THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. INDIA-ISRAEL TO WIDEN SCOPE OF INDUSTRIAL R&D &
TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION FUND
THE CONTEXT: Experts from both countries (India-Israel) deliberated on widening the scope of the
India-Israel Industrial R&D and Technological Innovation Fund (I4F) at its recently concluded
meeting.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The approval of three joint R&D projects totalling 5.4 million dollars. The projects were
titled Centrally Monitored IoT Nano sensors for Molecular Diagnostics in Healthcare and
Screening Applications, NoMoreMos- a mosquito control biological solution, and IoT
enabled satellite communication for real-time agriculture and environment data collection
across India. - Also, unanimously agreed on a strategy for the new phase of I4F 2.0, which included
broadening the fund’s scope by determining the technical feasibility and market
acceptability of new products or technologies, co-developing products or technologies for
commercialization, and co-testing products or technologies for commercialization in R&D
and pilot areas. - The members have also suggested the need to focus on Partnership Development Activities
like more business activities with Indian and Israeli companies and startups through a series
of online events, follow-up B2B meetings.
About India-Israel Industrial R&D and Technological Innovation Fund:
- India-Israel Industrial R&D and Technological Innovation Fund (I4F) fund is a collaboration
between the Department of Science and Technology (DST), and the Israel Innovation
Authority, to promote, facilitate and support joint industrial R&D projects between
companies from India and Israel to address the challenges in the agreed ‘Focus Sectors’. - The goal of I4F is to promote, facilitate and support joint industrial R&D, which would lead
to the co-development and commercialization of innovative technologies that can benefit
both nations. The Global Innovation & Technology Alliance (GITA) is appointed to
implement the I4F program in India, while Israel Innovation Authority is the implementing
agency in Israel.
India-Israel Relations:
- India announced its recognition of Israel in 1950. Since the upgradation of relations in 1992,
defence and agriculture formed the two main pillars of the bilateral engagement between
both nations. - In recent years, relations have seen rapid growth across a broad spectrum of areas and the future vision of cooperation, also bilateral trade has diversified into several sectors such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, IT and telecom, and homeland security.
About Indo-Israeli Agriculture Project:
In the agricultural sector, both countries have jointly developed new crop varieties and share post-
harvest technologies following the success of the 10-year-old Indo-Israeli Agriculture Project (IIAP)
whose accomplishments include the successful growing of cherry tomatoes in Haryana,
rejuvenating mango orchards in Maharashtra, and demonstrating to Indian farmers the
effectiveness of state-of-the-art irrigation technologies.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
2. START-UPS RAISED A RECORD: STUDY
THE CONTEXT: According to a new study by NASSCOM and Zinnov start-ups raised a record $24.1
billion in 2021, a two-fold increase over pre-COVID-19 levels.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the study, ‘Indian Tech Start-up Ecosystem: Year of The Titans’, more that
2,250 start-ups were added in 2021, over 600 more than what was added in the 2020. - Start-ups raised USD 24.1 billion in 2021, a two-fold increase over pre-COVID levels. In
comparison to 2020, there was a 3X increase in the number of high value deals (deals > USD
100 million), demonstrating investor confidence with a pool of active angel investors of
2400+ and a readiness to take significant risks.” - “According to the study, the last decade, the ecosystem has played a key role in growing
direct and indirect jobs, providing 6.6 lakh direct jobs and more than 34.1 lakh indirect
jobs”. The industries that saw the most net new job creation were BFSI (banking, financial
services and insurance), ed-tech, retail and retail tech, food-tech, supply chain
management, and logistics and mobility. - When compared to the U.K., U.S., Israel and China, 2021 has been an outstanding year for
the Indian startup ecosystem, with the highest growth rate in terms of deals, both in seed
stage and late-stage funding, and the number of startups.
Some Government Schemes For Start-ups:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana.
- Credit Guarantee Trust Fund for Micro & Small Enterprises (CGTSME).
- Standup India.
- Venture Capital
- 4E (End to End Energy Efficiency) by Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
THE INTERNAL SECURITY
3. THE STRATEGIC SIGNIFICANCE OF BRIDGE CHINA IS BUILDING ON PANGONG TSO
THE CONTEXT: The ongoing standoff in eastern Ladakh has led to construction of infrastructure on
both sides of the India-China border. One of the latest constructions is a bridge being built by China
on the Pangong Tso.
THE EXPLANATION:
- China is building the bridge, about 400 m long and 8 m wide, close to the friction points on
the north bank of the Pangong Tso, and the Chushul sub-sector on the south bank. It will
help China mobilise troops quicker, if needed. - The bridge is around 20 km east (35 km by road) of Finger 8 on the north bank. In India’s
perception, the Line of Actual Control lies at Finger 8. The site of the bridge is within India’s
claim line, although the area has been under Chinese control since 1958.
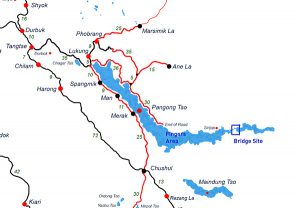
Significance of the bridge for China
- Construction of the bridge is significant, as it bridge will facilitate quick induction since it will
reduce the distance and time to reach the contested areas at the Pangong Lake. - It will connect the two banks and thus allow Chinese forces easy access on either side to
combat any threat. - The bridge site is just east of Khurnak Fort in Rutog county where the PLA (People’s Liberation Army) has frontier bases. Historically a part of India, Khurnak Fort has been under Chinese control since 1958.
- From Khurnak Fort, the LAC is considerably west, with India claiming it at Finger 8 and China
claiming it at Finger 4.
New Border Law
- On January 2021, China implemented its new border law. The new law calls to strengthen
its border defence, infrastructure near the borders and development of villages. - It also lays down conditions, under which emergency measures can be imposed across the
border areas.
What are India’s concerns?
Ever since tensions started in Ladakh, in May 2021, China has enhanced its troop deployment of
about 50,000 in this sector. Apart from Ladakh, China has been making aggressive moves in Eastern
Sector bordering Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh. Recently, China also renamed 15 places in
Arunachal Pradesh on its map.
Why is China increasing deployment and construction at the LAC?
Possible Reasons are:
- India’s decision to strengthen its border infrastructure (eg- construction of Darbuk-Shyok-
Daulat Beg Oldie road). - India’s tilt towards United States (eg- Quad).
- China consider India’s assertions on Gilgit-Baltistan, as an attack on the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) project of China.
- China’s growing assertiveness in South China Sea.
Importance of The Pangong Tso Lake
- In the Ladakhi language, Pangong means extensive concavity, and Tso is a lake in Tibetan.
- Pangong Tso is a long narrow, deep, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of
more than 14,000 ft in the Ladakh Himalayas. - The western end of Tso lies 54 km to the southeast of Leh. The 135 km-long lake sprawls
over 604 sq km in the shape of a boomerang and is 6 km wide at its broadest point. - The brackish water lake freezes over in winter and becomes ideal for ice skating and polo.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY 22 ND JANUARY 2022
Q1. According to 2018 Tiger census, which of the following statements is incorrect:
a) Rise of 33% over the previous census of 2014.
b) Karnataka has the highest tiger population.
c) There was no tiger found in Buxa tiger reserve.
d) There is no change in the tiger population in Odisha.
ANSWER FOR 21 ST JANUARY 2022.
Answer: B)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: It is a supersonic cruise missile.
- Statement 2 is correct: It can be launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against surface and sea-
based targets.

