Indian Polity
PESA Mahotsav:
-
- It is a two-day celebration of community-led governance under the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA).
- Celebrated on 23–24 December 2025 in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- Purpose: To spread awareness on PESA and strengthen local governance in Scheduled Areas where tribal communities reside.
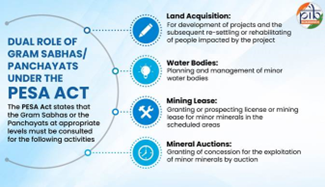
- About PESA:
- The Act extends Panchayati Raj provisions to Scheduled Areas (tribal regions) beyond the standard 73rd Constitutional Amendment framework, empowering Gram Sabhas with enhanced rights over land, natural resources, and traditional governance.
- It protects tribal land rights and promotes decentralised democracy.
- Significance of Mahotsav:
- Celebrates tribal culture, traditions, sports, cuisine and arts as part of community identity.
- Reinforces community participation, local autonomy and decision-making power of tribal Gram Sabhas.
- Highlights Government’s focus on inclusive governance, empowerment of tribal communities, and protection of customary rights.

(PIB)
Indian Society & Social Justice
Internationalisation of Higher Education in India:
-
- Report Released: NITI Aayog released a comprehensive policy report titled “Internationalisation of Higher Education in India: Prospects, Potential, and Policy Recommendations.”
- Launch & Participants: The report was launched by senior NITI Aayog leadership including the Vice Chairman, members in charge of Education and Economy, and the CEO, with participation from the Department of Higher Education and AICTE leadership.
- Focus of the Report: It examines how India can enhance the global integration of its higher education system through policies that attract international students, strengthen academic collaborations, research partnerships, and improve global rankings.
- Policy Recommendations: The report likely discusses strategic frameworks around curriculum internationalisation, partnerships with foreign universities, mobility programs, and improving India’s attractiveness as a higher education destination.
(PIB)
International Developments
United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS):
-
- Establishment: Set up in 1959 by the UN General Assembly to govern the peaceful use of outer space.
- Mandate: Develop international space law, promote international cooperation, and ensure peaceful, sustainable use of outer space.
- Structure: Works through two subcommittees-
- Scientific & Technical Subcommittee (STSC)
- Legal Subcommittee (LSC)
- Key Output: Responsible for formulation of five UN space treaties, including the Outer Space Treaty, 1967.
- Secretariat: Functions under UNOOSA (UN Office for Outer Space Affairs), headquartered in Vienna.
- Space Sustainability Focus (2024–25): UNCOPUOS discussions have increasingly focused on space debris management, mega-constellations, and Long-Term Sustainability (LTS) Guidelines for outer space activities.
- India’s Role: India actively participates in UNCOPUOS deliberations, aligning with its growing profile after missions like Chandrayaan-3, Gaganyaan, and expansion of commercial space activities via IN-SPACe.
- Global Concern: Rising satellite launches and private players have made space traffic management and weaponisation prevention key agenda items under UNCOPUOS.
(TH)
Economy
Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI):
-
- Context: The combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 1.8% in November compared with the same period last year, data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- ICI tracks the combined and individual performance of eight core industries, which form the backbone of India’s industrial sector.
- Weight in IIP: These eight industries together have a weight of about 40% in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- Base Year: 2011–12 (revised).
- Released by: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- Frequency: Monthly; used as a lead indicator of industrial and economic growth.
- Eight Core Industries: Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilisers, Steel, Cement, Electricity.

-
- Policy Relevance: Government uses ICI trends to assess infrastructure push, energy security, and manufacturing momentum under initiatives like PM Gati Shakti and Make in India.
(TH)
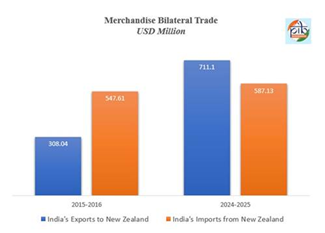
India-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement:

-
- India and New Zealand concluded a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement in December 2025.
- Duty‑Free Access: The agreement eliminates tariffs on 100% of Indian exports to New Zealand, significantly boosting market access.

- Investment Commitment: New Zealand commits USD 20 billion in investment over 15 years, strengthening economic and strategic ties.
-
- Safeguards & Sectoral Gains: Sensitive sectors like dairy and agriculture are protected; key labour‑intensive sectors (textiles, leather, gems, engineering goods) gain from zero‑duty access.
- Services & Mobility: The FTA includes novel provisions such as health and traditional medicine services (including AYUSH) and expanded student mobility/post‑study work visas for Indian youth.
- Strategic Outcomes: Expected to deepen bilateral trade, support MSME growth, create jobs, and enhance cooperation in services, education and cultural exchange, aligning with India’s global trade expansion goals.

(PIB)
Science & Technology
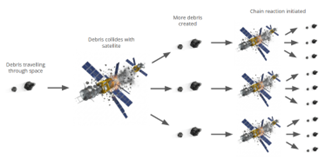
Kessler Syndrome:
-
- A theoretical scenario where collisions between objects in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) create cascading debris, triggering further collisions.
-
- Proposed by: Donald J. Kessler (NASA scientist) in 1978.
- Risk Zone: Most severe in LEO (≈ 200–2,000 km) due to high satellite density and orbital speeds (~7–8 km/s).
- Impacts: Can make certain orbits unusable for decades, affecting satellites, ISS safety, navigation, communication.
- Mitigation: Debris mitigation guidelines, post-mission disposal, active debris removal (ADR), and space traffic management.
- Mega-constellations (2023–25): Rapid deployment by private players has heightened collision risk in LEO, reviving concerns over Kessler Syndrome.
- UNCOPUOS & UNOOSA: Emphasis on Long-Term Sustainability (LTS) Guidelines to curb debris creation.
- India: ISRO’s de-orbiting experiments and adherence to space debris mitigation norms; relevance after Chandrayaan-3 success and expanding commercial launches via IN-SPACe.
- ISS Safety: Periodic collision avoidance maneuvers due to debris underline real-world risk.
(TH)
Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) spacecraft:
-
- Context: NASA loses touch with MAVEN craft which reached Mars just before Mangalyaan.

-
- Agency: A NASA mission to Mars.
- Launch & Orbit: Launched in 2013; entered Mars orbit in 2014.
- Objective: Study upper atmosphere, ionosphere and interactions with the Sun to understand loss of Mars’ atmosphere over time.
- Key Finding: Solar wind stripping played a major role in thinning Mars’ atmosphere, contributing to loss of liquid water.
- Scientific Importance: Explains climate evolution of Mars and its transition from warm-wet to cold-dry.
- Extended Mission (2024–25): MAVEN continues to provide critical data on solar storms and their impact on Mars’ atmosphere.
- Solar Activity Context: During periods of high solar activity, MAVEN has observed enhanced atmospheric escape, reaffirming theories of solar wind-driven loss.
- India Link: MAVEN’s findings complement ISRO’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) studies on Martian atmosphere, often cited together in comparative prelims questions.

(TH)
Defence & Security
Anjadip- Indigenous Anti-Submarine Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC):
-
- Anjadip is an indigenously built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) for the Indian Navy.

-
- Role: Designed for coastal waters, harbours, and choke points to detect, track and neutralise submarines, especially midget submarines.
- Indigenisation: Built under Make in India / Aatmanirbhar Bharat with major indigenous content.
- Capabilities: Equipped with sonars, torpedoes, rockets, and mine-laying capability; suited for low-depth operations.
- Strategic Value: Enhances coastal security, protection of ports and naval bases, and counters sub-surface threats in littoral zones.
- Commissioning Context (2024–25): Indian Navy has been inducting ASW-SWC class vessels, strengthening littoral anti-submarine capability amid rising submarine presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- China Factor: Increased deployment of foreign submarines in IOR has made shallow-water ASW platforms strategically critical.
- Defence Indigenisation: ASW-SWCs are often cited as examples of successful indigenous warship construction aligned with India’s defence export ambitions.
(TH)
Miscellaneous
Hardy–Ramanujan number:
-
- Context: National Mathematics Day, 22 December, every year to mark the birth anniversary of the Indian mathematician Srinivasa Ramanujan.

-
- Definition of 1729: 1729 is known as the Hardy-Ramanujan number, the smallest number expressible as the sum of two cubes in two different ways:
- 1³ + 12³ = 1729
- 9³ + 10³ = 1729
- Famous Anecdote: British mathematician G. H. Hardy visited Ramanujan in hospital and called the taxi number dull, but Ramanujan immediately recognized it as mathematically special.
- Insight into Genius: The story illustrates Ramanujan’s extraordinary intuition for numbers, grounded in deep study rather than random inspiration, he had insight into complex numerical patterns even when ill.
- Mathematical Significance: 1729 exemplifies taxicab numbers and highlights Ramanujan’s ability to perceive unusual patterns connected to deeper number‑theoretic structures.
- Definition of 1729: 1729 is known as the Hardy-Ramanujan number, the smallest number expressible as the sum of two cubes in two different ways:
(IE)
Spread the Word




