INTRODUCTION
Recent reporting in The Hindu and Indian Express emphasises that this transition is not merely about efficiency but about reconfiguring national mobility.
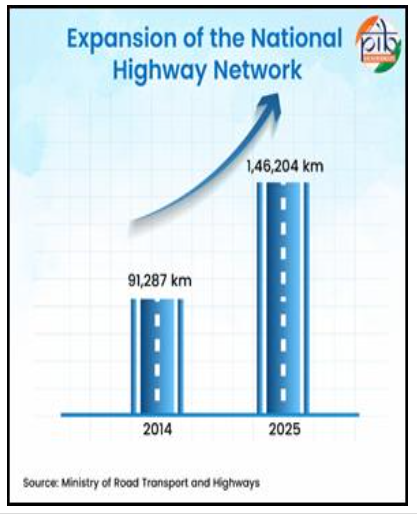
With over 63 lakh km of roads and the National Highways network expanding by nearly 60% since 2014, the focus is now on building smart, data-driven, resilient, and sustainable corridors aligned with the National Logistics Policy and PM Gati Shakti.
HOW INDIA’S HIGHWAYS ARE BEING REDEFINED
India’s highways are shifting from physical corridors to digital-cognitive systems supported by:
1. Digital tolling reforms
2. GIS-based planning
3. Intelligent Transport Systems
4. Smart citizen-facing applications
5. Sustainable construction and green norms
6. Integrated monitoring across lifecycle
This is moving India toward global benchmarks seen in Japan, South Korea, and parts of the EU.
DIGITAL TOLLING & PAYMENT REFORMS IN INDIA
1. FASTag & NETC
National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has developed the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) program, a unified, interoperable platform for electronic toll payments. The system facilitates smooth transactions through a centralized clearing house for settlements and dispute resolution.
At the core of NETC is FASTag, a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) based device affixed to a vehicle’s windscreen. It allows toll payments to be made automatically from the user’s linked account without stopping at the plaza. FASTag penetration at 98% and 8 crore+ users.
-
- FASTag Annual Pass with 25 lakh+ adopters reduces transaction friction and enhances predictability.
- PRS notes that digital tolling has reduced leakage and enabled higher revenue realisation.
- India’s first MLFF launched at Choryasi, Gujarat. Uses ANPR cameras, RFID, and back-end verification for tolling without stoppage. Indian Express reports MLFF could reduce queueing delays by nearly 50–70%, with major CO₂ savings.
2. Rajmargyatra App
Rajmargyatra serves as a digital travel companion, offering a wealth of information such as details about highways, toll plazas, nearby amenities, including petrol pumps, hospitals, EV charging stations, and even live weather updates.
3. NHAI One
NHAI One integrates five core areas of NHAI’s project operations: Field Staff Attendance, Highway Maintenance, Road Safety Audits, Toilet Maintenance, and Daily Construction Audits via Request for Inspections (RFI). NHAI One enhances accountability and ensures accurate documentation of on-site progress and compliance.
4. GIS & PM Gati Shakti
Digital maps and spatial intelligence are reshaping through GIS & GATI SHAKTI. The National Highway network of 1.46 lakh km is now fully mapped on a unified GIS portal with 550+ data layers covering economic clusters, ecology, utilities, and logistics hubs.
This shift supports:
-
- Better alignment planning,
- Faster clearances,
- Reduced duplication,
- Integrated multimodal connectivity.
5. Intelligent Transport Systems
ITS in India is being implemented primarily through Advanced Traffic Management System (ATMS) and is gradually being integrated into a broader Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication ecosystem. These systems are designed to significantly reduce road accidents, minimize traffic violations, and accelerate emergency response times. ITS and ATMS strengthen highway safety through:
-
- Automated incident detection,
- Speed enforcement,
- Variable message signs,
- Quick emergency response.
ATMS is operational on Delhi–Meerut, Trans-Haryana, Eastern Peripheral, Bengaluru–Mysuru expressways, reducing fatalities and improving response time. NSVs equipped with 3D lasers and 360° cameras help identify defects across 20,933 km.
6. Green Highways & Sustainable Construction
Its objectives include minimising pollution and noise, preventing soil erosion, and generating employment opportunities. In 2023–24, the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) planted over 56 lakh saplings, followed by another 67.47 lakh in 2024–25. 467 water bodies revived under Mission Amrit Sarovar, generating 2.4 crore m³ soil, saving ₹16,690 crore. Use of 631 lakh tonnes recycled materials strengthens eco-friendly construction.
CHALLENGES
-
- Reports highlight inconsistencies in ANPR accuracy, especially in regions with poor lighting, dust, or non-standard number plates. Ensuring error-free MLFF functioning remains a challenge.
- With increasing dependence on digital tolling, apps, and ITS, risks of data breaches and system disruptions have grown. PRS notes the need for stronger cybersecurity frameworks across highway digital systems.
- The Hindu points out that digital adoption varies across regions, impacting the uniformity of enforcement and tolling efficiency.
- ORF analysis suggests that multiple agencies managing logistics, transport, railways, and urban bodies require better synchronization for seamless planning under Gati Shakti.
- Indian Express has reported that rapid expansion of highways increases routine maintenance pressure, requiring more NSVs, trained manpower, and consistent monitoring.
- PRS highlights challenges in long-term financing for digital upgrades, especially in MLFF adoption, sensor deployment, and ATMS scaling.
WAY FORWARD
-
- PRS suggests unified protocols for data protection, cybersecurity, and privacy for all NHAI and NPCI-linked platforms.
- It has been recommended that structured integration between central ministries, state governments, and local bodies under PM Gati Shakti.
- ORF highlights the need for a skilled workforce trained in ITS management, geospatial systems, and digital maintenance tools.
- Awareness initiatives can ensure smoother adoption of digital tolling and encourage compliance with safety norms.
- Expanding recycled material use, plantation survival audits, and climate-resilient engineering strengthens sustainability efforts.
CONCLUSION
However, the long-term success of this transition depends on harmonised digital systems, robust data protection norms, capacity building among implementing agencies, and sustained investment in intelligent infrastructure. The goal ahead is to create highways that not only move vehicles but also move data, decisions, and economic growth efficiently and sustainably.
Spread the Word



