Day-764
Quiz-summary
0 of 20 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 20 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Furlough is the right of a prisoner and is given periodically irrespective of any reason.
2. Parole is not the right of a prisoner and is given for a specific reason.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Furlough:
● Furlough is given in cases of long-term imprisonment.
● The period of furlough granted to a prisoner is treated as remission of his sentence.
● Furlough is seen as a matter of right for a prisoner, to be granted periodically irrespective of any reason, and merely to enable the prisoner to retain family and social ties, and to counter the ill-effects of prolonged time spent in prison.
Statement 2 is correct:
Parole:
● Parole is a system of releasing a prisoner with suspension of the sentence.
● The release is conditional, usually subject to behaviour, and requires periodic reporting to the authorities for a set period of time.
● Parole is considered a reformative process.
● The provision was introduced with a view to humanising the prison system.
● Parole is not seen as a matter of right and is given to a prisoner for a specific reason, such as a death in the family or a wedding of a blood relative.
● Parole may be denied to a prisoner even when he makes out a sufficient case, if the competent authority is satisfied that releasing the convict would not be in the interest of society.
Additional Information-
● In India, parole (as well as furlough) is covered under The Prisons Act of 1894.
● Prisoners convicted of multiple murders or under the anti-terror Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) are not eligible for parole.
● Since prison is a State subject in the Constitution, the Prisons Act of each state government defines the rules under which parole is granted in that state.
● State governments have their own Prisoner Release on Parole Rules. For instance, in Rajasthan, initial parole is granted for 20 days; a second parole is for 30 days, and a third for 40 days. Thereafter, the prisoner can apply for permanent parole.
● Parole is granted by the state executive — the jail authorities submit the report to the State Government — and the competent authority takes a final decision on grant of parole on humanitarian considerations.
● If a plea for parole is rejected, the convict can move the High Court challenging the order of the competent authority.
● Apart from regular parole, the superintendent of a jail can also grant parole up to a period of seven days in emergencies.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Furlough:
● Furlough is given in cases of long-term imprisonment.
● The period of furlough granted to a prisoner is treated as remission of his sentence.
● Furlough is seen as a matter of right for a prisoner, to be granted periodically irrespective of any reason, and merely to enable the prisoner to retain family and social ties, and to counter the ill-effects of prolonged time spent in prison.
Statement 2 is correct:
Parole:
● Parole is a system of releasing a prisoner with suspension of the sentence.
● The release is conditional, usually subject to behaviour, and requires periodic reporting to the authorities for a set period of time.
● Parole is considered a reformative process.
● The provision was introduced with a view to humanising the prison system.
● Parole is not seen as a matter of right and is given to a prisoner for a specific reason, such as a death in the family or a wedding of a blood relative.
● Parole may be denied to a prisoner even when he makes out a sufficient case, if the competent authority is satisfied that releasing the convict would not be in the interest of society.
Additional Information-
● In India, parole (as well as furlough) is covered under The Prisons Act of 1894.
● Prisoners convicted of multiple murders or under the anti-terror Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) are not eligible for parole.
● Since prison is a State subject in the Constitution, the Prisons Act of each state government defines the rules under which parole is granted in that state.
● State governments have their own Prisoner Release on Parole Rules. For instance, in Rajasthan, initial parole is granted for 20 days; a second parole is for 30 days, and a third for 40 days. Thereafter, the prisoner can apply for permanent parole.
● Parole is granted by the state executive — the jail authorities submit the report to the State Government — and the competent authority takes a final decision on grant of parole on humanitarian considerations.
● If a plea for parole is rejected, the convict can move the High Court challenging the order of the competent authority.
● Apart from regular parole, the superintendent of a jail can also grant parole up to a period of seven days in emergencies. -
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
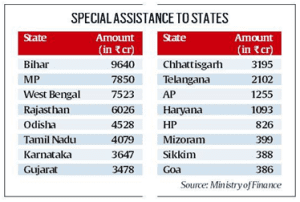
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’ Scheme:
1. Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the State Governments in the form of 30-year interest free loan.
2. Funds for meeting the States’ share of Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) have also been provided under this scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the State Governments in the form of 50-year interest free loan up to an overall sum of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore during the FY 2023-24.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Funds for meeting the State share of Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana have also been provided to the States under this scheme to enhance pace of the projects in these sectors.
About ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’ Scheme:
● Launched by: Ministry of Finance
● Objective: Launched in view of a higher multiplier effect of capital expenditure and in order to provide a boost to capital spending by States, the scheme was announced in the Union Budget 2023-24.
● The scheme was first instituted by the Ministry of Finance in 2020-21 in the wake of COVID-19 Pandemic. A similar scheme was also executed by the Ministry of Finance in the last financial year.
● The flexibility and simplicity of the scheme design has earned praise from CMs and FMs of States in successive pre-budget consultations.
● Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the State Governments in the form of 50-year interest free loan up to an overall sum of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore during the FY 2023-24.
● Capital investment projects in diverse sectors have been approved including health, education, irrigation, water supply, power, roads, bridges and railways.
● Funds for meeting the State share of Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana have also been provided to the States under this scheme to enhance pace of the projects in these sectors.
Components of the scheme: The scheme has 8 components/parts:
Part-I: This amount has been allocated amongst States in proportion to their share of central taxes & duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission. Other parts of the scheme are either linked to reforms or are for sector specific projects.
Part–II: Incentivise the states for scrapping of old vehicles.
Part III and IV: They aim at providing incentives to States for reforms in Urban Planning and Urban Finance.
Part V: Increasing the housing stock for the police personnel and their families within the police stations in urban areas.
Part VI: To promote national integration, carry forward the concept of “Make in India” and promote the concept of “One District, One Product (ODOP)” through construction of Unity Mall in each State.
Part-VII: For providing financial assistance to States for setting up libraries with digital infrastructure at Panchayat and Ward level for children and adolescents.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the State Governments in the form of 50-year interest free loan up to an overall sum of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore during the FY 2023-24.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Funds for meeting the State share of Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana have also been provided to the States under this scheme to enhance pace of the projects in these sectors.
About ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’ Scheme:
● Launched by: Ministry of Finance
● Objective: Launched in view of a higher multiplier effect of capital expenditure and in order to provide a boost to capital spending by States, the scheme was announced in the Union Budget 2023-24.
● The scheme was first instituted by the Ministry of Finance in 2020-21 in the wake of COVID-19 Pandemic. A similar scheme was also executed by the Ministry of Finance in the last financial year.
● The flexibility and simplicity of the scheme design has earned praise from CMs and FMs of States in successive pre-budget consultations.
● Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the State Governments in the form of 50-year interest free loan up to an overall sum of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore during the FY 2023-24.

● Capital investment projects in diverse sectors have been approved including health, education, irrigation, water supply, power, roads, bridges and railways.
● Funds for meeting the State share of Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana have also been provided to the States under this scheme to enhance pace of the projects in these sectors.
Components of the scheme: The scheme has 8 components/parts:
Part-I: This amount has been allocated amongst States in proportion to their share of central taxes & duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission. Other parts of the scheme are either linked to reforms or are for sector specific projects.
Part–II: Incentivise the states for scrapping of old vehicles.
Part III and IV: They aim at providing incentives to States for reforms in Urban Planning and Urban Finance.
Part V: Increasing the housing stock for the police personnel and their families within the police stations in urban areas.
Part VI: To promote national integration, carry forward the concept of “Make in India” and promote the concept of “One District, One Product (ODOP)” through construction of Unity Mall in each State.
Part-VII: For providing financial assistance to States for setting up libraries with digital infrastructure at Panchayat and Ward level for children and adolescents. -
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
Consider the following countries:
1. Malaysia
2. Indonesia
3. Brunei Darussalam
4. Singapore
5. Thailand
6. Cambodia
How many of the above countries are part of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation: Cambodia is not a member of IPEF.
14 Member countries of Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) are as follows:
Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand,
Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, the USA, and Vietnam.
Additional Information
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)-
● Launched in May, 2022 in Tokyo, Japan.
● Aim: To strengthen economic partnership among participating countries to enhance resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness and competitiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
● Pillars:
⮚ Pillar I: Trade
⮚ Pillar II: Supply chains
⮚ Pillar III: Clean economy
⮚ Pillar IV: Fair economy (issues like tax and anti-corruption).
● Recently, India has joined 3 pillars except the trade pillar to protect its domestic agricultural, labour and digital sectors.
● Region comprise of 40 percent of global GDP and 28 percent of global goods and services trade.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation: Cambodia is not a member of IPEF.
14 Member countries of Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) are as follows:
Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand,
Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, the USA, and Vietnam.
Additional Information
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)-
● Launched in May, 2022 in Tokyo, Japan.
● Aim: To strengthen economic partnership among participating countries to enhance resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness and competitiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
● Pillars:
⮚ Pillar I: Trade
⮚ Pillar II: Supply chains
⮚ Pillar III: Clean economy
⮚ Pillar IV: Fair economy (issues like tax and anti-corruption).
● Recently, India has joined 3 pillars except the trade pillar to protect its domestic agricultural, labour and digital sectors.
● Region comprise of 40 percent of global GDP and 28 percent of global goods and services trade. -
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
Consider the following statements in relation to the Section 8(3) of Representation of People Act, 1951:
1. As per this law, a person convicted of a criminal offence and sentenced to imprisonment for five years is permanently disqualified from contesting an election.
2. The disqualification takes effect only “after three months have elapsed” from the date of conviction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Section 8(3) of the Representation of People Act, 1951 (RPA, 1951) mandates that an MP can be disqualified for 6 years if convicted and sentenced to at least 2 years of imprisonment.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The Section 8(4) stated that the disqualification takes effect only “after three months have elapsed” from the date of conviction. Within that period, the convicted MP could file an appeal against the sentence before the High Court. (So, not Section 8(3))
● However, in the landmark 2013 ruling in ‘Lily Thomas V Union of India’, the Supreme Court declared the Section 8(4) of the RPA as unconstitutional.
About the Representation of People Act, 1951-
The Representation of the People Act (RPA), 1951 is an act of Parliament of India deals with:
● Elections – Conduction of election of the Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
● Disqualifications – The qualifications and disqualifications for membership of Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
● Offences – Other offences, decision of doubts and disputes for the election for Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
Section 8 of the RPA, 1951 – The Section (8) of the RPA, 1951 consists of the following provisions:
● Section 8 (1) – It includes specific offences such as promoting enmity between two groups, bribery, and undue influence or personation at an election.
● Section 8(2) – It lists offences that deal with hoarding or profiteering, adulteration of food or drugs and for conviction and sentence of at least six months for an offence under any provisions of the Dowry Prohibition Act.
● Section 8(3) – A person convicted of any offence and sentenced to imprisonment for not less than two years shall be disqualified from the date of such conviction and shall continue to be disqualified for a further period of 6 years since his release.
● Section 8(4) – The disqualification takes effect only after 3 months have elapsed from the date of conviction.
● However, in the landmark 2013 ruling in ‘Lily Thomas V Union of India’, the Supreme Court made Section 8(4) of the RPA as unconstitutional.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Section 8(3) of the Representation of People Act, 1951 (RPA, 1951) mandates that an MP can be disqualified for 6 years if convicted and sentenced to at least 2 years of imprisonment.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The Section 8(4) stated that the disqualification takes effect only “after three months have elapsed” from the date of conviction. Within that period, the convicted MP could file an appeal against the sentence before the High Court. (So, not Section 8(3))
● However, in the landmark 2013 ruling in ‘Lily Thomas V Union of India’, the Supreme Court declared the Section 8(4) of the RPA as unconstitutional.
About the Representation of People Act, 1951-
The Representation of the People Act (RPA), 1951 is an act of Parliament of India deals with:
● Elections – Conduction of election of the Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
● Disqualifications – The qualifications and disqualifications for membership of Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
● Offences – Other offences, decision of doubts and disputes for the election for Houses of Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
Section 8 of the RPA, 1951 – The Section (8) of the RPA, 1951 consists of the following provisions:
● Section 8 (1) – It includes specific offences such as promoting enmity between two groups, bribery, and undue influence or personation at an election.
● Section 8(2) – It lists offences that deal with hoarding or profiteering, adulteration of food or drugs and for conviction and sentence of at least six months for an offence under any provisions of the Dowry Prohibition Act.
● Section 8(3) – A person convicted of any offence and sentenced to imprisonment for not less than two years shall be disqualified from the date of such conviction and shall continue to be disqualified for a further period of 6 years since his release.
● Section 8(4) – The disqualification takes effect only after 3 months have elapsed from the date of conviction.
● However, in the landmark 2013 ruling in ‘Lily Thomas V Union of India’, the Supreme Court made Section 8(4) of the RPA as unconstitutional. -
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
In the context of Krishi UDAAN 2.0 scheme, consider the following statements:
1. The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the nodal ministry of the scheme.
2. E-NAM platform provides relevant information to all the stakeholders and assist in coordination, monitoring and evaluation of the scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) has launched the Krishi Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (Krishi Udan 2.0) scheme from 27 October 2021.
● The Krishi UDAN scheme was launched in August 2020 to assist farmers in transporting agricultural products on international and national routes so that it improves their value realisation.
● Krishi UDAN 2.0 will focus on bringing about a convergence between the agriculture and aviation sectors (A2A: Agriculture to Aviation).
● Krishi UDAN 2.0 will be implemented at 53 airports across the country, primarily focussing on the north-eastern States and tribal regions, and is expected to benefit farmers, freight forwarders and airlines.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● An online portal called E-KUSHAL (Krishi Udaan for Sustainable Holistic AgriLogistics) is developed as part of Krishi UDAN 2.0. It will facilitate information dissemination to all the stakeholders.
● This will be a single platform which will provide relevant information and will also assist in coordination, monitoring and evaluation of the scheme.
● Although there is a proposed convergence of E-Kushal with the National Agriculture Market (e-NAM).Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) has launched the Krishi Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (Krishi Udan 2.0) scheme from 27 October 2021.
● The Krishi UDAN scheme was launched in August 2020 to assist farmers in transporting agricultural products on international and national routes so that it improves their value realisation.
● Krishi UDAN 2.0 will focus on bringing about a convergence between the agriculture and aviation sectors (A2A: Agriculture to Aviation).
● Krishi UDAN 2.0 will be implemented at 53 airports across the country, primarily focussing on the north-eastern States and tribal regions, and is expected to benefit farmers, freight forwarders and airlines.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● An online portal called E-KUSHAL (Krishi Udaan for Sustainable Holistic AgriLogistics) is developed as part of Krishi UDAN 2.0. It will facilitate information dissemination to all the stakeholders.
● This will be a single platform which will provide relevant information and will also assist in coordination, monitoring and evaluation of the scheme.
● Although there is a proposed convergence of E-Kushal with the National Agriculture Market (e-NAM). -
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO):
1. The organisation’s members are divided into “producer” countries and “consumer” countries with India belonging to the group of the “producer” member countries.
2. The “Global Forest Resources Assessment” report is released by the ITTO every year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
● The 75 members of ITTO include 37 “producer” countries and 38 “consumer” countries.
● India is a founder member of ITTO. India belongs to the group of the “producer” member countries.
● The Ministry of environment, forest & climate change is the nodal ministry for ITTO related matters in India.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The “Global Forest Resources Assessment” report is released by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Additional Information
International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO)-
● ITTO is a treaty-based inter-governmental organisation headquartered in Yokohama, Japan.
● ITTO was established by the International Tropical Timber Agreement of 1983 (ITTA, 1983) to bring together governments to jointly consider issues facing the tropical forest sector and related international trade, including the crucial importance of the tropical forest resource base.
● Following the expiration of the 1983 agreement, ITTO continued operations under a successor agreement, the ITTA, 1994.
● At present, ITTO operates under the ITTA, 2006.
● ITTO is focused on promoting the sustainable management and conservation of tropical forests and the expansion and diversification of international trade in tropical timber from sustainably managed and legally harvested forests.
Main functions of ITTO:
● Develops internationally agreed policy guidelines and norms to encourage sustainable forest management (SFM) and sustainable tropical timber industries and trade.
● Assists tropical member countries to adapt such guidelines and norms to local circumstances and to implement them in the field through projects and other activities.
● Collects, analyzes and disseminates data on the production and trade of tropical timber.
● Promotes sustainable tropical timber supply chains.
● Helps develop capacity in tropical forestry.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
● The 75 members of ITTO include 37 “producer” countries and 38 “consumer” countries.
● India is a founder member of ITTO. India belongs to the group of the “producer” member countries.
● The Ministry of environment, forest & climate change is the nodal ministry for ITTO related matters in India.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The “Global Forest Resources Assessment” report is released by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Additional Information
International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO)-
● ITTO is a treaty-based inter-governmental organisation headquartered in Yokohama, Japan.
● ITTO was established by the International Tropical Timber Agreement of 1983 (ITTA, 1983) to bring together governments to jointly consider issues facing the tropical forest sector and related international trade, including the crucial importance of the tropical forest resource base.
● Following the expiration of the 1983 agreement, ITTO continued operations under a successor agreement, the ITTA, 1994.
● At present, ITTO operates under the ITTA, 2006.
● ITTO is focused on promoting the sustainable management and conservation of tropical forests and the expansion and diversification of international trade in tropical timber from sustainably managed and legally harvested forests.
Main functions of ITTO:
● Develops internationally agreed policy guidelines and norms to encourage sustainable forest management (SFM) and sustainable tropical timber industries and trade.
● Assists tropical member countries to adapt such guidelines and norms to local circumstances and to implement them in the field through projects and other activities.
● Collects, analyzes and disseminates data on the production and trade of tropical timber.
● Promotes sustainable tropical timber supply chains.
● Helps develop capacity in tropical forestry. -
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
Consider the following statements in relation to the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF):
1. It is a central sector scheme.
2. The interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance offered under the scheme is co-terminus.
3. ‘BHARAT’ campaign has been launched by the government under the scheme to create a competitive spirit among the banks and lending institutions to mobilize agriculture infrastructure projects loan at a faster pace.
How many of the statements given above are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme is a central sector scheme.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Agriculture Infra Fund (AIF) is a financing facility launched on 8th July 2020 for creation of post-harvest management infrastructure and community farm assets.
● Under this scheme, Rs 1 lakh crore is to be disbursed by financial year 2025-26 and the interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance will be given till the year 2032-33 (i.e both facilities are co-terminus).
Statement 3 is correct:
● A new campaign named ‘BHARAT’ (Banks Heralding Accelerated Rural & Agriculture Transformation) has been launched by the Government under Agriculture Infrastructure Fund Scheme.
● Aim: To provide maximum benefits to the people and to create a competitive spirit among the Banks and lending institutions to mobilize agriculture infrastructure projects loan at a faster pace.
● Top performing Banks under different categories i.e. commercial Banks in public and private Sector, Regional Rural Banks, Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and cooperative Banks will be selected at the end of the Campaign and their special contribution will be recognized.
Additional Information
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme-
● A central sector scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
● Objective: To mobilize a medium – long-term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through incentives and financial support.
● Target: The scheme envisages provision of Rs. 1 Lakh Crore by banks and financial institutions as loans.
● Provisions: Interest subvention of 3% per annum and credit guarantee coverage under Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) for loans up to Rs. 2 Crores.
● Timeline: Under this scheme, Rs 1 lakh crore is to be disbursed by financial year 2025-26 and the interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance will be given till the year 2032-33.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme is a central sector scheme.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Agriculture Infra Fund (AIF) is a financing facility launched on 8th July 2020 for creation of post-harvest management infrastructure and community farm assets.
● Under this scheme, Rs 1 lakh crore is to be disbursed by financial year 2025-26 and the interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance will be given till the year 2032-33 (i.e both facilities are co-terminus).
Statement 3 is correct:
● A new campaign named ‘BHARAT’ (Banks Heralding Accelerated Rural & Agriculture Transformation) has been launched by the Government under Agriculture Infrastructure Fund Scheme.
● Aim: To provide maximum benefits to the people and to create a competitive spirit among the Banks and lending institutions to mobilize agriculture infrastructure projects loan at a faster pace.
● Top performing Banks under different categories i.e. commercial Banks in public and private Sector, Regional Rural Banks, Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and cooperative Banks will be selected at the end of the Campaign and their special contribution will be recognized.
Additional Information
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme-
● A central sector scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
● Objective: To mobilize a medium – long-term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through incentives and financial support.
● Target: The scheme envisages provision of Rs. 1 Lakh Crore by banks and financial institutions as loans.
● Provisions: Interest subvention of 3% per annum and credit guarantee coverage under Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) for loans up to Rs. 2 Crores.
● Timeline: Under this scheme, Rs 1 lakh crore is to be disbursed by financial year 2025-26 and the interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance will be given till the year 2032-33. -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
Consider the following countries:
1. Finland
2. New Zealand
3. Republic of Korea
4. Italy
5. Denmark
6. Taiwan
How many of the above-mentioned countries are the members of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP)?Correct
Answer: A
Context: The theme of the question is derived from PIB information (link attached below) where it has been said that collaborative international efforts through multilateral and bilateral engagements have been made to build a resilient critical minerals value chain. Ministry of Mines is actively engaging in new partnerships and alliances like Minerals Security Partnership (MSP), the Australia-India Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA).
Explanation:
● Member nations of Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) are: 14 members
⮚ Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, Norway, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, the United Kingdom, US, the European Union, Italy and India.
More about Minerals Security Partnership (MSP):
● The Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) is a global initiative by the US to bolster critical mineral supply chains. It is also known as the critical minerals alliance.
● It was announced by the US and other key partner countries in June 2022 with an aim to ensure that critical minerals are produced, processed and recycled in a way that helps countries secure a stable supply of critical minerals for their economies. It also aims to weaken China’s grip on supplies of critical minerals worldwide.
● The MSP directly addresses four major critical minerals challenges:
⮚ Diversifying and stabilizing global supply chains;
⮚ Investment in those supply chains;
⮚ Promoting high environmental, social, and governance standards in the mining, processing, and recycling sectors; and
⮚ Increasing recycling of critical minerals.
● Aim: To accelerate the development of diverse and sustainable critical energy minerals supply chains through working with host governments and industry to facilitate targeted financial and diplomatic support for strategic projects along the value chain.
● India became a member in June, 2023.Incorrect
Answer: A
Context: The theme of the question is derived from PIB information (link attached below) where it has been said that collaborative international efforts through multilateral and bilateral engagements have been made to build a resilient critical minerals value chain. Ministry of Mines is actively engaging in new partnerships and alliances like Minerals Security Partnership (MSP), the Australia-India Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA).
Explanation:
● Member nations of Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) are: 14 members
⮚ Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, Norway, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, the United Kingdom, US, the European Union, Italy and India.
More about Minerals Security Partnership (MSP):
● The Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) is a global initiative by the US to bolster critical mineral supply chains. It is also known as the critical minerals alliance.
● It was announced by the US and other key partner countries in June 2022 with an aim to ensure that critical minerals are produced, processed and recycled in a way that helps countries secure a stable supply of critical minerals for their economies. It also aims to weaken China’s grip on supplies of critical minerals worldwide.
● The MSP directly addresses four major critical minerals challenges:
⮚ Diversifying and stabilizing global supply chains;
⮚ Investment in those supply chains;
⮚ Promoting high environmental, social, and governance standards in the mining, processing, and recycling sectors; and
⮚ Increasing recycling of critical minerals.
● Aim: To accelerate the development of diverse and sustainable critical energy minerals supply chains through working with host governments and industry to facilitate targeted financial and diplomatic support for strategic projects along the value chain.
● India became a member in June, 2023. -
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023:
1. According to the Bill, the selection committee will consist of the Prime Minister, the Chief Justice of India, and the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha.
2. The salary and conditions of service of the Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners will be equivalent to that of Cabinet Secretary.
3. According to the Bill, Election Commissioners may be removed only upon the recommendation of the Chief Election Commissioner.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Selection Committee will consist of the Prime Minister, a Union Cabinet Minister, and Leader of Opposition/leader of the largest opposition party in Lok Sabha.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Salary and pension: The salary, allowances, and other conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of the Cabinet Secretary. They will have an option to draw pension and other retirement benefits from the service that they belonged to previously.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Removal: The Bill retains the manner of removal of CEC and ECs as specified in the Constitution. The CEC may be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Supreme Court Judge. ECs may be removed only upon the recommendation of the CEC.
More about the Bill:
Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023:
Key features of the Bill-
● Election Commission: The Election Commission will consist of a Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and other Election Commissioners (ECs). The President will periodically fix the number of ECs.
● Appointment of the Commission: The Commission will be appointed by the President, upon the recommendation of the Selection Committee. The Selection Committee will comprise the Prime Minister, Cabinet Minister, and Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha (or leader of the single largest opposition party). A Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary will suggest five names to the Selection Committee. The Selection Committee may consider any person other than those suggested by the Search Committee.
● Eligibility criteria: The CEC and ECs must: (i) be persons of integrity, (ii) have knowledge and experience in the management and conduct of elections, and (iii) be or have been Secretary (or equivalent) to the government.
● Term and reappointment: Members of the Election Commission will hold office for six years, or until they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier. Members of the Commission cannot be re-appointed. If an EC is appointed as a CEC, the overall period of the term may not be more than six years.
● Salary and pension: The salary, allowances, and other conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of the Cabinet Secretary. They will have an option to draw pension and other retirement benefits from the service that they belonged to previously.
● Removal: The Bill retains the manner of removal of CEC and ECs as specified in the Constitution. The CEC may be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Supreme Court Judge. ECs may be removed only upon the recommendation of the CEC.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Selection Committee will consist of the Prime Minister, a Union Cabinet Minister, and Leader of Opposition/leader of the largest opposition party in Lok Sabha.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Salary and pension: The salary, allowances, and other conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of the Cabinet Secretary. They will have an option to draw pension and other retirement benefits from the service that they belonged to previously.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Removal: The Bill retains the manner of removal of CEC and ECs as specified in the Constitution. The CEC may be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Supreme Court Judge. ECs may be removed only upon the recommendation of the CEC.
More about the Bill:
Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023:
Key features of the Bill-
● Election Commission: The Election Commission will consist of a Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and other Election Commissioners (ECs). The President will periodically fix the number of ECs.
● Appointment of the Commission: The Commission will be appointed by the President, upon the recommendation of the Selection Committee. The Selection Committee will comprise the Prime Minister, Cabinet Minister, and Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha (or leader of the single largest opposition party). A Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary will suggest five names to the Selection Committee. The Selection Committee may consider any person other than those suggested by the Search Committee.
● Eligibility criteria: The CEC and ECs must: (i) be persons of integrity, (ii) have knowledge and experience in the management and conduct of elections, and (iii) be or have been Secretary (or equivalent) to the government.
● Term and reappointment: Members of the Election Commission will hold office for six years, or until they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier. Members of the Commission cannot be re-appointed. If an EC is appointed as a CEC, the overall period of the term may not be more than six years.
● Salary and pension: The salary, allowances, and other conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of the Cabinet Secretary. They will have an option to draw pension and other retirement benefits from the service that they belonged to previously.
● Removal: The Bill retains the manner of removal of CEC and ECs as specified in the Constitution. The CEC may be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Supreme Court Judge. ECs may be removed only upon the recommendation of the CEC. -
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Under the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) scheme, it is proposed to cover an additional area of 6.5 lakh hectare for oil palm till the year 2025-26.
Statement-II: India emerged as the biggest importer of palm oil in the world in 2021.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Statement-I is correct and Statement-II is a correct explanation for Statement-I:
About National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm-
● Approved by the Cabinet in August, 2021.
● A new Centrally Sponsored Scheme with a special focus on the North east region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
● Aim: To enhance the edible oilseeds production and oils availability in the country by harnessing Oil Palm area expansion, increasing CPO production and to reduce import burden on edible oils.
● Under this scheme, it is proposed to cover an additional area of 6.5 lakh hectare for oil palm till the year 2025-26 and thereby reaching the target of 10 lakh hectares ultimately.
● The production of Crude Palm Oil (CPO) is expected to go upto 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 and up-to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
● Reason to launch this special scheme: The scheme will immensely benefit the oil palm farmers, increase capital investment, create employment generation, shall reduce the import dependence and also increase the income of the farmers.
⮚ As on August, 2021 (The time when the scheme was launched)- India was the largest consumer of vegetable oil in the world. Of this, palm oil imports are almost 55% of its total vegetable oil imports.
⮚ Situation in case of imports is still not improving as of August, 2023.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Statement-I is correct and Statement-II is a correct explanation for Statement-I:
About National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm-
● Approved by the Cabinet in August, 2021.
● A new Centrally Sponsored Scheme with a special focus on the North east region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
● Aim: To enhance the edible oilseeds production and oils availability in the country by harnessing Oil Palm area expansion, increasing CPO production and to reduce import burden on edible oils.
● Under this scheme, it is proposed to cover an additional area of 6.5 lakh hectare for oil palm till the year 2025-26 and thereby reaching the target of 10 lakh hectares ultimately.
● The production of Crude Palm Oil (CPO) is expected to go upto 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 and up-to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
● Reason to launch this special scheme: The scheme will immensely benefit the oil palm farmers, increase capital investment, create employment generation, shall reduce the import dependence and also increase the income of the farmers.
⮚ As on August, 2021 (The time when the scheme was launched)- India was the largest consumer of vegetable oil in the world. Of this, palm oil imports are almost 55% of its total vegetable oil imports.
⮚ Situation in case of imports is still not improving as of August, 2023. -
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Logistics Performance Index (LPI) is released by the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
2. One of the targets of the National Logistics Policy (NLP)-2022 is to make India among the top 10 countries by 2030 in the Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
3. Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) report is released by the NITI Aayog.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Logistics Performance Index (LPI) is released by World Bank.
● India has climbed six places on the World Bank’s Logistic Performance Index (LPI) 2023, now ranking 38th in the 139 countries index.
● This is a significant improvement from its previous ranking of 44th in 2018 and 54th in 2014.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The targets of the NLP are to:
a) Reduce cost of logistics in India
b) Improve the Logistics Performance Index ranking – endeavor is to be among top 25 countries by 2030
c) Create data driven decision support mechanism for an efficient logistics ecosystem.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
● Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) report is released by the Department for Promotion of Industries and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
More about National Logistics Policy (NLP)-2022:
● To complement PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (NMP) , the National Logistics Policy (NLP) was launched on 17th September 2022. While the PM GatiShakti NMP addresses integrated development of the fixed infrastructure and network planning, the NLP addresses the soft infrastructure and logistics sector development aspect, inter alia, including process reforms, improvement in logistics services, digitization, human resource development and skilling.
Vision:
● The vision of NLP is to drive economic growth and business competitiveness of the country through an integrated, seamless, efficient, reliable, green, sustainable and cost-effective logistics network by leveraging best in class technology, processes and skilled manpower. This will reduce logistics cost and improve performance.
Targets:
● The targets of the NLP are to:
⮚ Reduce cost of logistics in India;
⮚ Improve the Logistics Performance Index ranking – endeavor is to be among top 25 countries by 2030,
⮚ Create data driven decision support mechanism for an efficient logistics ecosystem.
Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP)
● To achieve these targets, a Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) as part of the NLP was launched covering eight action areas including-
o Integrated Digital Logistics Systems;
o (ii) Standardization of Physical Assets and Benchmarking of Service Quality Standards;
o (iii) Logistics Human Resource Development and Capacity Building;
o (iv) State engagement;
o (v) EXIM Logistics;
o (vi) Services Improvement Framework;
o (vii) Sectoral Plans for Efficient Logistics (SPEL); and
o (viii) Facilitation of Development of Logistics Parks.
Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): For digital integration in the logistics sector and to provide a single sign to users who are trading goods and using multiple modes of transport – the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) was launched along with the NLP.
● ULIP is an indigenous data-based platform which integrates 34 logistics-related digital systems /portals across Ministries / Departments. It is worth noting that GST data is also being integrated with ULIP.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Logistics Performance Index (LPI) is released by World Bank.
● India has climbed six places on the World Bank’s Logistic Performance Index (LPI) 2023, now ranking 38th in the 139 countries index.
● This is a significant improvement from its previous ranking of 44th in 2018 and 54th in 2014.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● The targets of the NLP are to:
a) Reduce cost of logistics in India
b) Improve the Logistics Performance Index ranking – endeavor is to be among top 25 countries by 2030
c) Create data driven decision support mechanism for an efficient logistics ecosystem.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
● Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) report is released by the Department for Promotion of Industries and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
More about National Logistics Policy (NLP)-2022:
● To complement PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (NMP) , the National Logistics Policy (NLP) was launched on 17th September 2022. While the PM GatiShakti NMP addresses integrated development of the fixed infrastructure and network planning, the NLP addresses the soft infrastructure and logistics sector development aspect, inter alia, including process reforms, improvement in logistics services, digitization, human resource development and skilling.
Vision:
● The vision of NLP is to drive economic growth and business competitiveness of the country through an integrated, seamless, efficient, reliable, green, sustainable and cost-effective logistics network by leveraging best in class technology, processes and skilled manpower. This will reduce logistics cost and improve performance.
Targets:
● The targets of the NLP are to:
⮚ Reduce cost of logistics in India;
⮚ Improve the Logistics Performance Index ranking – endeavor is to be among top 25 countries by 2030,
⮚ Create data driven decision support mechanism for an efficient logistics ecosystem.
Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP)
● To achieve these targets, a Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) as part of the NLP was launched covering eight action areas including-
o Integrated Digital Logistics Systems;
o (ii) Standardization of Physical Assets and Benchmarking of Service Quality Standards;
o (iii) Logistics Human Resource Development and Capacity Building;
o (iv) State engagement;
o (v) EXIM Logistics;
o (vi) Services Improvement Framework;
o (vii) Sectoral Plans for Efficient Logistics (SPEL); and
o (viii) Facilitation of Development of Logistics Parks.
Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): For digital integration in the logistics sector and to provide a single sign to users who are trading goods and using multiple modes of transport – the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) was launched along with the NLP.
● ULIP is an indigenous data-based platform which integrates 34 logistics-related digital systems /portals across Ministries / Departments. It is worth noting that GST data is also being integrated with ULIP. -
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
Consider the following statements regarding recently launched PM Vishwakarma Scheme:
1) It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
2) The targeted beneficiaries of the scheme are the artisans and craftspeople of rural and urban areas across India.
3) Collateral-free credit support up to ₹3 lakh at a concessional interest rate of 5% will be provided under the scheme.
4) Initially, 20 traditional crafts will be covered under PM Vishwakarma.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is Incorrect:
● “PM Vishwakarma” is a new Central Sector Scheme with a financial outlay of Rs.13000 crore for a period of five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).

Statement 2 is correct:
● The scheme aims to strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishya parampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Under PM Vishwakarma scheme, the artisans and craftspeople will be provided recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card, Credit Support upto Rs.1 lakh (First Tranche) and Rs.2 lakh (Second Tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
Statement 4 is Incorrect:
● Initially, eighteen traditional trades will be covered in the first instance under PM Vishwakarma.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is Incorrect:
● “PM Vishwakarma” is a new Central Sector Scheme with a financial outlay of Rs.13000 crore for a period of five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).



Statement 2 is correct:
● The scheme aims to strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishya parampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Under PM Vishwakarma scheme, the artisans and craftspeople will be provided recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card, Credit Support upto Rs.1 lakh (First Tranche) and Rs.2 lakh (Second Tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
Statement 4 is Incorrect:
● Initially, eighteen traditional trades will be covered in the first instance under PM Vishwakarma. -
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI):
1. All the member nations of QUAD group are also the members of the SCRI.
2. ASEAN is the latest member to become a part of the SCRI.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Members of SCRI are India, Japan and Australia which are also the founding members of SCRI.
● Quad members: USA, India, Japan and Australia.
● So, USA is not a member of the SCRI.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● No other nation or international group has joined the SCRI as a member.
More about Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI):
● Mooted initially by Japan, the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative aims to diversify a country’s supply risk across various supplying countries instead of being dependent on just one (or a few).
● Japan conceptualised the SCRI as a trilateral approach to trade, with India and Australia as founding partners while keeping the doors open for ASEAN and Pacific-Rim nations for the future.
● This was a direct response to economies and individual companies concerned by the uncertainty of supplies from China.
The Objective of the SCRI:
● The partner countries in the SCRI seek to increase the supply chain’s resilience by restructuring supply chains away from China due to the increased security risks associated with production networks significantly embedded in, or connected to, China.
Targets:
● (i) Sharing of best practices on supply chain resilience
● (ii) Holding investment promotion events and buyer-seller matching events to provide opportunities for stakeholders to explore the possibility of diversification of their supply chains.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Members of SCRI are India, Japan and Australia which are also the founding members of SCRI.
● Quad members: USA, India, Japan and Australia.
● So, USA is not a member of the SCRI.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● No other nation or international group has joined the SCRI as a member.
More about Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI):
● Mooted initially by Japan, the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative aims to diversify a country’s supply risk across various supplying countries instead of being dependent on just one (or a few).
● Japan conceptualised the SCRI as a trilateral approach to trade, with India and Australia as founding partners while keeping the doors open for ASEAN and Pacific-Rim nations for the future.
● This was a direct response to economies and individual companies concerned by the uncertainty of supplies from China.
The Objective of the SCRI:
● The partner countries in the SCRI seek to increase the supply chain’s resilience by restructuring supply chains away from China due to the increased security risks associated with production networks significantly embedded in, or connected to, China.
Targets:
● (i) Sharing of best practices on supply chain resilience
● (ii) Holding investment promotion events and buyer-seller matching events to provide opportunities for stakeholders to explore the possibility of diversification of their supply chains.



-
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
Which of the following group is known as the ‘West Asian Quad’?
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: I2U2 is known as the ‘West Asian Quad’.
About I2U2:
● The I2U2 Group is a new strategic partnership formed between India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States.



● It was established to enhance cooperation and collaboration in various areas such as water, energy, transportation, space, health, and food security.
● The main objective of this grouping is to promote economic development, scientific innovation, and regional stability.
● Member countries committed to working together to address common challenges and explore new opportunities for growth and progress.
Additional Information
Middle East Strategic Alliance (MESA)-
● MESA was first announced during U.S. President Donald Trump’s visit to Saudi Arabia in May 2017.
● The Riyadh Declaration described the alliance as contributing “to peace and security in the region and the world.”
● It will include all Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states—Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE—as well as Egypt, Jordan, and the United States.
● The idea revolves primarily around security, but more recently, it has adopted economic and political aspects as well.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: I2U2 is known as the ‘West Asian Quad’.
About I2U2:
● The I2U2 Group is a new strategic partnership formed between India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States.



● It was established to enhance cooperation and collaboration in various areas such as water, energy, transportation, space, health, and food security.
● The main objective of this grouping is to promote economic development, scientific innovation, and regional stability.
● Member countries committed to working together to address common challenges and explore new opportunities for growth and progress.
Additional Information
Middle East Strategic Alliance (MESA)-
● MESA was first announced during U.S. President Donald Trump’s visit to Saudi Arabia in May 2017.
● The Riyadh Declaration described the alliance as contributing “to peace and security in the region and the world.”
● It will include all Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states—Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE—as well as Egypt, Jordan, and the United States.
● The idea revolves primarily around security, but more recently, it has adopted economic and political aspects as well. -
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme:
1. The Ministry of labour and employment is the nodal ministry for the implementation of the scheme.
2. The collateral-free loan facility under the scheme can be extended up-to Rs. 50,000.
3. Provision of interest subsidy is also available under this scheme.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Ministry of housing & urban affairs is the nodal ministry of the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme.
Statement 2 is correct:
● It is a micro credit scheme for urban street vendors that aim to provide collateral-free working capital loans up to ₹50,000.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Under the scheme regular repayments are incentivized with a 7% interest subsidy and digital transactions are rewarded with cashback up to ₹1,200 per year.
Additional Information
About Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme-
● PM SVANidhi is a central-sector micro-credit scheme launched on 1st June 2020 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
● Aim: To provide handholding support to street vendors.
● The scheme facilitates a working capital collateral-free loan of ₹10,000, with subsequent loans of ₹20,000 and ₹50,000 with a 7% interest subsidy.
● The scheme focuses on increasing the digital footprint in India by promoting the use of digital transactions among street vendors.
● To incentivize the adoption of digital transactions, a cashback of up to ₹100 per month is given to Street Vendors.
● The scheme aims to formalize the street vendors and open up new opportunities for this sector to move up the economic ladder.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● The Ministry of housing & urban affairs is the nodal ministry of the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme.
Statement 2 is correct:
● It is a micro credit scheme for urban street vendors that aim to provide collateral-free working capital loans up to ₹50,000.
Statement 3 is correct:
● Under the scheme regular repayments are incentivized with a 7% interest subsidy and digital transactions are rewarded with cashback up to ₹1,200 per year.
Additional Information
About Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme-
● PM SVANidhi is a central-sector micro-credit scheme launched on 1st June 2020 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
● Aim: To provide handholding support to street vendors.
● The scheme facilitates a working capital collateral-free loan of ₹10,000, with subsequent loans of ₹20,000 and ₹50,000 with a 7% interest subsidy.
● The scheme focuses on increasing the digital footprint in India by promoting the use of digital transactions among street vendors.
● To incentivize the adoption of digital transactions, a cashback of up to ₹100 per month is given to Street Vendors.
● The scheme aims to formalize the street vendors and open up new opportunities for this sector to move up the economic ladder. -
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
Malaviya Mission, seen in the news recently, is an initiative of which of the following organisation?
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: University Grants Commission (UGC) is the implementing agency of the scheme
About Malaviya Mission:
● Known as – Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme
● Launched at Teachers Day i.e. September 5th, 2023.
● It aims to provide tailored training programes for teachers.
● This programme will work for the capacity building of faculty members in higher educational institutions (HEI).
● It will ensure continuous professional development and help in building capacities of 15 lakh teachers of HEIs through 111 Malaviya Mission centres across India in a time-bound manner.
● It aims to improve the quality of teachers’ training, build leadership skills in teachers and help realise the goals of NEP.
● The Indian knowledge system has been included in the modules of the Programme.
● Human Resource Development Centres to be revamped and known as Madan Mohan Malaviya Teachers Training Centres.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: University Grants Commission (UGC) is the implementing agency of the scheme
About Malaviya Mission:
● Known as – Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme
● Launched at Teachers Day i.e. September 5th, 2023.
● It aims to provide tailored training programes for teachers.
● This programme will work for the capacity building of faculty members in higher educational institutions (HEI).
● It will ensure continuous professional development and help in building capacities of 15 lakh teachers of HEIs through 111 Malaviya Mission centres across India in a time-bound manner.
● It aims to improve the quality of teachers’ training, build leadership skills in teachers and help realise the goals of NEP.
● The Indian knowledge system has been included in the modules of the Programme.
● Human Resource Development Centres to be revamped and known as Madan Mohan Malaviya Teachers Training Centres. -
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023:
1. The Act is also known as the Constitution (105th Amendment) Act, 2023.
2. The Act has a sunset clause according to which provisions relating to reservation of seats for women shall cease to have effect after the expiration of 15 years.
3. The provisions of reservation apply for both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023 is also known as Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023.
Statement 2 is correct:
● The Act has a sunset clause according to which provisions relating to reservation of seats for women shall cease to have effect after the expiration of 15 years.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
● Reservation in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: Act does not contain any provision for reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils of the States.
● Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended providing reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils as well.
More about Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023-
Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023
Objective: To provide for one-third reservation to women in the Lok Sabha, State Assemblies and the assembly of NCT of Delhi.
Key provisions of the Act-
● Articles amended
⮚ Article 239AA: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
● Articles inserted
⮚ Article 330A: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the House of People (Lok Sabha).
o It also includes reservation of 1/3rd seats for women under the total number of seats reserved for SCs/STs under Article 330.
⮚ Article 332A: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of every State.
o It also includes reservation of 1/3rd seats for women under the total number of seats reserved for SCs/STs under Article 332.
⮚ Article 334A: Provisions of this act shall come into effect after delimitation after the first census taken after the commencement of this act.
● Sunset clause: Provisions relating to reservation of seats for women shall cease to have effect after the expiration of 15 years.
⮚ The reservation for women, however, can be extended by the Parliament by law.
⮚ Periodic rotation of seats reserved for women after each subsequent delimitation as Parliament may by law determine.
⮚ Provisions of this act shall not affect any representation in legislative assemblies and the Lok Sabha until their dissolution.
● Concern: Reservation in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: Act does not contain any provision for reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils of the States.
⮚ Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended providing reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils as well.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023 is also known as Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023.
Statement 2 is correct:
● The Act has a sunset clause according to which provisions relating to reservation of seats for women shall cease to have effect after the expiration of 15 years.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
● Reservation in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: Act does not contain any provision for reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils of the States.
● Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended providing reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils as well.
More about Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023-
Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023
Objective: To provide for one-third reservation to women in the Lok Sabha, State Assemblies and the assembly of NCT of Delhi.
Key provisions of the Act-
● Articles amended
⮚ Article 239AA: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
● Articles inserted
⮚ Article 330A: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the House of People (Lok Sabha).
o It also includes reservation of 1/3rd seats for women under the total number of seats reserved for SCs/STs under Article 330.
⮚ Article 332A: Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of every State.
o It also includes reservation of 1/3rd seats for women under the total number of seats reserved for SCs/STs under Article 332.
⮚ Article 334A: Provisions of this act shall come into effect after delimitation after the first census taken after the commencement of this act.
● Sunset clause: Provisions relating to reservation of seats for women shall cease to have effect after the expiration of 15 years.
⮚ The reservation for women, however, can be extended by the Parliament by law.
⮚ Periodic rotation of seats reserved for women after each subsequent delimitation as Parliament may by law determine.
⮚ Provisions of this act shall not affect any representation in legislative assemblies and the Lok Sabha until their dissolution.
● Concern: Reservation in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: Act does not contain any provision for reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils of the States.
⮚ Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended providing reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils as well. -
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
Consider the following statements about PM JI-VAN yojana:
1. This yojana is launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
2. Achieving the GHG emissions reduction targets is one of the objectives of this yojana.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● This yojana is launched by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
● It was notified in March, 2019.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Some of the objectives of PM JI-VAN are:
⮚ Meeting Government of India vision of reducing import dependence by way of substituting fossil fuels with Biofuels.
⮚ Achieving the GHG emissions reduction targets through progressive blending/ substitution of fossil fuels.
⮚ Addressing environmental concerns caused due to burning of biomass/ crop residues and improving the health of citizens.
⮚ Improving farmer income by providing them remunerative income for their otherwise waste agriculture residues.
⮚ Creating rural & urban employment opportunities in 2G Ethanol projects and Biomass supply chain.
⮚ Contributing to Swachh Bharat Mission by supporting the aggregation of nonfood biofuel feedstocks such as waste biomass and urban waste.
⮚ Indigenizing of Second Generation Biomass to Ethanol technologies.Additional Information
Pradhan Mantri Jaiv Indhan – Vatavaran Anukool Fasal Awashesh Nivaran Yojana:
● Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
● Aim: For providing support to integrated bio-ethanol projects and to encourage setting up of second generation (2G) bio-fuel plants, using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable bio stock.



Targets:
● PM JI-VAN envisages setting up of 12 commercial scale 2G bioethanol projects and 10 demonstration scale 2G bioethanol projects based on non-food biomass feedstocks and other renewable feedstocks with a total financial outlay of Rs. 1969.50 crore.
● The scheme will provide support to these 2G bioethanol Projects with a Viability Gap Funding in two phases:
⮚ Phase-I (2018-19 to 2022-23): wherein six commercial projects and five demonstration projects will be supported.
⮚ Phase-II (2020-21 to 2023-24): wherein remaining six commercial projects and five demonstration projects will be supported.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● This yojana is launched by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
● It was notified in March, 2019.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Some of the objectives of PM JI-VAN are:
⮚ Meeting Government of India vision of reducing import dependence by way of substituting fossil fuels with Biofuels.
⮚ Achieving the GHG emissions reduction targets through progressive blending/ substitution of fossil fuels.
⮚ Addressing environmental concerns caused due to burning of biomass/ crop residues and improving the health of citizens.
⮚ Improving farmer income by providing them remunerative income for their otherwise waste agriculture residues.
⮚ Creating rural & urban employment opportunities in 2G Ethanol projects and Biomass supply chain.
⮚ Contributing to Swachh Bharat Mission by supporting the aggregation of nonfood biofuel feedstocks such as waste biomass and urban waste.
⮚ Indigenizing of Second Generation Biomass to Ethanol technologies.Additional Information
Pradhan Mantri Jaiv Indhan – Vatavaran Anukool Fasal Awashesh Nivaran Yojana:
● Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
● Aim: For providing support to integrated bio-ethanol projects and to encourage setting up of second generation (2G) bio-fuel plants, using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable bio stock.



Targets:
● PM JI-VAN envisages setting up of 12 commercial scale 2G bioethanol projects and 10 demonstration scale 2G bioethanol projects based on non-food biomass feedstocks and other renewable feedstocks with a total financial outlay of Rs. 1969.50 crore.
● The scheme will provide support to these 2G bioethanol Projects with a Viability Gap Funding in two phases:
⮚ Phase-I (2018-19 to 2022-23): wherein six commercial projects and five demonstration projects will be supported.
⮚ Phase-II (2020-21 to 2023-24): wherein remaining six commercial projects and five demonstration projects will be supported. -
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
Consider the following statements:
1.‘National Policy on Biofuels’ has an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2030.
2. Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) was announced by G-7 group in Hiroshima Summit, 2023.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● ‘National Policy on Biofuels’ notified by the Government in 2018 envisaged an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by year 2030.
● However, considering the encouraging performance, due to various interventions made by the Government since 2014, the target of 20% ethanol blending was advanced from 2030 to 2025-26.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) was announced by the Indian Prime Minister on September 9, 2023, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit held in New Delhi.
Additional Information
Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) –


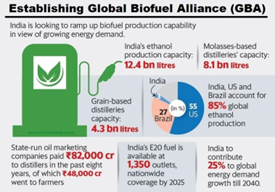
● Announced: By Indian Prime Minister on September 9, 2023, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit held in New Delhi.
● It is an initiative to develop an alliance of governments, international organisations and industry to facilitate adoption of biofuels by bringing together the biggest consumers and producers of biofuels and positioning biofuels as a key to energy transition.
● It is also expected to contribute to job creation and economic growth.
● GBA will support global development and deployment of sustainable biofuels by offering capacity-building exercises across the value chain, technical support for national programs and promoting policy lessons-sharing.
● It will facilitate mobilising a virtual marketplace to assist industries, countries, ecosystem players and key stakeholders in mapping demand and supply, as well as connecting technology providers to end users.
● It will also work on developing, adopting and implementing internationally recognised standards, codes, sustainability principles and regulations to incentivise biofuels adoption and trade.
● The mandate is also to support research and advocacy for improvements in biofuel technology across supply chains, expand the range of sustainable feedstock and convert feedstock to biofuels.
Members:
GBA Members constitute major producers and consumers of biofuels, such as the USA (52 per cent), Brazil (30 percent) and India (3 percent), contributing about 85 per cent share in production and about 81 per cent in consumption of ethanol.
Benefits for India:
● This will help India become the voice of the global south by getting countries which are still to start their biofuels programme.
● For India, it will provide additional opportunities to its industries by exporting technology and equipment.
● It will help accelerate India’s existing biofuel programes such as – PM-JIVAN Yojana, SATAT, and GOBARdhan scheme — thereby contributing to increased farmers’ income, creating jobs and overall development of the Indian eco-system.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
● ‘National Policy on Biofuels’ notified by the Government in 2018 envisaged an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by year 2030.
● However, considering the encouraging performance, due to various interventions made by the Government since 2014, the target of 20% ethanol blending was advanced from 2030 to 2025-26.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) was announced by the Indian Prime Minister on September 9, 2023, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit held in New Delhi.
Additional Information
Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) –



● Announced: By Indian Prime Minister on September 9, 2023, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit held in New Delhi.
● It is an initiative to develop an alliance of governments, international organisations and industry to facilitate adoption of biofuels by bringing together the biggest consumers and producers of biofuels and positioning biofuels as a key to energy transition.
● It is also expected to contribute to job creation and economic growth.
● GBA will support global development and deployment of sustainable biofuels by offering capacity-building exercises across the value chain, technical support for national programs and promoting policy lessons-sharing.
● It will facilitate mobilising a virtual marketplace to assist industries, countries, ecosystem players and key stakeholders in mapping demand and supply, as well as connecting technology providers to end users.
● It will also work on developing, adopting and implementing internationally recognised standards, codes, sustainability principles and regulations to incentivise biofuels adoption and trade.
● The mandate is also to support research and advocacy for improvements in biofuel technology across supply chains, expand the range of sustainable feedstock and convert feedstock to biofuels.
Members:
GBA Members constitute major producers and consumers of biofuels, such as the USA (52 per cent), Brazil (30 percent) and India (3 percent), contributing about 85 per cent share in production and about 81 per cent in consumption of ethanol.
Benefits for India:
● This will help India become the voice of the global south by getting countries which are still to start their biofuels programme.
● For India, it will provide additional opportunities to its industries by exporting technology and equipment.
● It will help accelerate India’s existing biofuel programes such as – PM-JIVAN Yojana, SATAT, and GOBARdhan scheme — thereby contributing to increased farmers’ income, creating jobs and overall development of the Indian eco-system. -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: PM-PRANAM was launched to promote the balanced use of chemical and alternative fertilisers.
Statement-II: India is the largest consumer of urea in the world.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
PM- PRANAM (PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth)-
● Launch- PM-PRANAM (PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth) was announced in Union Budget 2023–24.
● Aim- To promote the balanced use of chemical and alternative fertilisers, generating awareness of regenerative agriculture (RA).
⮚ Regenerative Agriculture is an outcome-based food production system that
o Nurtures and restores soil health,
o Protects the climate, water resources and biodiversity, and
o Enhances farms’ productivity and profitability.
● Objective – To incentivise the States and UTs to promote usage of alternative fertilizers and balanced use of chemical fertilizers.
● Budget – While the PRANAM scheme has no separate budget, a 50% subsidy savings will be provided to States/UTs.
⮚ 70% of the grant provided under the scheme can be used for asset creation related to technological adoption of alternate fertilisers and alternate fertiliser production units.
⮚ 30% grant money can be used for incentivising farmers, panchayats, farmer producer organisations, self-help groups, etc.
● Data- iFMS (Integrated fertilisers Management System) data available in the Fertiliser Ministry dashboard will be used for this purpose.
Fertilizer Consumption in India-
● India has consumed about 500 LMT of fertilizer over the last ten years.
● In 2020, the overall consumption of fertilisers stood at about 61 million tonnes, of which urea consumption increased exponentially.
● India is a major buyer of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
● India is the 2nd largest consumer and the 3rd largest producer of urea in the world. China is the world’s largest consumer of urea. In 2021, the Asian country consumed more than 30% of global urea.
● India consumes around 33 million tonnes of urea annually, of which almost 70% is domestically produced and the rest is imported from other countries.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
PM- PRANAM (PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth)-
● Launch- PM-PRANAM (PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth) was announced in Union Budget 2023–24.
● Aim- To promote the balanced use of chemical and alternative fertilisers, generating awareness of regenerative agriculture (RA).
⮚ Regenerative Agriculture is an outcome-based food production system that
o Nurtures and restores soil health,
o Protects the climate, water resources and biodiversity, and
o Enhances farms’ productivity and profitability.
● Objective – To incentivise the States and UTs to promote usage of alternative fertilizers and balanced use of chemical fertilizers.
● Budget – While the PRANAM scheme has no separate budget, a 50% subsidy savings will be provided to States/UTs.
⮚ 70% of the grant provided under the scheme can be used for asset creation related to technological adoption of alternate fertilisers and alternate fertiliser production units.
⮚ 30% grant money can be used for incentivising farmers, panchayats, farmer producer organisations, self-help groups, etc.
● Data- iFMS (Integrated fertilisers Management System) data available in the Fertiliser Ministry dashboard will be used for this purpose.
Fertilizer Consumption in India-
● India has consumed about 500 LMT of fertilizer over the last ten years.
● In 2020, the overall consumption of fertilisers stood at about 61 million tonnes, of which urea consumption increased exponentially.
● India is a major buyer of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
● India is the 2nd largest consumer and the 3rd largest producer of urea in the world. China is the world’s largest consumer of urea. In 2021, the Asian country consumed more than 30% of global urea.
● India consumes around 33 million tonnes of urea annually, of which almost 70% is domestically produced and the rest is imported from other countries.




