-20.
- A central sector scheme on ‘Promotion of Agricultural Mechanisation for In-Situ Management of Crop Residue in the states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi’ is being implemented in the states since 2018-19. Under this scheme, financial assistance of 50 per cent the cost of machinery is provided to the farmers for the purchase of crop residue management machinery. Financial assistance of 80 per cent of the project cost is also provided to the cooperative societies of farmers, farmers producers organisations, registered farmers societies and panchayats for establishment of custom hiring centres (CHC) of crop residue management machinery.
- From 2018-19 to 2020-21, more than 30,900 CHCs have been established and more than 158,000 crop residue management machines have been supplied to them and individual farmers of these four states.
SOURCE: DTE
7. DEVELOPMENT OF NEW CROPS
THE CONTEXT: The National Agricultural Research System (NARS) is involved in development of new high yielding and biotic/abiotic stress tolerant crop varieties of field and horticultural crops.
Analysis:
- During last 3 years (2018-2020) and current year, 1017 varieties of 69 field crops and 206 varieties of 58 horticultural crops have been developed.
- ICAR has a strong network of All India Coordinated Research Projects (AICRPs)/ All India Network Projects (AINPs), coordinated by different ICAR institutes, which are operational in the various Central and State Agricultural Universities and ICAR institutes for development of new crop varieties of field and horticultural crops.
- Presently, 44 AICRPs/AINPs of field and horticultural crops are operational through 50 SAUs/CAUs/DUs and 55 ICAR institutes across the country at 1017 locations.
SOURCE: PIB
8. ABOUT 96,000 SALMON DIE AFTER CHLORINE LEAK IN ARCTIC NORWAY
THE CONTEXT: About 96,000 farmed salmon are believed to have died when a leak in a nearby tank sent 15,000 liters (4,000 gallons) of chlorine into a fjord in Arctic Norway.
Analysis:
- The leak happened at one of its fish slaughterhouses in the town of Alta and the fish were in a waiting cage nearby at the time.
- The chlorine is used to disinfect the water after the slaughtering.
- Alta sits 175 kilometers (109 miles) northeast of Tromsoe, the largest city in Arctic Norway.
SOURCE: IE
9. KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA (KVK)
THE CONTEXT: The Government has made a provision for the opening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) in each of the rural districts across the country. A total of 725 KVKs have been established across the country till date.
ABOUT KVKS
- KVKs are mandated for frontline extension which acts as a bridge between research organizations and the main extension system operated by different development departments of the State Governments.
- Considering the role and resources of a KVK, it caters to the requirement of the selected farmers of the district and provides capacity development support to State Development Departments. The coverage of entire district is the responsibility of development departments of State Governments.
- Sanctioned staff strength of each KVK is 16 including one Senior Scientist-cum-Head, six Subject Matter Specialists, one Farm Manager, two Programme Assistants, two Administrative Staff, one Tractor Driver, one Jeep Driver and 2 Skilled Support Staff. At present, 68.44% posts in KVKs are filled.
- As many as 657 KVKs have administrative building and 521 KVKs have Farmers’ hostel. The Government aims to provide required infrastructure in the remaining KVKs expeditiously.
- As per requirement, large number of KVKs have been strengthened with other infrastructure facilities like, pulses seed hubs, soil testing kits, micro-irrigation systems, Integrated Farming Systems units, farm machineries and equipment, District Agro-Met Units, etc. during last five years.
SOURCE: PIB
10. DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURAL COOPERATIVE SECTOR
THE CONTEXT: Since inception and till 31.03.2021, National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) has disbursed Rs.1.77 lakh crore to cooperatives for their development. It includes assistance to agricultural and horticulture cooperative societies.
ABOUT NCDC
- National Cooperative Development Corporation Act, 1962 Provides for planning and promoting programmes for the production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, foodstuffs, industrial goods, livestock, certain other commodities and services on co-operative principles and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The “Central Sector Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Cooperation (CSISAC)” is a Central Sector Scheme for assistance to NCDC programmes for development of Cooperatives. Under the scheme, loan is extended by NCDC from its own resources and subsidy is provided by the Government of India.
- NCDC plans and promotes programmes on co-operative principles. It assists cooperatives only.
- NCDC financial assistance schemes encourage and attract people to form new cooperatives for carrying out business activities.
- Finance schemes of NCDC cover activities such as agro-processing, horti-processing, credit, inputs, computerization, storage, cold chain, textile, handloom, sugar, ethanol, dairy, fisheries, livestock, piggery, poultry, renewable energy, rural housing, scheduled caste & scheduled tribes, women cooperatives, animal care/health, hospitality & transport, electricity & power, hospitals, healthcare and education etc.
- Under its SAHAKAR-22 initiatives, NCDC has in the last two years, has reached out to over 10000 primary level cooperative societies.
- To encourage youth towards cooperatives, NCDC has launched its YUVA SAHAKAR Cooperative Enterprise Support and Innovation Scheme which aims at enabling Start-Ups in cooperative sector with different types of business activities.
- Under its SAHAKAR MITRA scheme, NCDC offers internship opportunities to students get experience in areas of functioning of NCDC and related aspects of cooperatives.
- Under its AYUSHMAN SAHAKAR scheme, NCDC offers finance to cooperatives set up healthcare infrastructure and provide services.
- Government of India schemes such as the Formation and Promotion of 10,000 Farmers Producer Organizations (FPO) provide for registration and support of new cooperatives as FPOs. NCDC is one of the implementing agencies promoting such FPOs.
- The Formation and Promotion of Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPO) under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) provides for registration and support of new cooperatives as FFPOs, NCDC being an implementing agency for promoting such FFPOs.
SOURCE: PIB
11. DEEP OCEAN MISSION
THE CONTEXT: Deep Ocean Mission to be implemented by Ministry of Earth Sciences at a total budget of Rs. 4077 Cr for 5 years during the period 2021-2026.
ANALYSIS:
- Even private institutions will be included for the development of technologies for this mission to explore the possibilities of mining, bio-diversity, energy, fresh water etc. in Deep Ocean and to support the ‘blue economy’.
- Ministry of Earth Sciences through contractual agreements with the International Seabed Authority (ISA), is carrying out exploration activities for Poly-metallic Nodules (PMN) in the Central Indian Ocean Basin and for Poly-metallic Sulphides (PMS) in parts of Central and South-West Indian ridges.
- Preliminary estimates indicate 380 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) of Polymetallic Nodules comprising Copper, Nickel, Cobalt and Manganese are available within an allocated area of 75000 sq. km for exploration of PMN in Central Indian Ocean Basin.
- The estimated value of these metals is about 110 billion US$. The polymetallic sulphides are expected to contain rare earth minerals including gold and silver.
ABOUT THE DEEP OCEAN MISSION
- It consists of the six major components:
-
- Development of Technologies for Deep Sea Mining, and Manned Submersible
- Development of Ocean Climate Change Advisory Services
- Technological innovations for exploration and conservation of deep-sea biodiversity
- Deep Ocean Survey and Exploration
- Energy and freshwater from the Ocean
- Advanced Marine Station for Ocean Biology.
SOURCE: PIB
August 11, 2021 Prelim Practice Questions
Q 1. Consider the following statements about the Ujjwala scheme:
1. It was launched in 2015 with an aim to provide deposit-free LPG connections to BPL households.
2. The LPG connection under the scheme is given only in the name of the adult woman of the household.
3. Second phase of the scheme provides the first refill of the cylinder free of cost.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Q2. The Kakori Train Action was organized by?
a) Hindustan Republican Association
b) Hindustan Socialist Republican Association Army
c) Swadesh Bandhab Samiti
d) Bharat Naujawan Sabha
Answer for August 10, 2021 Prelims Practice Questions
ANSWER: C)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: was established in 1988 by WMO and UNEP.
- Statement 2 is correct: Its headquarter is hosted at WMO headquarters in Geneva.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: It is the scientific body that reviews data submitted by countries and does not conduct any research nor does it monitor climate-related data or parameters
Spread the Word


