Indian Polity
Article 32:
-
- Context: Article 32 enables people to approach SC for fundamental rights, says CJI Gavai.
- He also observed that it was born out of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s vision articulated during the Constituent Assembly debates.
- Provision:
- Article 32 provides the right to move the Supreme Court for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights.
- It is called the “Heart and Soul of the Constitution” by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
- Nature of Right:
- Fundamental Right as well as a constitutional remedy.
- Ensures judicial review to protect fundamental rights.
- Writs under Article 32: Supreme Court can issue Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Certiorari, and Quo Warranto.
- Scope:
- Applies only for enforcement of Fundamental Rights, not other legal rights.
- Writ jurisdiction is original; individuals can directly approach the Supreme Court.
- Judicial Importance:
- Recognized as a safeguard against executive or legislative excesses.
- Can be suspended only under Article 359 during a national emergency.
(TH)
International Developments
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU):
-
- Context: The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) negotiation on a Free Trade Agreement with India was reviewed in Moscow by the Rajesh Agrawal, Commerce Secretary, during meetings with trade officials from Russia and EAEU.
- A Terms of Reference (ToR) signed on 20 August 2025 outlines an 18‑month work plan to diversify Indian businesses’ access to EAEU goods markets, covering MSMEs, farmers and fishermen.
- Discussions centred on key sectors: pharmaceuticals, telecom equipment, machinery, leather, automobiles, chemicals and critical minerals; emphasis on supply‑chain resilience, regulatory predictability, and logistics/payment standards to facilitate trade.
- Bilateral trade target: India and EAEU aim to reach US $100 billion by 2030, boosting exports and co‑
- Indian emphasis: leveraging India’s digital public infrastructure, logistics upgrades and attractiveness as a partner for co‑investment/co‑production in goods and services.
- About EAEU:
- Context: The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) negotiation on a Free Trade Agreement with India was reviewed in Moscow by the Rajesh Agrawal, Commerce Secretary, during meetings with trade officials from Russia and EAEU.
-
- Formation & Members: Formed in 2015; members include Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Kyrgyzstan.
- Purpose: Aims for economic integration, free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor, and common trade policy among member states.
- India–EAEU Relations: India is negotiating a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the EAEU.
- Focus areas: pharmaceuticals, machinery, telecom, chemicals, automobiles, critical minerals.
- Trade & Strategic Significance:
- Enhances India’s market access to Eurasia and diversifies trade partners beyond traditional markets.
- Supports supply-chain resilience and co-production/investment opportunities.
- Trade Target: India–EAEU bilateral trade aims to reach US$ 100 billion by 2030.
(PIB)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Senkaku Islands:
-
- These are group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, northeast of Taiwan and southwest of Japan’s Okinawa.
- Claimants / Dispute:
- Japan administers the islands.
- China claims them as Diaoyu Islands.
- Taiwan also claims them.
- The dispute involves sovereignty, maritime boundaries, and exclusive economic zones (EEZs).
- Strategic Importance:
- Lies in key shipping lanes.
- Rich in fisheries and potential undersea oil & gas reserves.
- Proximity to important military and trade routes makes it strategically sensitive.
- Recent Context:
- Tensions often flare due to naval patrols, air incursions, and resource exploration.
- Relevant in discussions of China–Japan maritime security, East China Sea disputes, and Indo-Pacific strategy.
(TH)
Congo cobalt mines:
-
- Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the world’s largest producer of cobalt, contributing around 70% of global production.
- Cobalt is a critical mineral used in lithium-ion batteries, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy storage systems.
- Global Strategic Importance:
- The DRC’s cobalt is vital for the global clean energy transition and high-tech industries.
- Geopolitically sensitive due to resource dependency of countries like China, USA, and EU.
- Concerns & Challenges:
- Child labor and unsafe working conditions in artisanal and small-scale mines.
- Environmental degradation and lack of sustainable mining practices.
- India’s Context:
- India imports cobalt to support EV battery manufacturing, electronics, and green energy technologies.
- Part of India’s critical minerals strategy to reduce import dependence.
(TH)
Defence & Security
INDIAN NAVY TO COMMISSION MAHE:
-
- The Indian Navy will commission the ship ‘Mahe’ (first of the Mahe‑class Anti‑Submarine Warfare Shallow‑Water Craft) at the Naval Dockyard, Mumbai, on 24 November 2025.

-
- It is being built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi, with over 80 % indigenous content, reflecting India’s push for “Atmanirbhar Bharat” in naval shipbuilding.
- The Mahe‑class craft is designed for anti‑submarine warfare (ASW) in shallow waters, coastal patrol and securing India’s littoral zones, featuring stealth, agility and endurance.
- Named after the coastal town of Mahe on the Malabar Coast, the ship’s crest carries a ‘Urumi’ (flexible sword of Kalaripayattu) symbolising precision, agility and lethal grace.


(PIB)
USI Hosts Third Annual Indian Military Heritage Festival:
-
- The United Service Institution of India (USI) hosted the 3rd Annual Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) in New Delhi on 14–15 November 2025.
- The event saw participation from:
- Senior military leaders
- Policymakers
- Diplomats
- Scholars, authors, think-tanks, and the public
- The festival included:
- Military-themed exhibitions (e.g., paintings by Lt Col Arul Raj, Retd)
- Release of books: The Sukraniti: Statecraft and Warcraft, Honours and Awards of the Indian Armed Forces, 75 Years of India’s Contribution to UN Peacekeeping
- Key discussion themes:
- “Operation Sindoor: Catalysing Atmanirbhar Bharat”
- India’s “Strategic Autonomy”
- Future conflicts and technology in warfare
(PIB)
History, Art & Culture
20th International Tipitaka Chanting Ceremony:
-
- The 20th International Tipitaka Chanting Ceremony will be held in Bodhgaya (Mahabodhi Temple) from 2–13 December 2025.
- Organised by 17 Buddhist organisations across India — first-ever collective effort.
- Significance: Revives the ancient Pali Tipitaka tradition, reaffirming India’s Buddhist heritage.
- Scale: More than 15,000 Indian monks and lay devotees, plus international participants from several Southeast Asian countries.
- Cultural & Spiritual Elements: Includes chanting, Dhamma talks, cultural performances, Q&A with teachers, and a pilgrimage walk (Jethian Valley → Venuvana, Rajgir).
- Symbolic Gesture: 220 handcrafted golden Buddha statues from Odisha to be consecrated and donated — symbolizing spiritual revival.
- The Tipitaka is the traditional term for the sacred scriptures of Buddhism, meaning “three baskets” because it is divided into three main divisions: the Vinaya Piṭaka (rules for monks and nuns), the Sutta Piṭaka (discourses of the Buddha), and the Abhidhamma Piṭaka (systematic philosophy and teachings on mind and matter).

-
- It is the scriptural canon of the Theravada Buddhist tradition, preserving the teachings of the Buddha.

(PIB)
Miscellaneous
National Press Day 2025:
-
- National Press Day is celebrated on 16 November, marking the founding of the Press Council of India (PCI) in 1966.

-
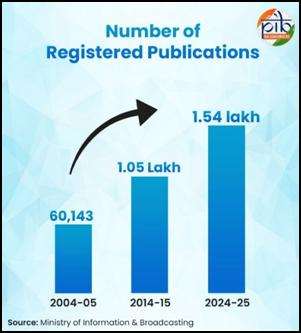
- Media growth: Registered publications in India have grown from ~60,143 in 2004–05 to 1.54 lakh in 2024–25.
-
- Press and Registration of Periodicals (PRP) Act, 2023: Replaces old colonial-era law; digitises and streamlines periodical registration via the Press Sewa Portal.
- Press Sewa Portal: Onboarded 40,000 publishers and 3,000 presses within six months; enables paperless registration and e‑sign; offers QR‑coded digital certificates.

-
- Media governance:
- Press Council of India (PCI) ensures ethical journalism and freedom of press.
- Media governance:

-
-
- Press Registrar General of India (PRGI) (formerly RNI) handles periodical registration under the new law.
- Journalist welfare: The Journalist Welfare Scheme provides financial assistance for death, disability, and medical emergencies of journalists.
-
(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. With reference to India’s trade relations with the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), consider the following statements:
1. India is negotiating a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the EAEU to enhance market access for goods and services.
2. EAEU member states include Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Uzbekistan.
3. The bilateral trade target between India and EAEU is US$ 100 billion by 2030.
4. Priority sectors for India include pharmaceuticals, telecom equipment, machinery, chemicals, automobiles, and critical minerals.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2, and 3 only
b) 1, 3, and 4 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) All four statements
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: India is negotiating a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with EAEU.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Uzbekistan is not an EAEU member; members are Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan.
- Statement 3 is correct: India–EAEU trade target is US$ 100 billion by 2030.
- Statement 4 is correct: Key sectors include pharmaceuticals, telecom, machinery, chemicals, automobiles, and critical minerals.
Q2. Consider the following statements regarding the Tipitaka:
1. Tipitaka is the sacred canon of Buddhism, written primarily in Pali language.
2. It consists of three “baskets” – Vinaya Pitaka, Sutta Pitaka, and Abhidhamma Pitaka – covering rules, discourses, and philosophy.
3. Tipitaka was compiled during the reign of Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE.
4. Tipitaka is considered authoritative only in Theravada Buddhism and has no influence in Mahayana or Vajrayana traditions.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 3 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) All four statements
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: Tipitaka is the sacred text of Buddhism, primarily in Pali (Theravada tradition).
- Statement 2 is correct: Composed of three baskets:
Vinaya Pitaka → monastic rules
Sutta Pitaka → discourses of Buddha
Abhidhamma Pitaka → philosophy and psychology
-
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Tipitaka was compiled in 1st–2nd century BCE (Third Buddhist Council, during King Kashyapa’s period) and not directly during Ashoka’s reign.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: While authoritative in Theravada, Tipitaka influenced Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism as well.
Q3. With reference to the Senkaku Islands, consider the following statements:
1. The Senkaku Islands are uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan.
2. Both China and Taiwan claim sovereignty over these islands, calling them Diaoyu Islands.
3. The islands have no strategic or economic significance and are only symbolically important.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All three statements
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: Japan administers the islands; they are uninhabited.
- Statement 2 is correct: China and Taiwan claim them as Diaoyu Islands.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The islands are strategically important (shipping lanes, proximity to military routes) and potentially rich in fisheries and undersea hydrocarbons.
Q4. Consider the following statements regarding India’s strategic maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR):
1. India’s Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) policy aims to enhance maritime security cooperation, protect sea lanes, and provide humanitarian assistance in the IOR.
2. India is a part of Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), which promotes economic and security collaboration among member states in the region.
3. The Indian Navy’s ‘Mission Based Deployment’ (MBD) ensures continuous presence in the IOR for deterrence, maritime domain awareness, and anti-piracy operations.
4. India maintains permanent military bases in all Indian Ocean littoral countries to monitor regional maritime traffic.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 3 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) All four statements
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: SAGAR policy emphasizes: Maritime security cooperation
Protection of sea lines of communication (SLOCs)
Humanitarian assistance & disaster relief (HADR) in the IOR.
-
- Statement 2 is correct: India is a founding member of IORA, which promotes economic, scientific, and security collaboration in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Statement 3 is correct: Mission Based Deployment (MBD) is India’s operational approach to ensure continuous naval presence, monitor maritime traffic, and counter piracy.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: India does not maintain permanent military bases in all IOR countries.
It has port access agreements and collaborations (e.g., Chabahar, Seychelles, Mauritius) but not bases in every littoral state.
Q5. With reference to Article 32 of the Indian Constitution, consider the following statements:
1. Article 32 provides the right to move the Supreme Court for enforcement of all legal and constitutional rights.
2. The Supreme Court can issue Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Certiorari, and Quo Warranto under Article 32.
3. Article 32 can be suspended only during national emergency under Article 359.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All three statements
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Article 32 is applicable only for enforcement of Fundamental Rights, not all legal or constitutional rights.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Supreme Court can issue five writs under Article 32:
Habeas Corpus – protection against illegal detention
Mandamus – command to public authorities
Prohibition – prohibit lower courts from exceeding jurisdiction
Certiorari – quash lower court orders
Quo Warranto – question the legality of a person holding public office
-
- Statement 3 is correct: The right under Article 32 can be suspended only during national emergency under Article 359.




